Chan Lee
Multispectral Pedestrian Detection with Sparsely Annotated Label
Jan 05, 2025



Abstract:Although existing Sparsely Annotated Object Detection (SAOD) approches have made progress in handling sparsely annotated environments in multispectral domain, where only some pedestrians are annotated, they still have the following limitations: (i) they lack considerations for improving the quality of pseudo-labels for missing annotations, and (ii) they rely on fixed ground truth annotations, which leads to learning only a limited range of pedestrian visual appearances in the multispectral domain. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework called Sparsely Annotated Multispectral Pedestrian Detection (SAMPD). For limitation (i), we introduce Multispectral Pedestrian-aware Adaptive Weight (MPAW) and Positive Pseudo-label Enhancement (PPE) module. Utilizing multispectral knowledge, these modules ensure the generation of high-quality pseudo-labels and enable effective learning by increasing weights for high-quality pseudo-labels based on modality characteristics. To address limitation (ii), we propose an Adaptive Pedestrian Retrieval Augmentation (APRA) module, which adaptively incorporates pedestrian patches from ground-truth and dynamically integrates high-quality pseudo-labels with the ground-truth, facilitating a more diverse learning pool of pedestrians. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our SAMPD significantly enhances performance in sparsely annotated environments within the multispectral domain.
Performance Analysis of Series Elastic Actuator based on Maximum Torque Transmissibility
Feb 14, 2019



Abstract:The use of the Series Elastic Actuator (SEA) system as an actuator system equipped with a compliant element has contributed not only to advances in human interacting robots but also to a wide range of improvements in the robotics area. Nevertheless, there are still limitations in its performance; the elastic spring that is adopted to provide compliance is considered to limit the actuator performance thus lowering the frequency bandwidth of force/torque generation, and the bandwidth decreases even more when it is supposed to provide large torque. This weakness is in turn owing to the limitations of motor and motor drives such as torque and velocity limits. In this paper, mathematical tools to analyze the impact of these limitations on the performance of SEA as a transmission system are provided. A novel criterion called Maximum Torque Transmissibility (MTT)is defined to assess the ability of SEA to fully utilize maximum continuous motor torque. Moreover, an original frequency bandwidth concept, maximum torque frequency bandwidth, which can indicate the maximum frequency up to which the SEA can generate the maximum torque, is proposed based on the proposed MTT. The proposed MTT can be utilized as a unique criterion of the performance, and thus various design parameters including the load condition, mechanical design parameters, and controller parameters of a SEA can be evaluated with its use. Experimental results under various conditions verify that MTT can precisely indicate the limitation of the performance of SEA, and that it can be utilized to accurately analyze the limitation of the controller of SEA.
Towards Accurate Force Control of Series Elastic Actuators Exploiting a Robust Transmission Force Observer
Feb 14, 2019
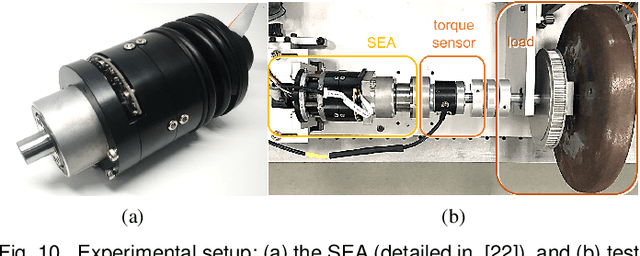
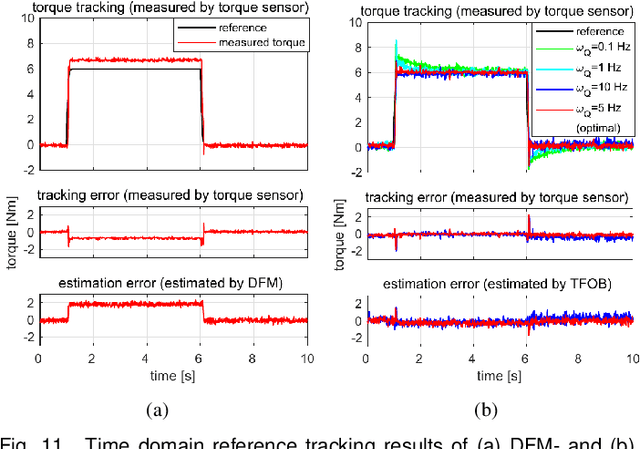
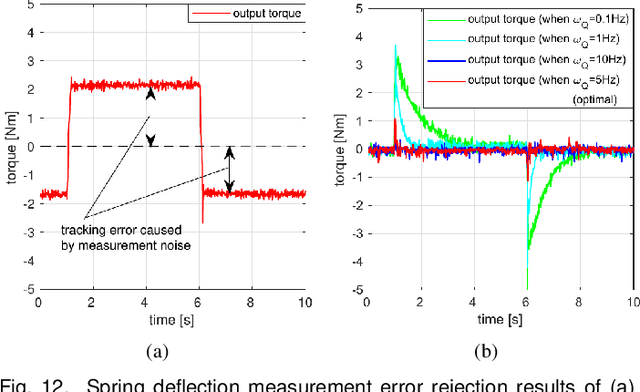
Abstract:This paper develops an accurate force control algorithm for series elastic actuators (SEAs) based on a novel force estimation scheme, called transmission force observer (TFOB). The proposed method is designed to improve an inferior force measurement of the SEA caused by nonlinearities of the elastic transmission and measurement noise and error of its deformation sensor. This paper first analyzes the limitation of the conventional methods for the SEA transmission force sensing and then investigates its stochastic characteristics, which indeed provide the base to render the accurate force control performance incorporated with the TFOB. In particular, a tuning parameter is introduced from holistic closed-loop system analyses in the frequency domain. This gives a guideline to attain optimum performance of the force-controlled SEA system. The proposed algorithm is experimentally verified in an actual SEA hardware setup.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge