Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Brice D. Denoun
Metrics and Benchmarks for Remote Shared Controllers in Industrial Applications
Jun 19, 2019Authors:Claudio Zito, Maxime Adjigble, Brice D. Denoun, Lorenzo Jamone, Miles Hansard, Rustam Stolkin
Figures and Tables:

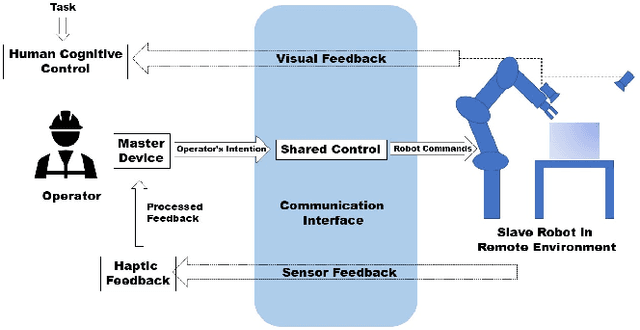





Abstract:Remote manipulation is emerging as one of the key robotics tasks needed in extreme environments. Several researchers have investigated how to add AI components into shared controllers to improve their reliability. Nonetheless, the impact of novel research approaches in real-world applications can have a very slow in-take. We propose a set of benchmarks and metrics to evaluate how the AI components of remote shared control algorithms can improve the effectiveness of such frameworks for real industrial applications. We also present an empirical evaluation of a simple intelligent share controller against a manually operated manipulator in a tele-operated grasping scenario.
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge