Binyu Tian
AVA: Adversarial Vignetting Attack against Visual Recognition
May 12, 2021



Abstract:Vignetting is an inherited imaging phenomenon within almost all optical systems, showing as a radial intensity darkening toward the corners of an image. Since it is a common effect for photography and usually appears as a slight intensity variation, people usually regard it as a part of a photo and would not even want to post-process it. Due to this natural advantage, in this work, we study vignetting from a new viewpoint, i.e., adversarial vignetting attack (AVA), which aims to embed intentionally misleading information into vignetting and produce a natural adversarial example without noise patterns. This example can fool the state-of-the-art deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) but is imperceptible to humans. To this end, we first propose the radial-isotropic adversarial vignetting attack (RI-AVA) based on the physical model of vignetting, where the physical parameters (e.g., illumination factor and focal length) are tuned through the guidance of target CNN models. To achieve higher transferability across different CNNs, we further propose radial-anisotropic adversarial vignetting attack (RA-AVA) by allowing the effective regions of vignetting to be radial-anisotropic and shape-free. Moreover, we propose the geometry-aware level-set optimization method to solve the adversarial vignetting regions and physical parameters jointly. We validate the proposed methods on three popular datasets, i.e., DEV, CIFAR10, and Tiny ImageNet, by attacking four CNNs, e.g., ResNet50, EfficientNet-B0, DenseNet121, and MobileNet-V2, demonstrating the advantages of our methods over baseline methods on both transferability and image quality.
Bias Field Poses a Threat to DNN-based X-Ray Recognition
Sep 19, 2020
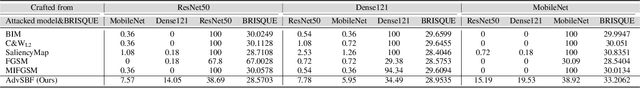
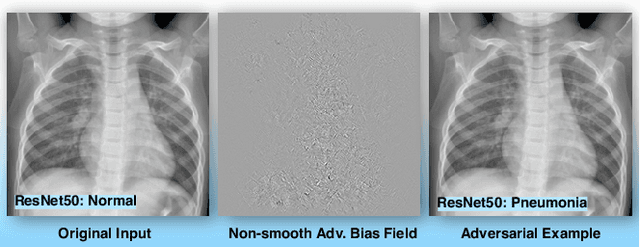
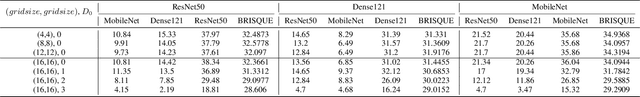
Abstract:The chest X-ray plays a key role in screening and diagnosis of many lung diseases including the COVID-19. More recently, many works construct deep neural networks (DNNs) for chest X-ray images to realize automated and efficient diagnosis of lung diseases. However, bias field caused by the improper medical image acquisition process widely exists in the chest X-ray images while the robustness of DNNs to the bias field is rarely explored, which definitely poses a threat to the X-ray-based automated diagnosis system. In this paper, we study this problem based on the recent adversarial attack and propose a brand new attack, i.e., the adversarial bias field attack where the bias field instead of the additive noise works as the adversarial perturbations for fooling the DNNs. This novel attack posts a key problem: how to locally tune the bias field to realize high attack success rate while maintaining its spatial smoothness to guarantee high realisticity. These two goals contradict each other and thus has made the attack significantly challenging. To overcome this challenge, we propose the adversarial-smooth bias field attack that can locally tune the bias field with joint smooth & adversarial constraints. As a result, the adversarial X-ray images can not only fool the DNNs effectively but also retain very high level of realisticity. We validate our method on real chest X-ray datasets with powerful DNNs, e.g., ResNet50, DenseNet121, and MobileNet, and show different properties to the state-of-the-art attacks in both image realisticity and attack transferability. Our method reveals the potential threat to the DNN-based X-ray automated diagnosis and can definitely benefit the development of bias-field-robust automated diagnosis system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge