Chang Choi
Classification of vertices on social networks by multiple approaches
Jan 13, 2023Abstract:Due to the advent of the expressions of data other than tabular formats, the topological compositions which make samples interrelated came into prominence. Analogically, those networks can be interpreted as social connections, dataflow maps, citation influence graphs, protein bindings, etc. However, in the case of social networks, it is highly crucial to evaluate the labels of discrete communities. The reason underneath for such a study is the non-negligible importance of analyzing graph networks to partition the vertices by using the topological features of network graphs, solely. For each of these interaction-based entities, a social graph, a mailing dataset, and two citation sets are selected as the testbench repositories. This paper, it was not only assessed the most valuable method but also determined how graph neural networks work and the need to improve against non-neural network approaches which are faster and computationally cost-effective. Also, this paper showed a limit to be excesses by prospective graph neural network variations by using the topological features of networks trialed.
* This is a paper whose final and definite form is published open access by 'Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering' (ISSN: 1551-0018)
A high performance computing method for accelerating temporal action proposal generation
Aug 02, 2019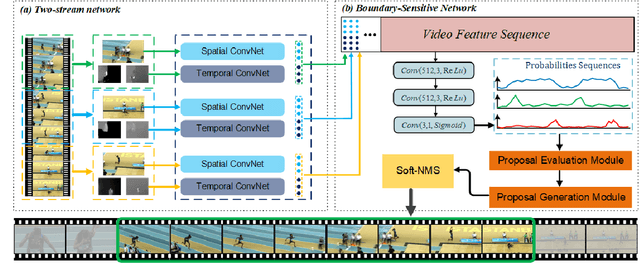
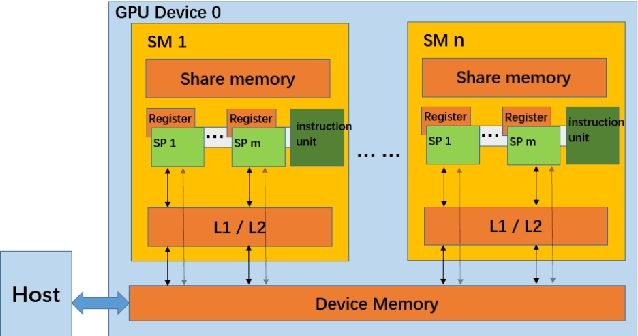
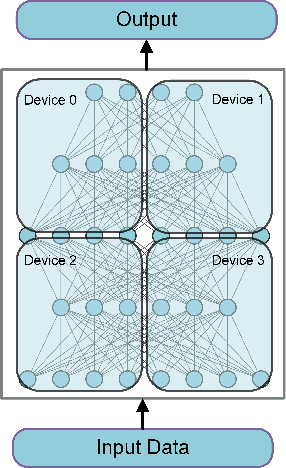
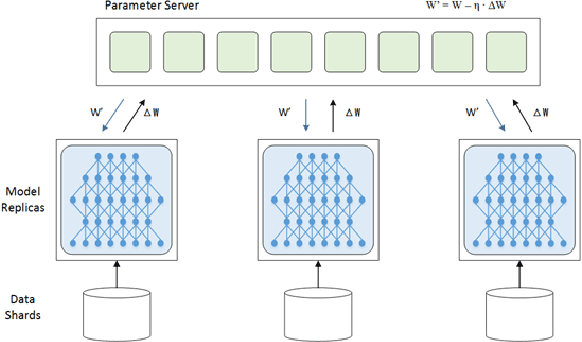
Abstract:Temporal action proposal generation, coming from temporal action recognition, is an important and challenging problem in computer vision. Because of the big capacity of video files, the speed of temporal action recognition is difficult for both researchers and companies. To training a convolutional neural network (CNN) for temporal action recognition, a lot of videos are required to put into the CNN. A speed-up for the task should be proposed for the training process to achieve the faster response of temporal action recognition system. To address it, we implement ring parallel architecture by Massage Passing Interface (MPI). Different from traditional parameter server architecture, total data transmission is reduced by adding a connection between multiple computing load in our new architecture. Compared to parameter server architecture, our parallel architecture has higher efficiency on temporal action proposal generation task with multiple GPUs, which is significant to dealing with large-scale video database. And based on the absence of evaluating time consumption in a distributed deep learning system, we proposed a concept of training time metrics which can assess the performance in the distributed training process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge