César González-Gutiérrez
Analyzing Text Representations under Tight Annotation Budgets: Measuring Structural Alignment
Oct 11, 2022
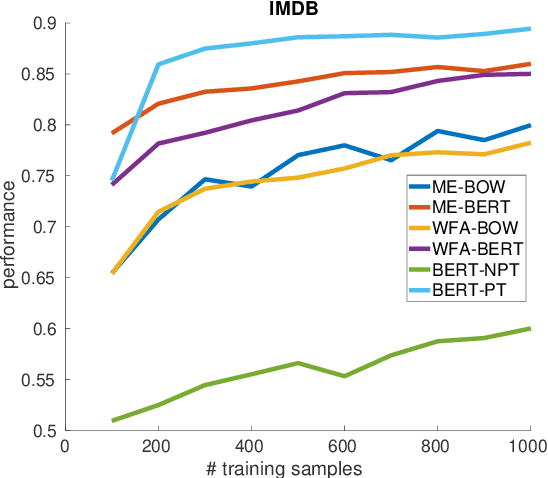
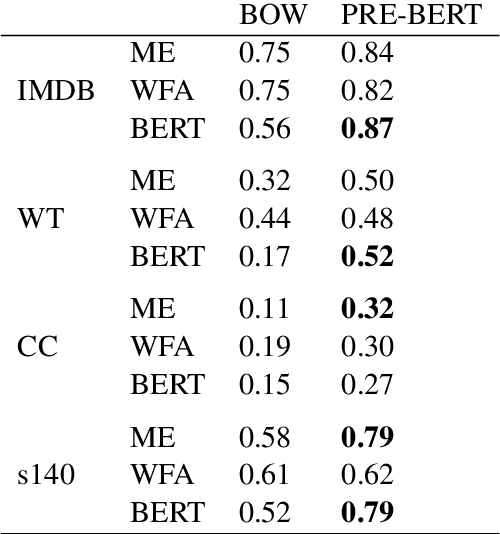
Abstract:Annotating large collections of textual data can be time consuming and expensive. That is why the ability to train models with limited annotation budgets is of great importance. In this context, it has been shown that under tight annotation budgets the choice of data representation is key. The goal of this paper is to better understand why this is so. With this goal in mind, we propose a metric that measures the extent to which a given representation is structurally aligned with a task. We conduct experiments on several text classification datasets testing a variety of models and representations. Using our proposed metric we show that an efficient representation for a task (i.e. one that enables learning from few samples) is a representation that induces a good alignment between latent input structure and class structure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge