Cem Sazara
Discovering Mental Health Research Topics with Topic Modeling
Aug 25, 2023Abstract:Mental health significantly influences various aspects of our daily lives, and its importance has been increasingly recognized by the research community and the general public, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. This heightened interest is evident in the growing number of publications dedicated to mental health in the past decade. In this study, our goal is to identify general trends in the field and pinpoint high-impact research topics by analyzing a large dataset of mental health research papers. To accomplish this, we collected abstracts from various databases and trained a customized Sentence-BERT based embedding model leveraging the BERTopic framework. Our dataset comprises 96,676 research papers pertaining to mental health, enabling us to examine the relationships between different topics using their abstracts. To evaluate the effectiveness of the model, we compared it against two other state-of-the-art methods: Top2Vec model and LDA-BERT model. The model demonstrated superior performance in metrics that measure topic diversity and coherence. To enhance our analysis, we also generated word clouds to provide a comprehensive overview of the machine learning models applied in mental health research, shedding light on commonly utilized techniques and emerging trends. Furthermore, we provide a GitHub link* to the dataset used in this paper, ensuring its accessibility for further research endeavors.
Detecting floodwater on roadways from image data with handcrafted features and deep transfer learning
Aug 31, 2019
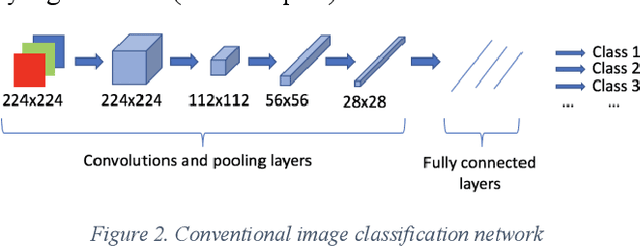
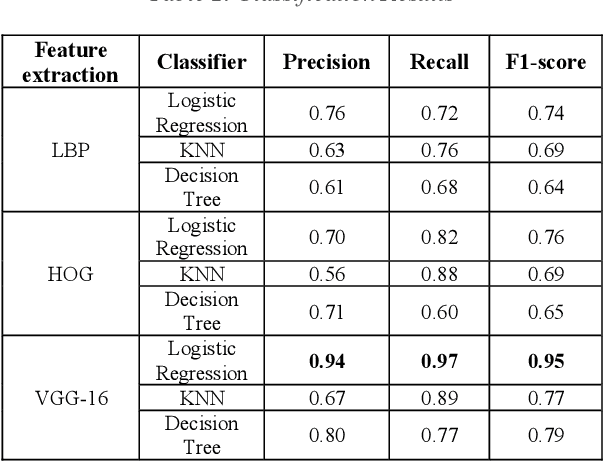
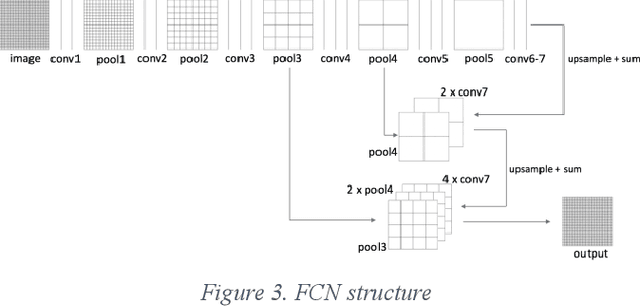
Abstract:Detecting roadway segments inundated due to floodwater has important applications for vehicle routing and traffic management decisions. This paper proposes a set of algorithms to automatically detect floodwater that may be present in an image captured by mobile phones or other types of optical cameras. For this purpose, image classification and flood area segmentation methods are developed. For the classification task, we used Local Binary Patterns (LBP), Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) and pre-trained deep neural network (VGG-16) as feature extractors and trained logistic regression, k-nearest neighbors, and decision tree classifiers on the extracted features. Pre-trained VGG-16 network with logistic regression classifier outperformed all other methods. For the flood area segmentation task, we investigated superpixel based methods and Fully Convolutional Neural Network (FCN). Similar to the classification task, we trained logistic regression and k-nearest neighbors classifiers on the superpixel areas and compared that with an end-to-end trained FCN. Conditional Random Fields (CRF) method was applied after both segmentation methods to post-process coarse segmentation results. FCN offered the highest scores in all metrics; it was followed by superpixel-based logistic regression and then superpixel-based KNN.
Offline reconstruction of missing vehicle trajectory data from 3D LIDAR
Sep 16, 2017



Abstract:LIDAR has become an important part of many autonomous vehicles with its advantages on distance measurement and obstacle detection. LIDAR produces point clouds which have important information about surrounding environment. In this paper, we collected trajectory data on a two lane urban road using a Velodyne VLP-16 Lidar. Due to dynamic nature of data collection and limited range of the sensor, some of these trajectories have missing points or gaps. In this paper, we propose a novel method for recovery of missing vehicle trajectory data points using microscopic traffic flow models. While short gaps (less than 5 seconds) can be recovered with simple linear regression, and longer gaps are recovered with the proposed method that makes use of car following models calibrated by assigning weights to known points based on proximity to the gaps. Newell's, Pipes, IDM and Gipps' car following models are calibrated and tested with the ground truth trajectory data from LIDAR and NGSIM I-80 dataset. Gipps' calibrated model yielded the best result.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge