Petrica C. Pop
On the Resilience of an Ant-based System in Fuzzy Environments. An Empirical Study
Feb 16, 2014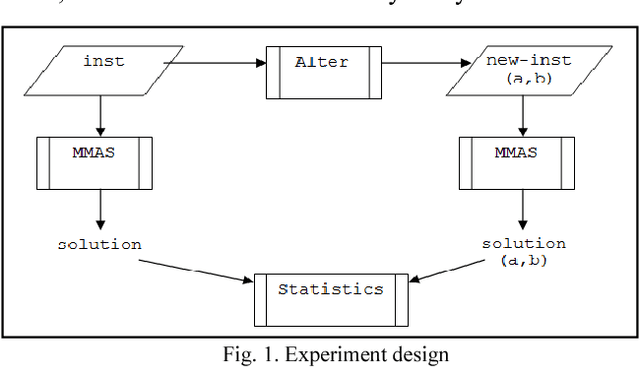
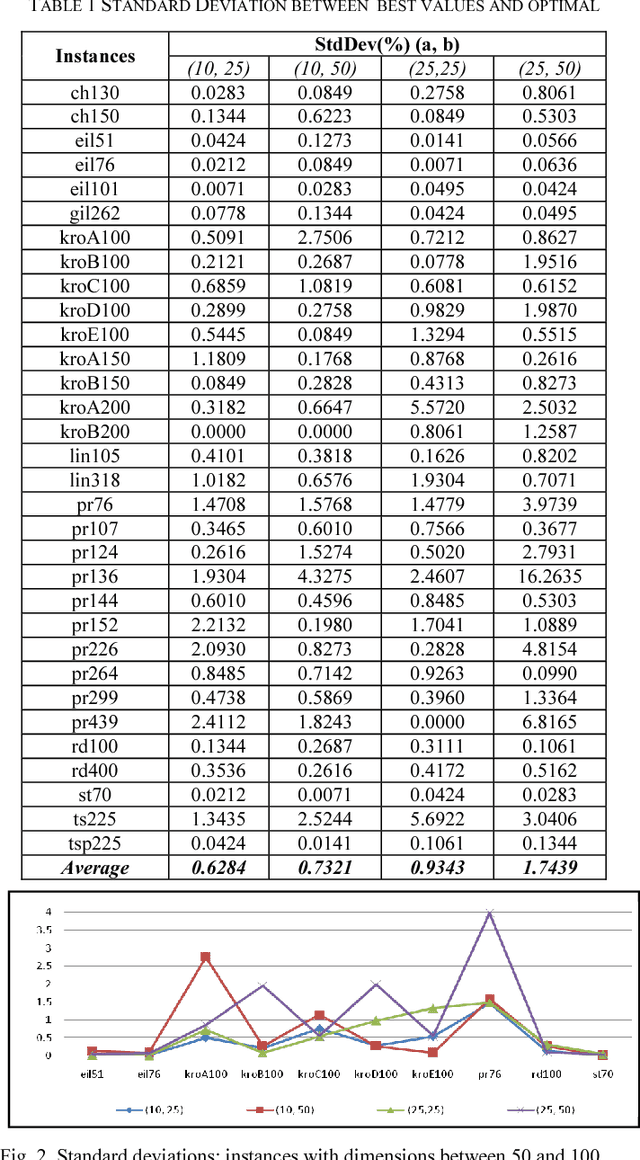
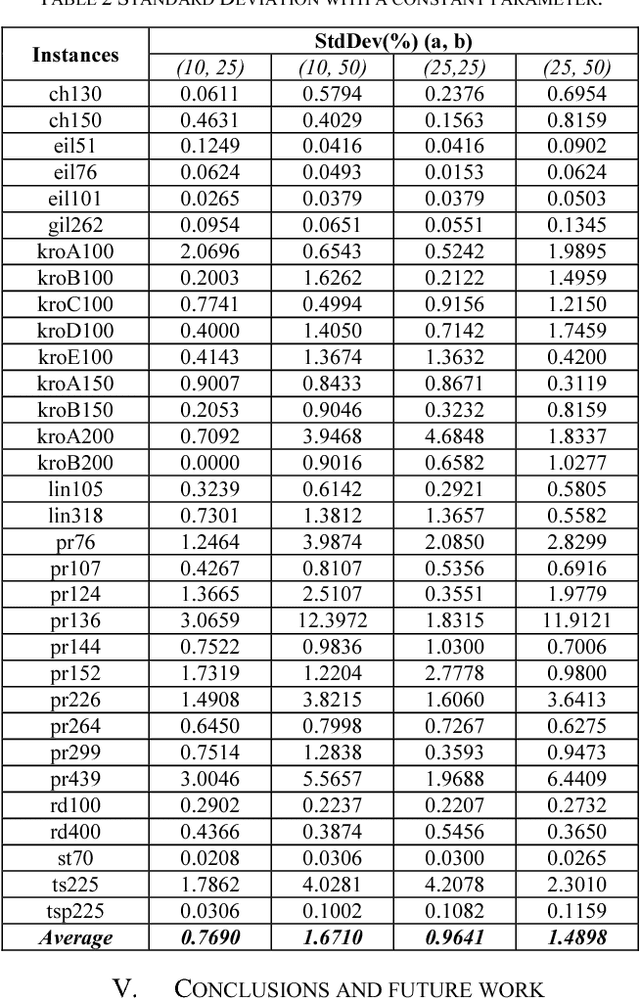
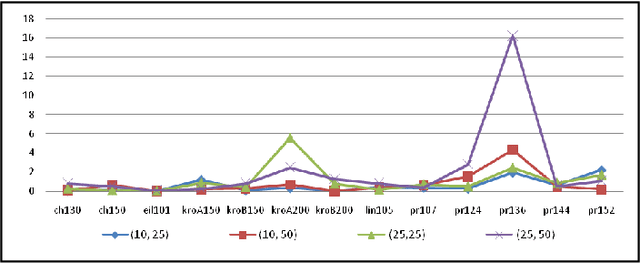
Abstract:The current work describes an empirical study conducted in order to investigate the behavior of an optimization method in a fuzzy environment. MAX-MIN Ant System, an efficient implementation of a heuristic method is used for solving an optimization problem derived from the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP). Several publicly-available symmetric TSP instances and their fuzzy variants are tested in order to extract some general features. The entry data was adapted by introducing a two-dimensional systematic degree of fuzziness, proportional with the number of nodes, the dimension of the instance and also with the distances between nodes, the scale of the instance. The results show that our proposed method can handle the data uncertainty, showing good resilience and adaptability.
The Generalized Traveling Salesman Problem solved with Ant Algorithms
Oct 09, 2013
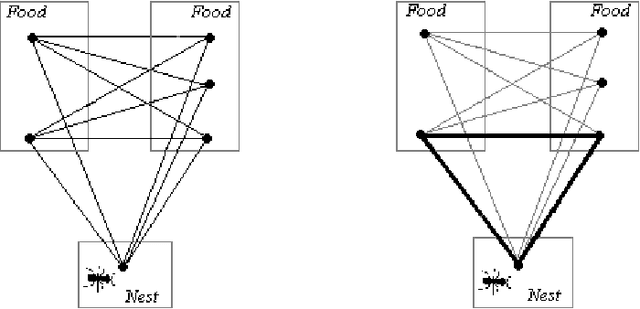
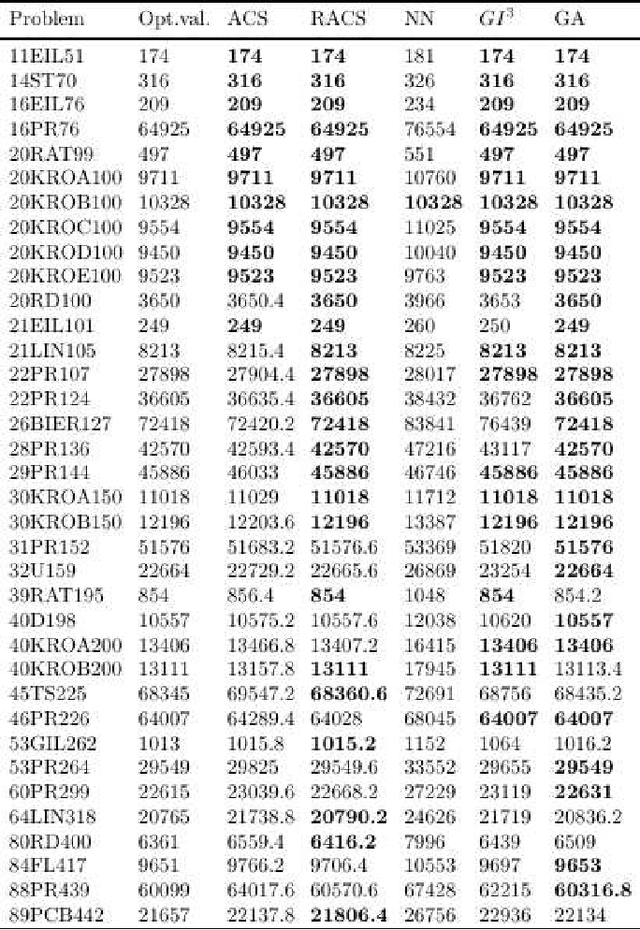
Abstract:A well known N P-hard problem called the Generalized Traveling Salesman Problem (GTSP) is considered. In GTSP the nodes of a complete undirected graph are partitioned into clusters. The objective is to find a minimum cost tour passing through exactly one node from each cluster. An exact exponential time algorithm and an effective meta-heuristic algorithm for the problem are presented. The meta-heuristic proposed is a modified Ant Colony System (ACS) algorithm called Reinforcing Ant Colony System (RACS) which introduces new correction rules in the ACS algorithm. Computational results are reported for many standard test problems. The proposed algorithm is competitive with the other already proposed heuristics for the GTSP in both solution quality and computational time.
* indexed in Scopus, ORCID
Sensitive Ants in Solving the Generalized Vehicle Routing Problem
Aug 27, 2012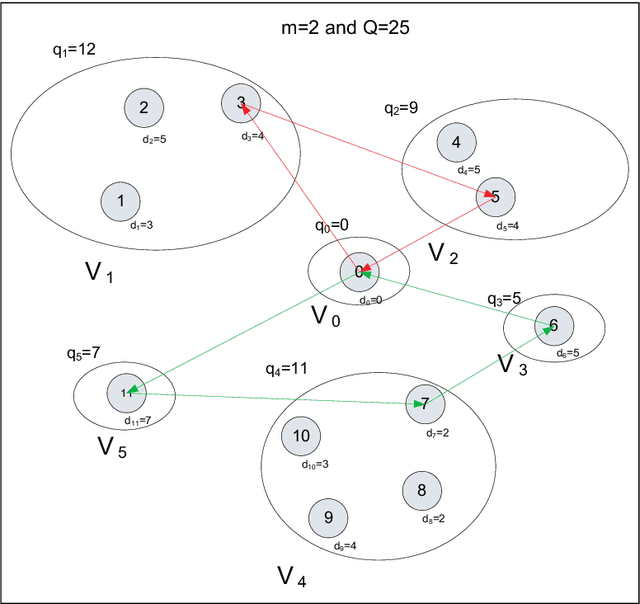
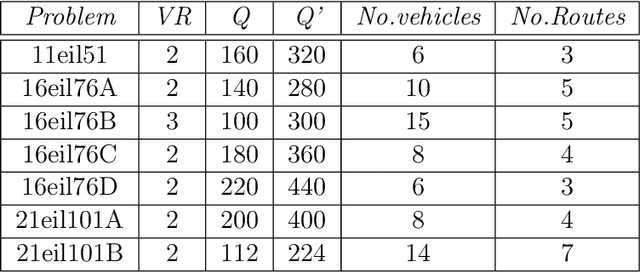
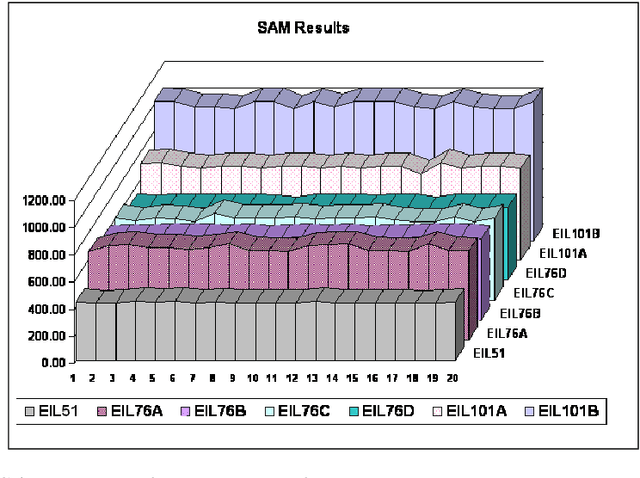
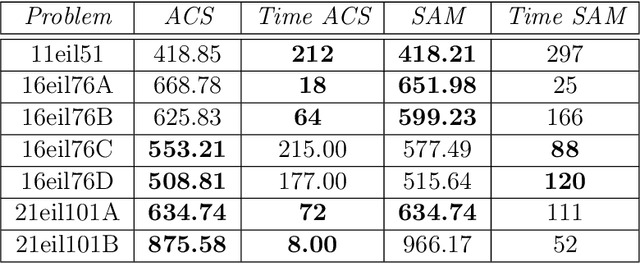
Abstract:The idea of sensitivity in ant colony systems has been exploited in hybrid ant-based models with promising results for many combinatorial optimization problems. Heterogeneity is induced in the ant population by endowing individual ants with a certain level of sensitivity to the pheromone trail. The variable pheromone sensitivity within the same population of ants can potentially intensify the search while in the same time inducing diversity for the exploration of the environment. The performance of sensitive ant models is investigated for solving the generalized vehicle routing problem. Numerical results and comparisons are discussed and analysed with a focus on emphasizing any particular aspects and potential benefits related to hybrid ant-based models.
* 5 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge