Bo-Ying Su
Temporal Relation Extraction with a Graph-Based Deep Biaffine Attention Model
Jan 16, 2022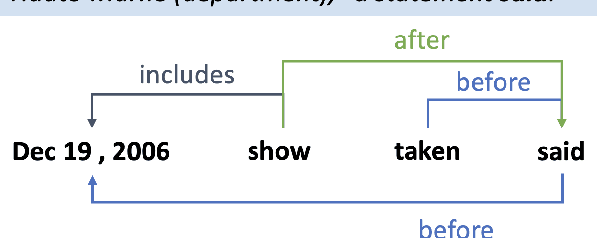
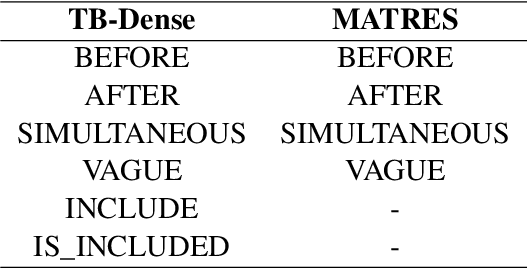
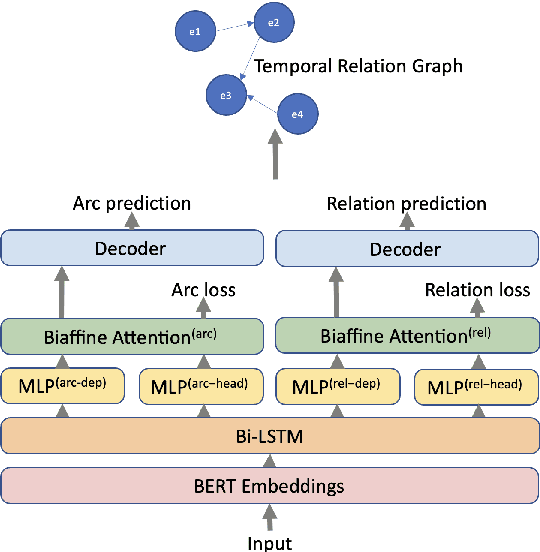
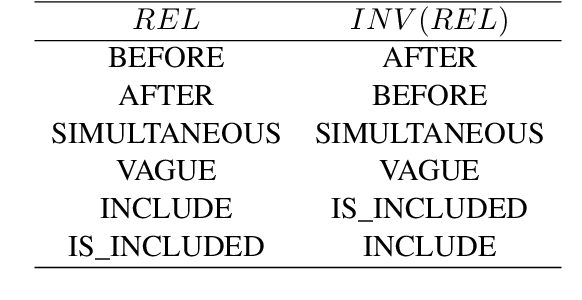
Abstract:Temporal information extraction plays a critical role in natural language understanding. Previous systems have incorporated advanced neural language models and have successfully enhanced the accuracy of temporal information extraction tasks. However, these systems have two major shortcomings. First, they fail to make use of the two-sided nature of temporal relations in prediction. Second, they involve non-parallelizable pipelines in inference process that bring little performance gain. To this end, we propose a novel temporal information extraction model based on deep biaffine attention to extract temporal relationships between events in unstructured text efficiently and accurately. Our model is performant because we perform relation extraction tasks directly instead of considering event annotation as a prerequisite of relation extraction. Moreover, our architecture uses Multilayer Perceptrons (MLP) with biaffine attention to predict arcs and relation labels separately, improving relation detecting accuracy by exploiting the two-sided nature of temporal relationships. We experimentally demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance in temporal relation extraction.
Context-Dependent Semantic Parsing for Temporal Relation Extraction
Dec 02, 2021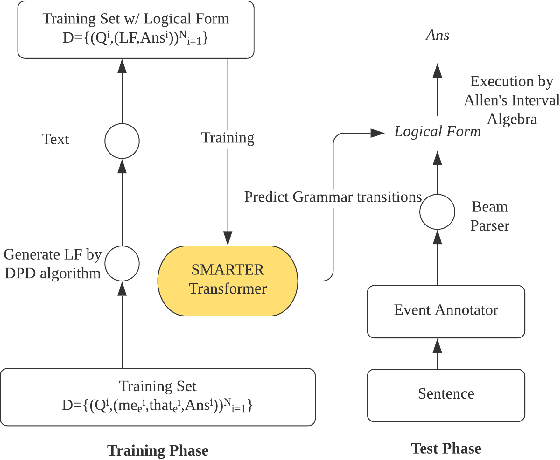

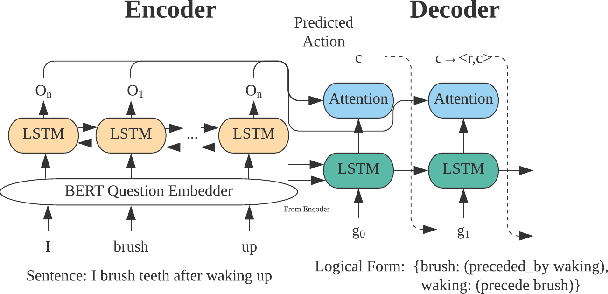
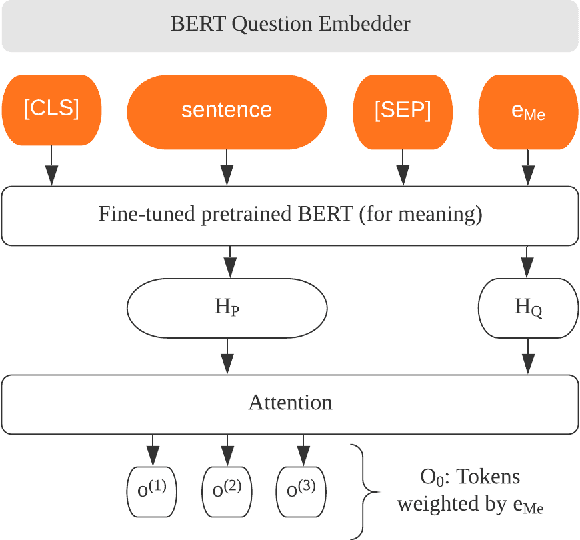
Abstract:Extracting temporal relations among events from unstructured text has extensive applications, such as temporal reasoning and question answering. While it is difficult, recent development of Neural-symbolic methods has shown promising results on solving similar tasks. Current temporal relation extraction methods usually suffer from limited expressivity and inconsistent relation inference. For example, in TimeML annotations, the concept of intersection is absent. Additionally, current methods do not guarantee the consistency among the predicted annotations. In this work, we propose SMARTER, a neural semantic parser, to extract temporal information in text effectively. SMARTER parses natural language to an executable logical form representation, based on a custom typed lambda calculus. In the training phase, dynamic programming on denotations (DPD) technique is used to provide weak supervision on logical forms. In the inference phase, SMARTER generates a temporal relation graph by executing the logical form. As a result, our neural semantic parser produces logical forms capturing the temporal information of text precisely. The accurate logical form representations of an event given the context ensure the correctness of the extracted relations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge