Camelia Chira
Classifiers With a Reject Option for Early Time-Series Classification
Dec 14, 2013



Abstract:Early classification of time-series data in a dynamic environment is a challenging problem of great importance in signal processing. This paper proposes a classifier architecture with a reject option capable of online decision making without the need to wait for the entire time series signal to be present. The main idea is to classify an odor/gas signal with an acceptable accuracy as early as possible. Instead of using posterior probability of a classifier, the proposed method uses the "agreement" of an ensemble to decide whether to accept or reject the candidate label. The introduced algorithm is applied to the bio-chemistry problem of odor classification to build a novel Electronic-Nose called Forefront-Nose. Experimental results on wind tunnel test-bed facility confirms the robustness of the forefront-nose compared to the standard classifiers from both earliness and recognition perspectives.
The Generalized Traveling Salesman Problem solved with Ant Algorithms
Oct 09, 2013
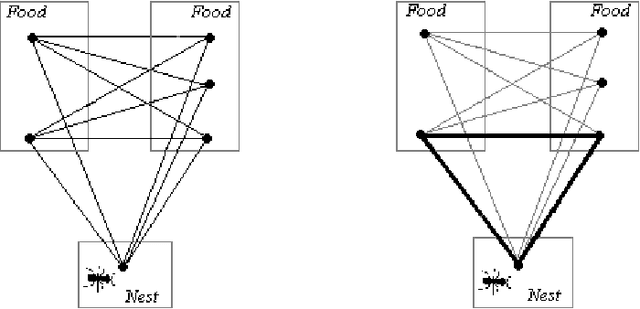
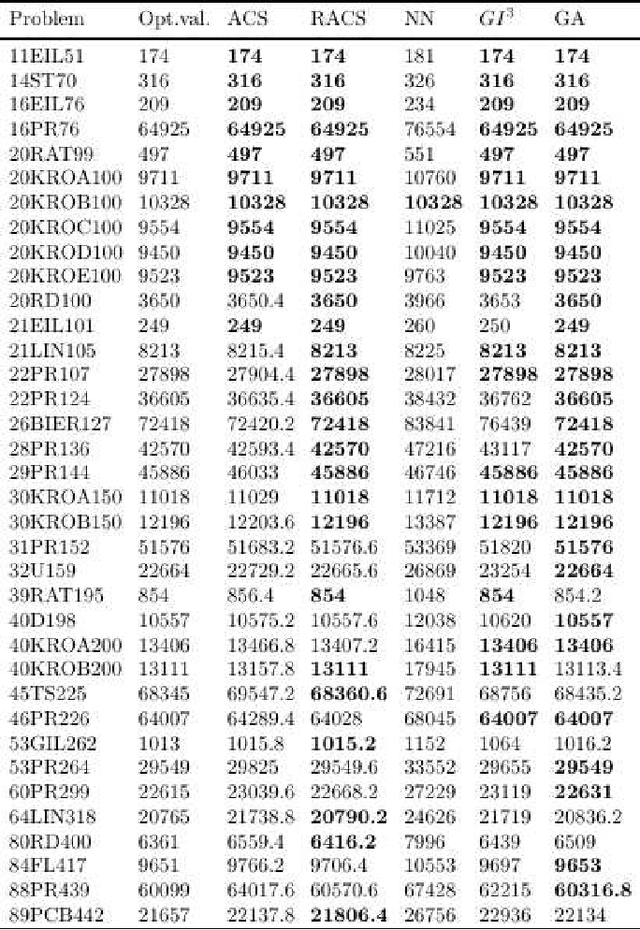
Abstract:A well known N P-hard problem called the Generalized Traveling Salesman Problem (GTSP) is considered. In GTSP the nodes of a complete undirected graph are partitioned into clusters. The objective is to find a minimum cost tour passing through exactly one node from each cluster. An exact exponential time algorithm and an effective meta-heuristic algorithm for the problem are presented. The meta-heuristic proposed is a modified Ant Colony System (ACS) algorithm called Reinforcing Ant Colony System (RACS) which introduces new correction rules in the ACS algorithm. Computational results are reported for many standard test problems. The proposed algorithm is competitive with the other already proposed heuristics for the GTSP in both solution quality and computational time.
* indexed in Scopus, ORCID
A hybrid ACO approach to the Matrix Bandwidth Minimization Problem
Sep 16, 2012Abstract:The evolution of the human society raises more and more difficult endeavors. For some of the real-life problems, the computing time-restriction enhances their complexity. The Matrix Bandwidth Minimization Problem (MBMP) seeks for a simultaneous permutation of the rows and the columns of a square matrix in order to keep its nonzero entries close to the main diagonal. The MBMP is a highly investigated P-complete problem, as it has broad applications in industry, logistics, artificial intelligence or information recovery. This paper describes a new attempt to use the Ant Colony Optimization framework in tackling MBMP. The introduced model is based on the hybridization of the Ant Colony System technique with new local search mechanisms. Computational experiments confirm a good performance of the proposed algorithm for the considered set of MBMP instances.
* This paper has been withdrawn by the author, due to an error
Sensitive Ants in Solving the Generalized Vehicle Routing Problem
Aug 27, 2012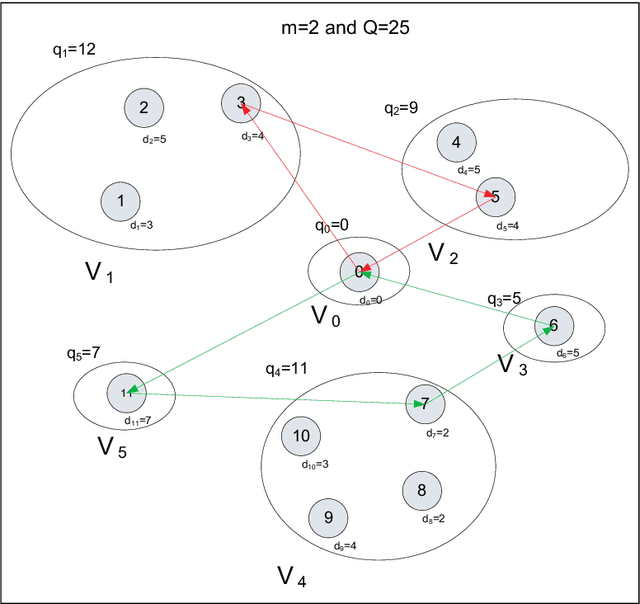
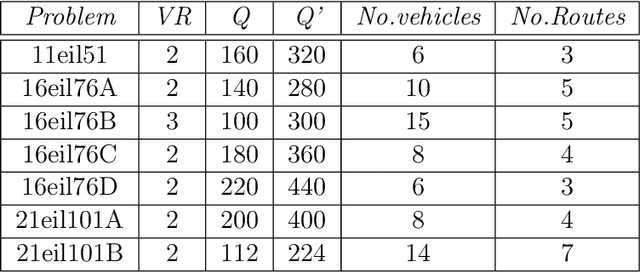
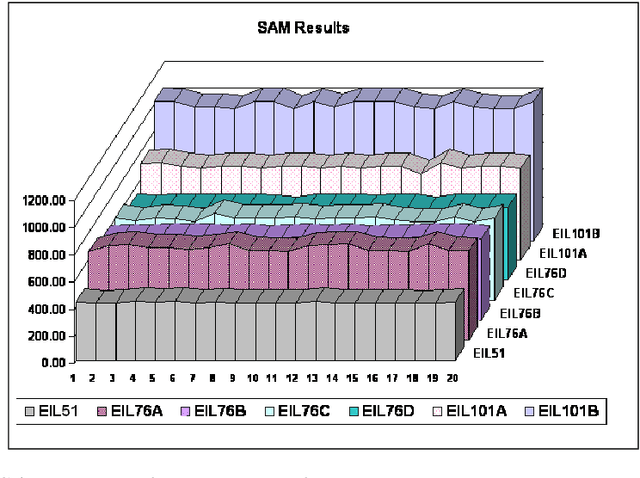
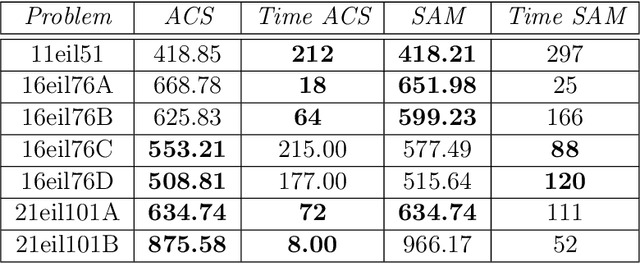
Abstract:The idea of sensitivity in ant colony systems has been exploited in hybrid ant-based models with promising results for many combinatorial optimization problems. Heterogeneity is induced in the ant population by endowing individual ants with a certain level of sensitivity to the pheromone trail. The variable pheromone sensitivity within the same population of ants can potentially intensify the search while in the same time inducing diversity for the exploration of the environment. The performance of sensitive ant models is investigated for solving the generalized vehicle routing problem. Numerical results and comparisons are discussed and analysed with a focus on emphasizing any particular aspects and potential benefits related to hybrid ant-based models.
* 5 pages
New results of ant algorithms for the Linear Ordering Problem
Aug 27, 2012



Abstract:Ant-based algorithms are successful tools for solving complex problems. One of these problems is the Linear Ordering Problem (LOP). The paper shows new results on some LOP instances, using Ant Colony System (ACS) and the Step-Back Sensitive Ant Model (SB-SAM).
* 5 pages, 5 figures Zbl:06048718
A Route Confidence Evaluation Method for Reliable Hierarchical Text Categorization
Jun 02, 2012



Abstract:Hierarchical Text Categorization (HTC) is becoming increasingly important with the rapidly growing amount of text data available in the World Wide Web. Among the different strategies proposed to cope with HTC, the Local Classifier per Node (LCN) approach attains good performance by mirroring the underlying class hierarchy while enforcing a top-down strategy in the testing step. However, the problem of embedding hierarchical information (parent-child relationship) to improve the performance of HTC systems still remains open. A confidence evaluation method for a selected route in the hierarchy is proposed to evaluate the reliability of the final candidate labels in an HTC system. In order to take into account the information embedded in the hierarchy, weight factors are used to take into account the importance of each level. An acceptance/rejection strategy in the top-down decision making process is proposed, which improves the overall categorization accuracy by rejecting a few percentage of samples, i.e., those with low reliability score. Experimental results on the Reuters benchmark dataset (RCV1- v2) confirm the effectiveness of the proposed method, compared to other state-of-the art HTC methods.
New parallel programming language design: a bridge between brain models and multi-core/many-core computers?
Dec 15, 2008



Abstract:The recurrent theme of this paper is that sequences of long temporal patterns as opposed to sequences of simple statements are to be fed into computation devices, being them (new proposed) models for brain activity or multi-core/many-core computers. In such models, parts of these long temporal patterns are already committed while other are predicted. This combination of matching patterns and making predictions appears as a key element in producing intelligent processing in brain models and getting efficient speculative execution on multi-core/many-core computers. A bridge between these far-apart models of computation could be provided by appropriate design of massively parallel, interactive programming languages. Agapia is a recently proposed language of this kind, where user controlled long high-level temporal structures occur at the interaction interfaces of processes. In this paper Agapia is used to link HTMs brain models with TRIPS multi-core/many-core architectures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge