Camille Goudeseune
Fast transcription of speech in low-resource languages
Sep 16, 2019
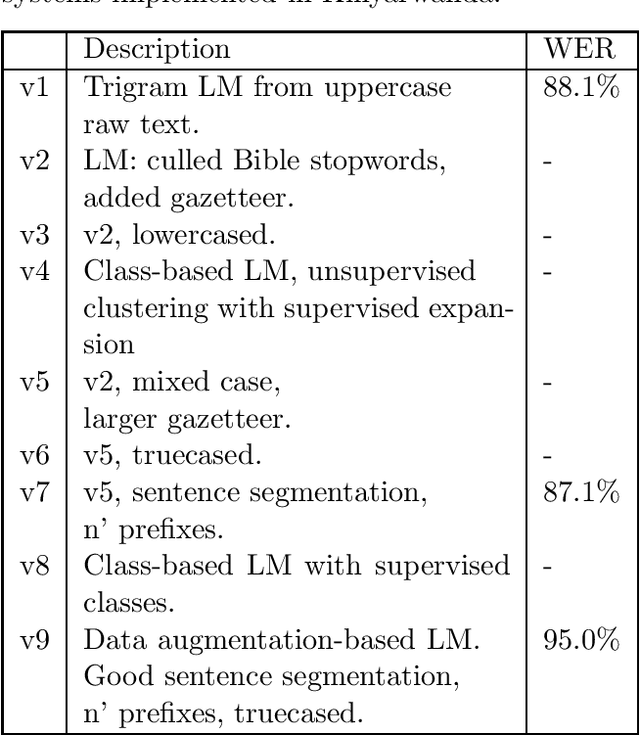

Abstract:We present software that, in only a few hours, transcribes forty hours of recorded speech in a surprise language, using only a few tens of megabytes of noisy text in that language, and a zero-resource grapheme to phoneme (G2P) table. A pretrained acoustic model maps acoustic features to phonemes; a reversed G2P maps these to graphemes; then a language model maps these to a most-likely grapheme sequence, i.e., a transcription. This software has worked successfully with corpora in Arabic, Assam, Kinyarwanda, Russian, Sinhalese, Swahili, Tagalog, and Tamil.
Generating Nontrivial Melodies for Music as a Service
Oct 06, 2017
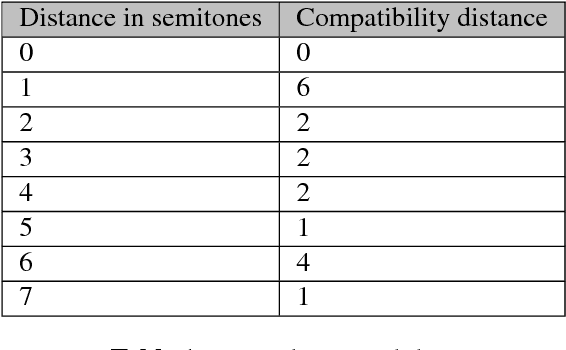
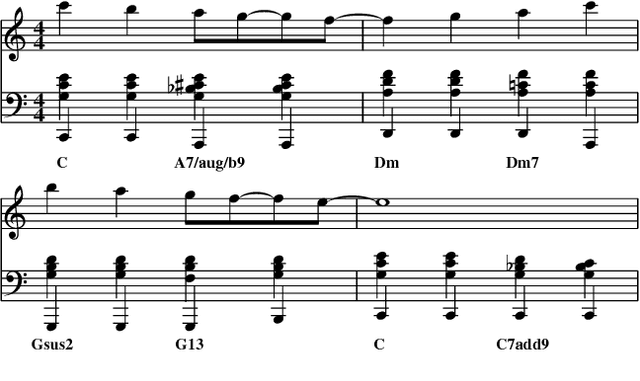

Abstract:We present a hybrid neural network and rule-based system that generates pop music. Music produced by pure rule-based systems often sounds mechanical. Music produced by machine learning sounds better, but still lacks hierarchical temporal structure. We restore temporal hierarchy by augmenting machine learning with a temporal production grammar, which generates the music's overall structure and chord progressions. A compatible melody is then generated by a conditional variational recurrent autoencoder. The autoencoder is trained with eight-measure segments from a corpus of 10,000 MIDI files, each of which has had its melody track and chord progressions identified heuristically. The autoencoder maps melody into a multi-dimensional feature space, conditioned by the underlying chord progression. A melody is then generated by feeding a random sample from that space to the autoencoder's decoder, along with the chord progression generated by the grammar. The autoencoder can make musically plausible variations on an existing melody, suitable for recurring motifs. It can also reharmonize a melody to a new chord progression, keeping the rhythm and contour. The generated music compares favorably with that generated by other academic and commercial software designed for the music-as-a-service industry.
Motion trails from time-lapse video
Dec 04, 2015
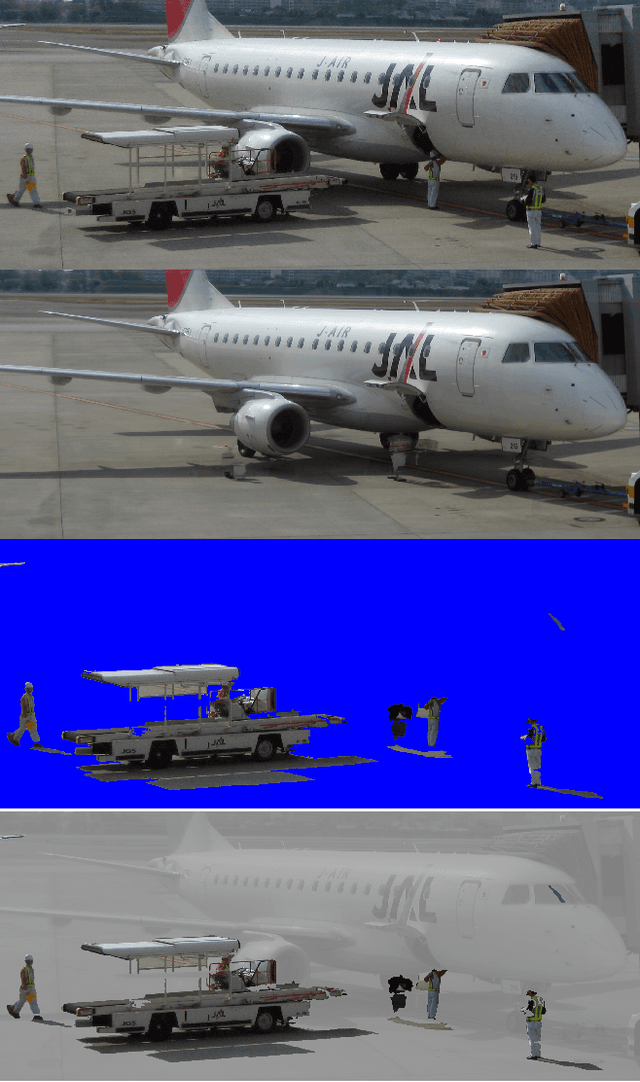



Abstract:From an image sequence captured by a stationary camera, background subtraction can detect moving foreground objects in the scene. Distinguishing foreground from background is further improved by various heuristics. Then each object's motion can be emphasized by duplicating its positions as a motion trail. These trails clarify the objects' spatial relationships. Also, adding motion trails to a video before previewing it at high speed reduces the risk of overlooking transient events.
Stitched Panoramas from Toy Airborne Video Cameras
Nov 11, 2013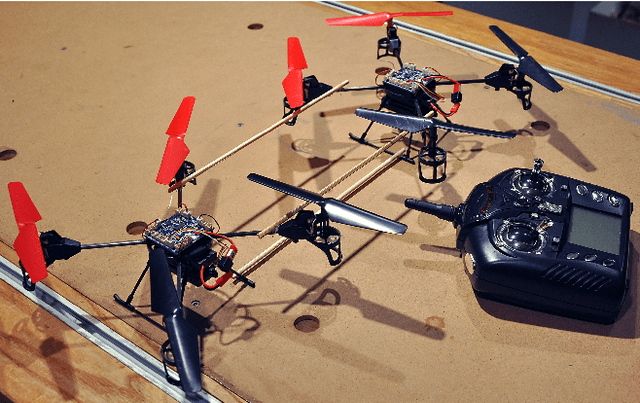



Abstract:Effective panoramic photographs are taken from vantage points that are high. High vantage points have recently become easier to reach as the cost of quadrotor helicopters has dropped to nearly disposable levels. Although cameras carried by such aircraft weigh only a few grams, their low-quality video can be converted into panoramas of high quality and high resolution. Also, the small size of these aircraft vastly reduces the risks inherent to flight.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge