Bodo Winter
The Sociolinguistic Foundations of Language Modeling
Jul 12, 2024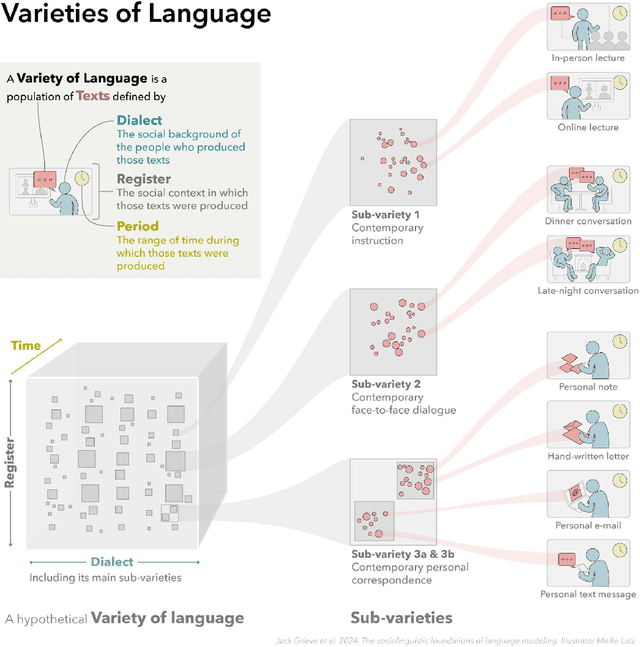
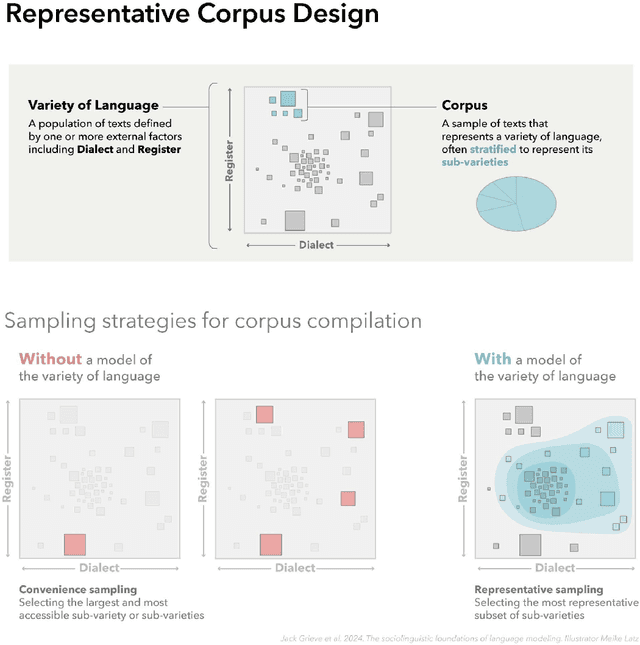
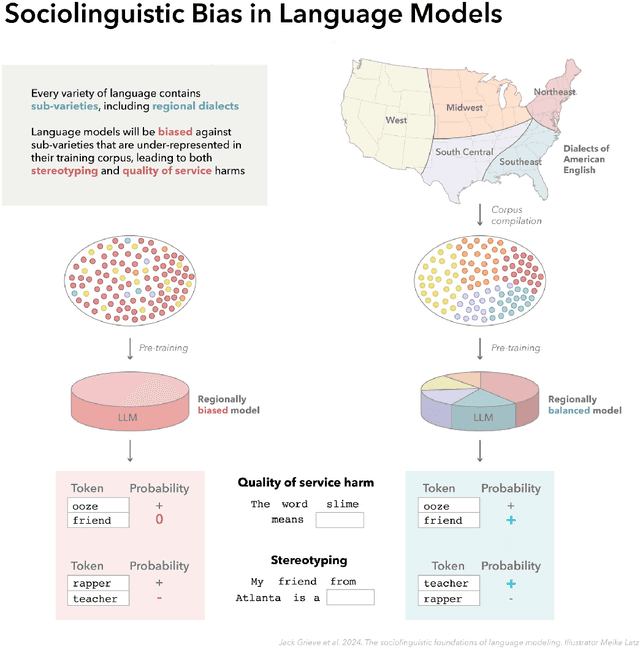
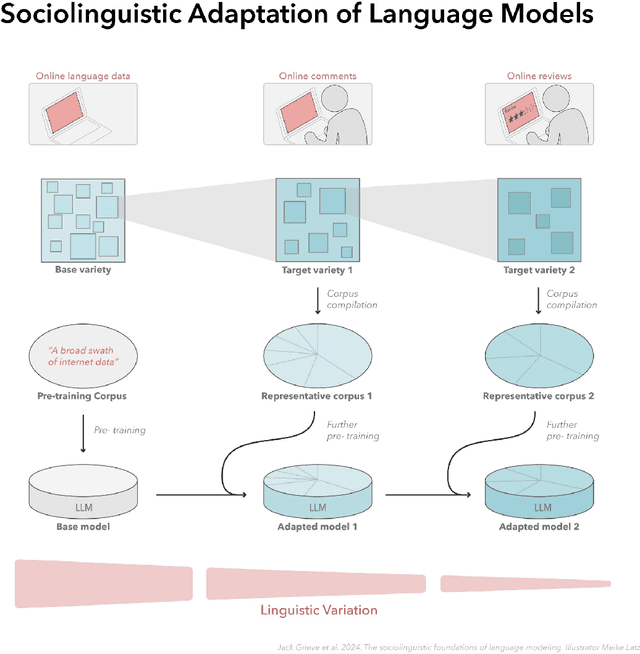
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a sociolinguistic perspective on language modeling. We claim that large language models are inherently models of varieties of language, and we consider how this insight can inform the development and deployment of large language models. We begin by presenting a technical definition of the concept of a variety of language as developed in sociolinguistics. We then discuss how this perspective can help address five basic challenges in language modeling: social bias, domain adaptation, alignment, language change, and scale. Ultimately, we argue that it is crucial to carefully define and compile training corpora that accurately represent the specific varieties of language being modeled to maximize the performance and societal value of large language models.
Linear models and linear mixed effects models in R with linguistic applications
Aug 26, 2013Abstract:This text is a conceptual introduction to mixed effects modeling with linguistic applications, using the R programming environment. The reader is introduced to linear modeling and assumptions, as well as to mixed effects/multilevel modeling, including a discussion of random intercepts, random slopes and likelihood ratio tests. The example used throughout the text focuses on the phonetic analysis of voice pitch data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge