Cara M. Nunez
Curvature-Aware Calibration of Tactile Sensors for Accurate Force Estimation on Non-Planar Surfaces
Oct 29, 2025



Abstract:Flexible tactile sensors are increasingly used in real-world applications such as robotic grippers, prosthetic hands, wearable gloves, and assistive devices, where they need to conform to curved and irregular surfaces. However, most existing tactile sensors are calibrated only on flat substrates, and their accuracy and consistency degrade once mounted on curved geometries. This limitation restricts their reliability in practical use. To address this challenge, we develop a calibration model for a widely used resistive tactile sensor design that enables accurate force estimation on one-dimensional curved surfaces. We then train a neural network (a multilayer perceptron) to predict local curvature from baseline sensor outputs recorded under no applied load, achieving an R2 score of 0.91. The proposed approach is validated on five daily objects with varying curvatures under forces from 2 N to 8 N. Results show that the curvature-aware calibration maintains consistent force accuracy across all surfaces, while flat-surface calibration underestimates force as curvature increases. Our results demonstrate that curvature-aware modeling improves the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of flexible tactile sensors, enabling dependable performance across real-world applications.
CIVIL: Causal and Intuitive Visual Imitation Learning
Apr 24, 2025



Abstract:Today's robots learn new tasks by imitating human examples. However, this standard approach to visual imitation learning is fundamentally limited: the robot observes what the human does, but not why the human chooses those behaviors. Without understanding the features that factor into the human's decisions, robot learners often misinterpret the data and fail to perform the task when the environment changes. We therefore propose a shift in perspective: instead of asking human teachers just to show what actions the robot should take, we also enable humans to indicate task-relevant features using markers and language prompts. Our proposed algorithm, CIVIL, leverages this augmented data to filter the robot's visual observations and extract a feature representation that causally informs human actions. CIVIL then applies these causal features to train a transformer-based policy that emulates human behaviors without being confused by visual distractors. Our simulations, real-world experiments, and user study demonstrate that robots trained with CIVIL can learn from fewer human demonstrations and perform better than state-of-the-art baselines, especially in previously unseen scenarios. See videos at our project website: https://civil2025.github.io
Investigating Social Haptic Illusions for Tactile Stroking (SHIFTS)
Mar 02, 2020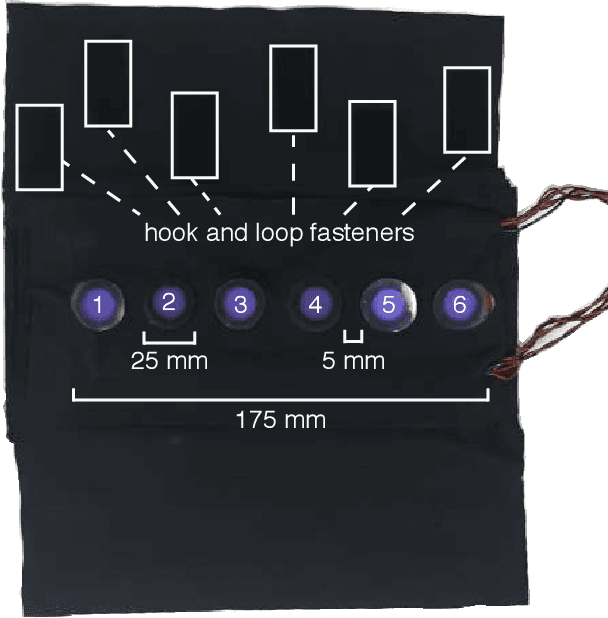


Abstract:A common and effective form of social touch is stroking on the forearm. We seek to replicate this stroking sensation using haptic illusions. This work compares two methods that provide sequential discrete stimulation: sequential normal indentation and sequential lateral skin-slip using discrete actuators. Our goals are to understand which form of stimulation more effectively creates a continuous stroking sensation, and how many discrete contact points are needed. We performed a study with 20 participants in which they rated sensations from the haptic devices on continuity and pleasantness. We found that lateral skin-slip created a more continuous sensation, and decreasing the number of contact points decreased the continuity. These results inform the design of future wearable haptic devices and the creation of haptic signals for effective social communication.
Understanding Continuous and Pleasant Linear Sensations on the Forearm from a Sequential Discrete Lateral Skin-Slip Haptic Device
Sep 03, 2019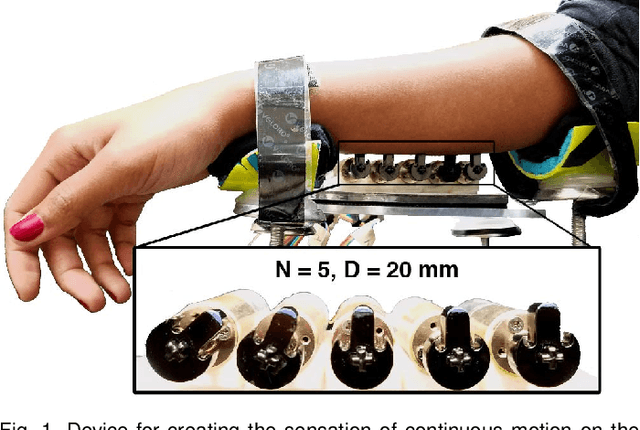

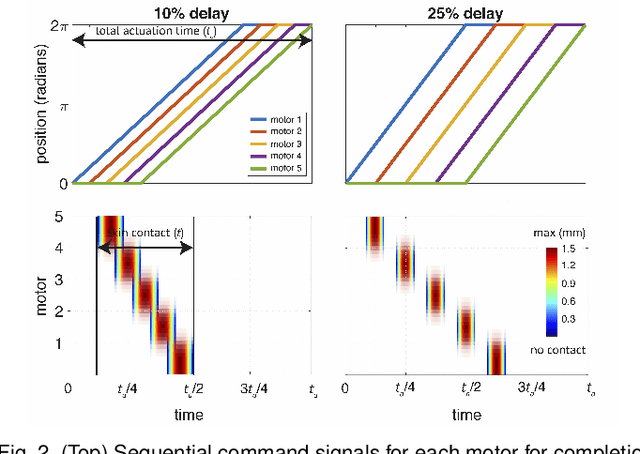

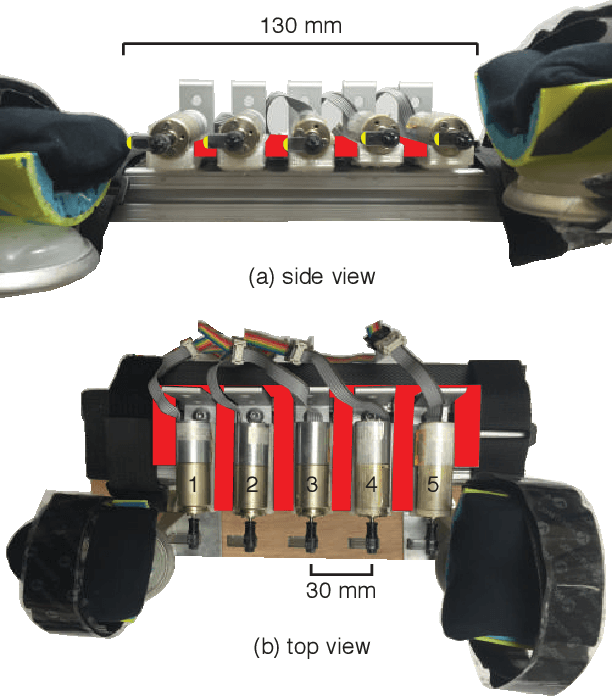
Abstract:A continuous stroking sensation on the skin can convey messages or emotion cues. We seek to induce this sensation using a combination of illusory motion and lateral stroking via a haptic device. Our system provides discrete lateral skin-slip on the forearm with rotating tactors, which independently provide lateral skin-slip in a timed sequence. We vary the sensation by changing the angular velocity and delay between adjacent tactors, such that the apparent speed of the perceived stroke ranges from 2.5 to 48.2 cm/s. We investigated which actuation parameters create the most pleasant and continuous sensations through a user study with 16 participants. On average, the sensations were rated by participants as both continuous and pleasant. The most continuous and pleasant sensations were created by apparent speeds of 7.7 and 5.1 cm/s, respectively. We also investigated the effect of spacing between contact points on the pleasantness and continuity of the stroking sensation, and found that the users experience a pleasant and continuous linear sensation even when the space between contact points is relatively large (40 mm). Understanding how sequential discrete lateral skin-slip creates continuous linear sensations can influence the design and control of future wearable haptic devices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge