C. Xiao
Highly Efficient and Unsupervised Framework for Moving Object Detection in Satellite Videos
Nov 24, 2024Abstract:Moving object detection in satellite videos (SVMOD) is a challenging task due to the extremely dim and small target characteristics. Current learning-based methods extract spatio-temporal information from multi-frame dense representation with labor-intensive manual labels to tackle SVMOD, which needs high annotation costs and contains tremendous computational redundancy due to the severe imbalance between foreground and background regions. In this paper, we propose a highly efficient unsupervised framework for SVMOD. Specifically, we propose a generic unsupervised framework for SVMOD, in which pseudo labels generated by a traditional method can evolve with the training process to promote detection performance. Furthermore, we propose a highly efficient and effective sparse convolutional anchor-free detection network by sampling the dense multi-frame image form into a sparse spatio-temporal point cloud representation and skipping the redundant computation on background regions. Coping these two designs, we can achieve both high efficiency (label and computation efficiency) and effectiveness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method can not only process 98.8 frames per second on 1024x1024 images but also achieve state-of-the-art performance. The relabeled dataset and code are available at https://github.com/ChaoXiao12/Moving-object-detection-in-satellite-videos-HiEUM.
* 8 pages, 8 figures
An Experimental Study of Class Imbalance in Federated Learning
Sep 09, 2021
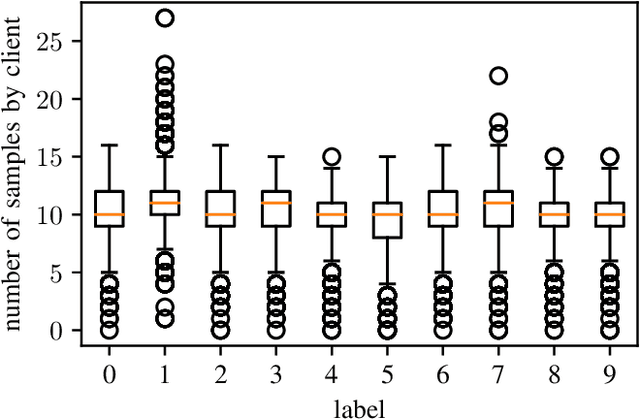
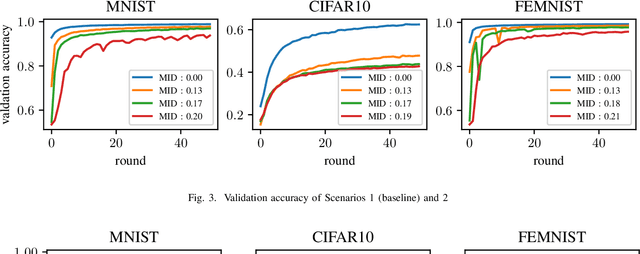
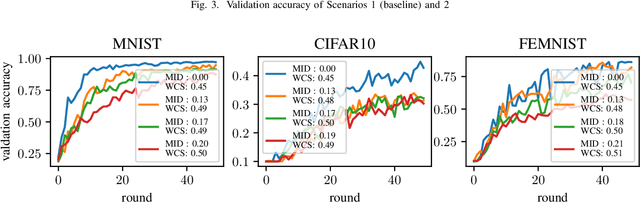
Abstract:Federated learning is a distributed machine learning paradigm that trains a global model for prediction based on a number of local models at clients while local data privacy is preserved. Class imbalance is believed to be one of the factors that degrades the global model performance. However, there has been very little research on if and how class imbalance can affect the global performance. class imbalance in federated learning is much more complex than that in traditional non-distributed machine learning, due to different class imbalance situations at local clients. Class imbalance needs to be re-defined in distributed learning environments. In this paper, first, we propose two new metrics to define class imbalance -- the global class imbalance degree (MID) and the local difference of class imbalance among clients (WCS). Then, we conduct extensive experiments to analyze the impact of class imbalance on the global performance in various scenarios based on our definition. Our results show that a higher MID and a larger WCS degrade more the performance of the global model. Besides, WCS is shown to slow down the convergence of the global model by misdirecting the optimization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge