Chae Yeon Lim
Enhanced artificial intelligence-based diagnosis using CBCT with internal denoising: Clinical validation for discrimination of fungal ball, sinusitis, and normal cases in the maxillary sinus
Nov 29, 2022



Abstract:The cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) provides 3D volumetric imaging of a target with low radiation dose and cost compared with conventional computed tomography, and it is widely used in the detection of paranasal sinus disease. However, it lacks the sensitivity to detect soft tissue lesions owing to reconstruction constraints. Consequently, only physicians with expertise in CBCT reading can distinguish between inherent artifacts or noise and diseases, restricting the use of this imaging modality. The development of artificial intelligence (AI)-based computer-aided diagnosis methods for CBCT to overcome the shortage of experienced physicians has attracted substantial attention. However, advanced AI-based diagnosis addressing intrinsic noise in CBCT has not been devised, discouraging the practical use of AI solutions for CBCT. To address this issue, we propose an AI-based computer-aided diagnosis method using CBCT with a denoising module. This module is implemented before diagnosis to reconstruct the internal ground-truth full-dose scan corresponding to an input CBCT image and thereby improve the diagnostic performance. The external validation results for the unified diagnosis of sinus fungal ball, chronic rhinosinusitis, and normal cases show that the proposed method improves the micro-, macro-average AUC, and accuracy by 7.4, 5.6, and 9.6% (from 86.2, 87.0, and 73.4 to 93.6, 92.6, and 83.0%), respectively, compared with a baseline while improving human diagnosis accuracy by 11% (from 71.7 to 83.0%), demonstrating technical differentiation and clinical effectiveness. This pioneering study on AI-based diagnosis using CBCT indicates denoising can improve diagnostic performance and reader interpretability in images from the sinonasal area, thereby providing a new approach and direction to radiographic image reconstruction regarding the development of AI-based diagnostic solutions.
Comparative Validation of AI and non-AI Methods in MRI Volumetry to Diagnose Parkinsonian Syndromes
Jul 23, 2022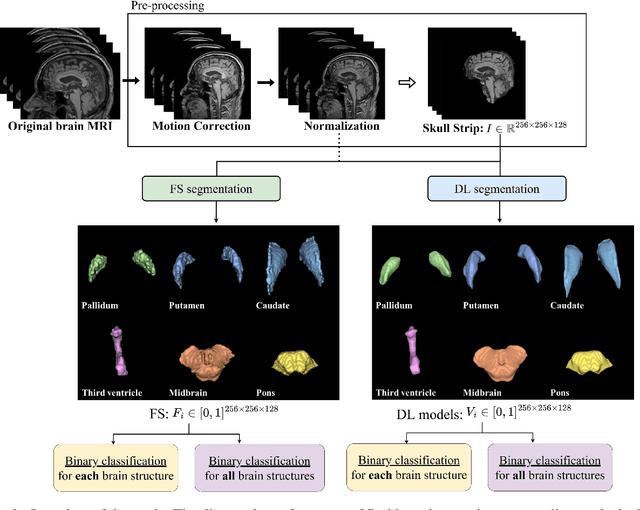

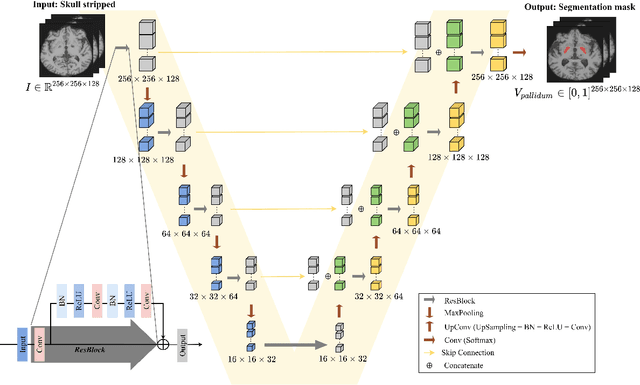
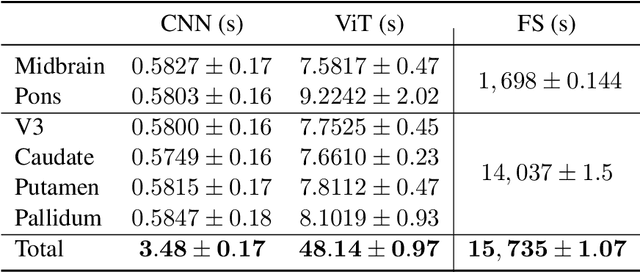
Abstract:Automated segmentation and volumetry of brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are essential for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease (PD) and Parkinson's plus syndromes (P-plus). To enhance the diagnostic performance, we adopt deep learning (DL) models in brain segmentation and compared their performance with the gold-standard non-DL method. We collected brain MRI scans of healthy controls (n=105) and patients with PD (n=105), multiple systemic atrophy (n=132), and progressive supranuclear palsy (n=69) at Samsung Medical Center from January 2017 to December 2020. Using the gold-standard non-DL model, FreeSurfer (FS), we segmented six brain structures: midbrain, pons, caudate, putamen, pallidum, and third ventricle, and considered them as annotating data for DL models, the representative V-Net and UNETR. The Dice scores and area under the curve (AUC) for differentiating normal, PD, and P-plus cases were calculated. The segmentation times of V-Net and UNETR for the six brain structures per patient were 3.48 +- 0.17 and 48.14 +- 0.97 s, respectively, being at least 300 times faster than FS (15,735 +- 1.07 s). Dice scores of both DL models were sufficiently high (>0.85), and their AUCs for disease classification were superior to that of FS. For classification of normal vs. P-plus and PD vs. multiple systemic atrophy (cerebellar type), the DL models and FS showed AUCs above 0.8. DL significantly reduces the analysis time without compromising the performance of brain segmentation and differential diagnosis. Our findings may contribute to the adoption of DL brain MRI segmentation in clinical settings and advance brain research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge