C. V. Krishnakumar Iyer
SeMAnD: Self-Supervised Anomaly Detection in Multimodal Geospatial Datasets
Sep 26, 2023Abstract:We propose a Self-supervised Anomaly Detection technique, called SeMAnD, to detect geometric anomalies in Multimodal geospatial datasets. Geospatial data comprises of acquired and derived heterogeneous data modalities that we transform to semantically meaningful, image-like tensors to address the challenges of representation, alignment, and fusion of multimodal data. SeMAnD is comprised of (i) a simple data augmentation strategy, called RandPolyAugment, capable of generating diverse augmentations of vector geometries, and (ii) a self-supervised training objective with three components that incentivize learning representations of multimodal data that are discriminative to local changes in one modality which are not corroborated by the other modalities. Detecting local defects is crucial for geospatial anomaly detection where even small anomalies (e.g., shifted, incorrectly connected, malformed, or missing polygonal vector geometries like roads, buildings, landcover, etc.) are detrimental to the experience and safety of users of geospatial applications like mapping, routing, search, and recommendation systems. Our empirical study on test sets of different types of real-world geometric geospatial anomalies across 3 diverse geographical regions demonstrates that SeMAnD is able to detect real-world defects and outperforms domain-agnostic anomaly detection strategies by 4.8-19.7% as measured using anomaly classification AUC. We also show that model performance increases (i) up to 20.4% as the number of input modalities increase and (ii) up to 22.9% as the diversity and strength of training data augmentations increase.
Scalable Self-Supervised Representation Learning from Spatiotemporal Motion Trajectories for Multimodal Computer Vision
Oct 07, 2022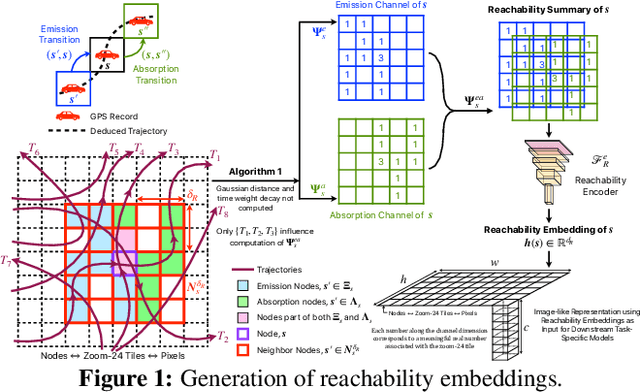
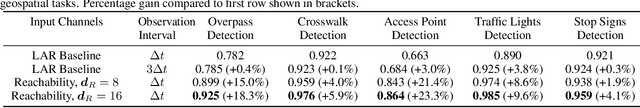
Abstract:Self-supervised representation learning techniques utilize large datasets without semantic annotations to learn meaningful, universal features that can be conveniently transferred to solve a wide variety of downstream supervised tasks. In this work, we propose a self-supervised method for learning representations of geographic locations from unlabeled GPS trajectories to solve downstream geospatial computer vision tasks. Tiles resulting from a raster representation of the earth's surface are modeled as nodes on a graph or pixels of an image. GPS trajectories are modeled as allowed Markovian paths on these nodes. A scalable and distributed algorithm is presented to compute image-like representations, called reachability summaries, of the spatial connectivity patterns between tiles and their neighbors implied by the observed Markovian paths. A convolutional, contractive autoencoder is trained to learn compressed representations, called reachability embeddings, of reachability summaries for every tile. Reachability embeddings serve as task-agnostic, feature representations of geographic locations. Using reachability embeddings as pixel representations for five different downstream geospatial tasks, cast as supervised semantic segmentation problems, we quantitatively demonstrate that reachability embeddings are semantically meaningful representations and result in 4-23% gain in performance, as measured using area under the precision-recall curve (AUPRC) metric, when compared to baseline models that use pixel representations that do not account for the spatial connectivity between tiles. Reachability embeddings transform sequential, spatiotemporal mobility data into semantically meaningful tensor representations that can be combined with other sources of imagery and are designed to facilitate multimodal learning in geospatial computer vision.
Reachability Embeddings: Scalable Self-Supervised Representation Learning from Markovian Trajectories for Geospatial Computer Vision
Oct 24, 2021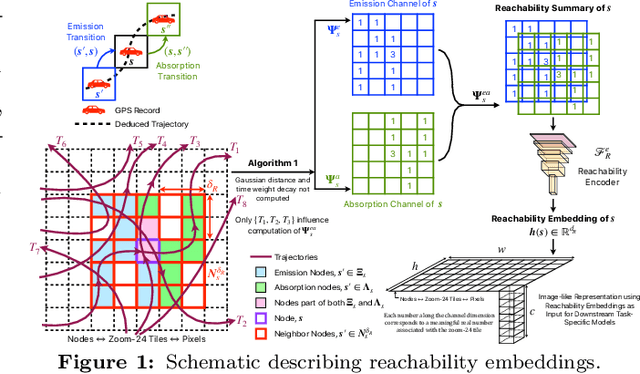
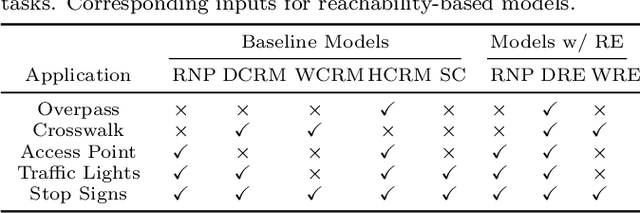
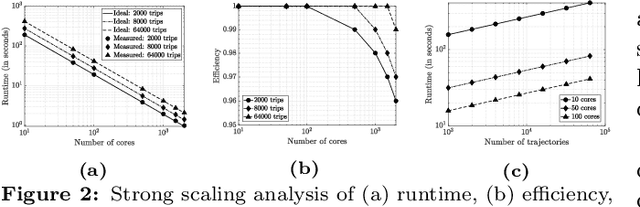
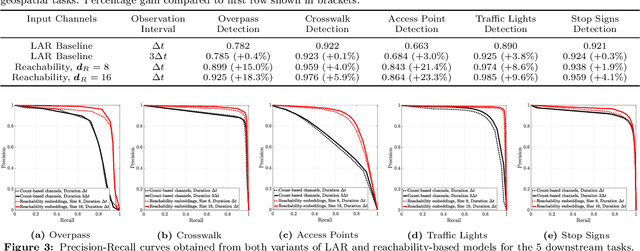
Abstract:Self-supervised representation learning techniques utilize large datasets without semantic annotations to learn meaningful, universal features that can be conveniently transferred to solve a wide variety of downstream supervised tasks. In this paper, we propose a self-supervised method for learning representations of geographic locations from unlabeled GPS trajectories to solve downstream geospatial computer vision tasks. Tiles resulting from a raster representation of the earth's surface are modeled as nodes on a graph or pixels of an image. GPS trajectories are modeled as allowed Markovian paths on these nodes. A scalable and distributed algorithm is presented to compute image-like representations, called reachability summaries, of the spatial connectivity patterns between tiles and their neighbors implied by the observed Markovian paths. A convolutional, contractive autoencoder is trained to learn compressed representations, called reachability embeddings, of reachability summaries for every tile. Reachability embeddings serve as task-agnostic, feature representations of geographic locations. Using reachability embeddings as pixel representations for five different downstream geospatial tasks, cast as supervised semantic segmentation problems, we quantitatively demonstrate that reachability embeddings are semantically meaningful representations and result in 4-23% gain in performance, while using upto 67% less trajectory data, as measured using area under the precision-recall curve (AUPRC) metric, when compared to baseline models that use pixel representations that do not account for the spatial connectivity between tiles. Reachability embeddings transform sequential, spatiotemporal mobility data into semantically meaningful image-like representations that can be combined with other sources of imagery and are designed to facilitate multimodal learning in geospatial computer vision.
Trinity: A No-Code AI platform for complex spatial datasets
Jul 01, 2021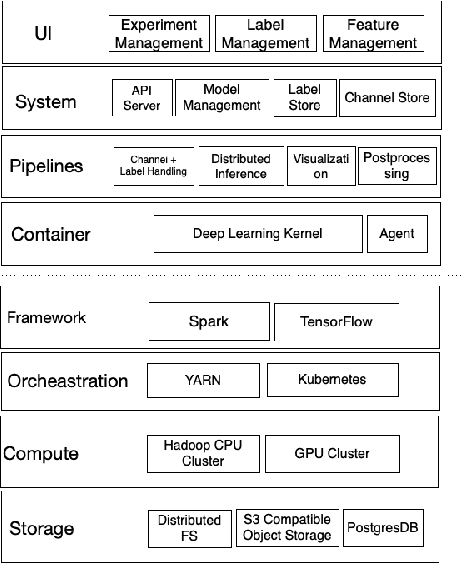
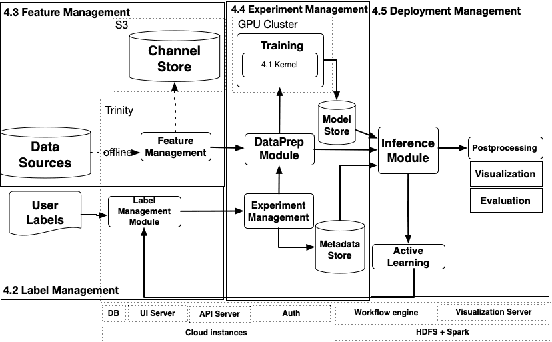
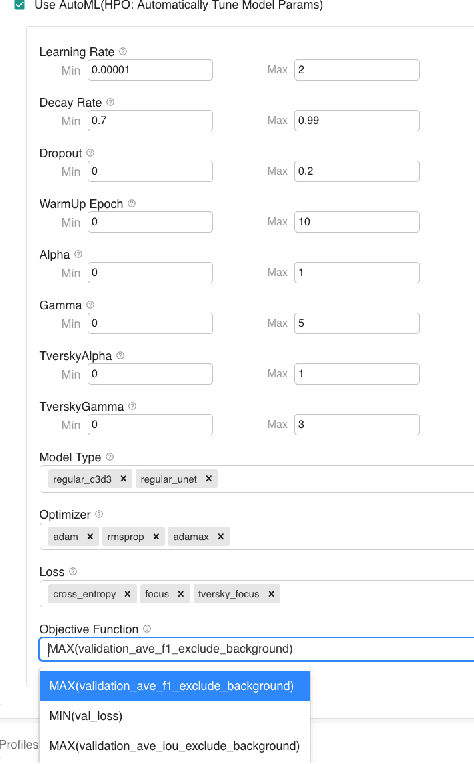
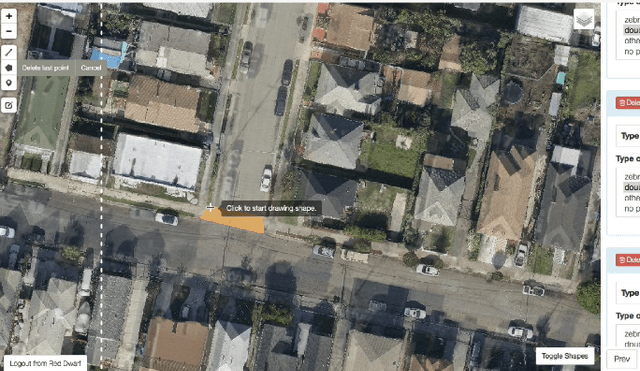
Abstract:We present a no-code Artificial Intelligence (AI) platform called Trinity with the main design goal of enabling both machine learning researchers and non-technical geospatial domain experts to experiment with domain-specific signals and datasets for solving a variety of complex problems on their own. This versatility to solve diverse problems is achieved by transforming complex Spatio-temporal datasets to make them consumable by standard deep learning models, in this case, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), and giving the ability to formulate disparate problems in a standard way, eg. semantic segmentation. With an intuitive user interface, a feature store that hosts derivatives of complex feature engineering, a deep learning kernel, and a scalable data processing mechanism, Trinity provides a powerful platform for domain experts to share the stage with scientists and engineers in solving business-critical problems. It enables quick prototyping, rapid experimentation and reduces the time to production by standardizing model building and deployment. In this paper, we present our motivation behind Trinity and its design along with showcasing sample applications to motivate the idea of lowering the bar to using AI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge