Bochao Cao
Improving agent performance in fluid environments by perceptual pretraining
Sep 05, 2024


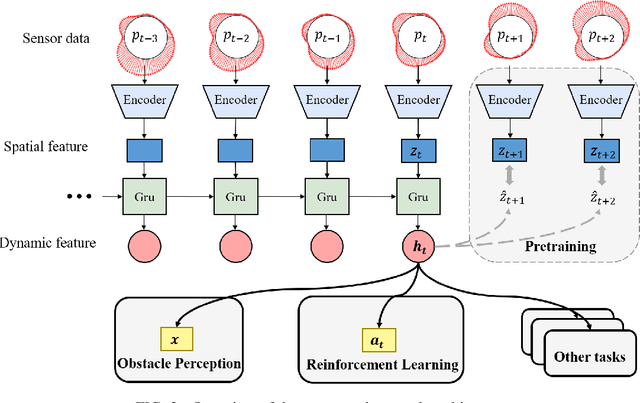
Abstract:In this paper, we construct a pretraining framework for fluid environment perception, which includes an information compression model and the corresponding pretraining method. We test this framework in a two-cylinder problem through numerical simulation. The results show that after unsupervised pretraining with this framework, the intelligent agent can acquire key features of surrounding fluid environment, thereby adapting more quickly and effectively to subsequent multi-scenario tasks. In our research, these tasks include perceiving the position of the upstream obstacle and actively avoiding shedding vortices in the flow field to achieve drag reduction. Better performance of the pretrained agent is discussed in the sensitivity analysis.
Learning swimming via deep reinforcement learning
Sep 22, 2022



Abstract:For decades, people have been seeking for fishlike flapping motions that can realize underwater propulsion with low energy cost. Complexity of the nonstationary flow field around the flapping body makes this problem very difficult. In earlier studies, motion patterns are usually prescribed as certain periodic functions which constrains the following optimization process in a small subdomain of the whole motion space. In this work, to avoid this motion constraint, a variational autoencoder (VAE) is designed to compress various flapping motions into a simple action vector. Then we let a flapping airfoil continuously interact with water tunnel environment and adjust its action accordingly through a reinforcement learning (RL) framework. By this automatic close-looped experiment, we obtain several motion patterns that can result in high hydrodynamic efficiency comparing to pure harmonic motions with the same thrust level. And we find that, after numerous trials and errors, RL trainings in current experiment always converge to motion patterns that are close to harmonic motions. In other words, current work proves that harmonic motion with appropriate amplitude and frequency is always an optimal choice for efficient underwater propulsion. Furthermore, the RL framework proposed here can be also extended to the study of other complex swimming problems, which might pave the way for the creation of a robotic fish that can swim like a real fish.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge