Binoy Saha
Conditioning Covert Geo-Location (CGL) Detection on Semantic Class Information
Nov 27, 2022
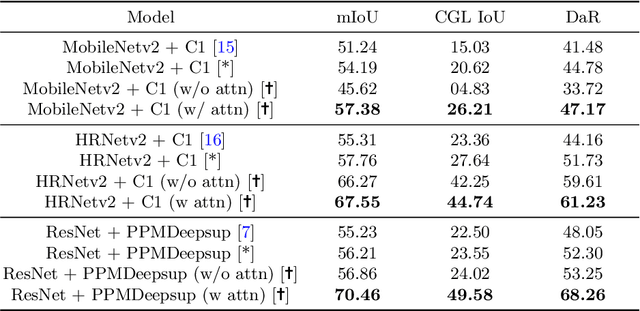
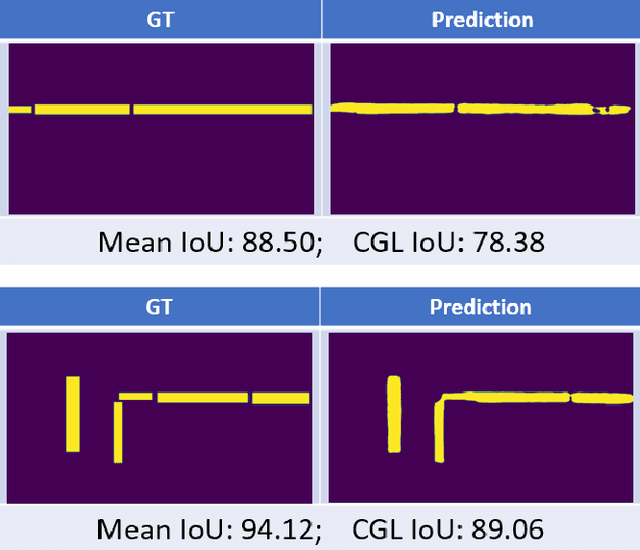
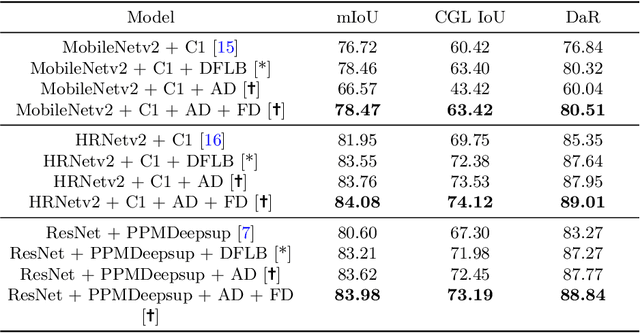
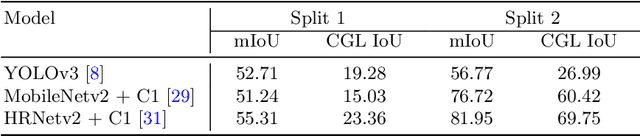
Abstract:The primary goal of artificial intelligence is to mimic humans. Therefore, to advance toward this goal, the AI community attempts to imitate qualities/skills possessed by humans and imbibes them into machines with the help of datasets/tasks. Earlier, many tasks which require knowledge about the objects present in an image are satisfactorily solved by vision models. Recently, with the aim to incorporate knowledge about non-object image regions (hideouts, turns, and other obscured regions), a task for identification of potential hideouts termed Covert Geo-Location (CGL) detection was proposed by Saha et al. It involves identification of image regions which have the potential to either cause an imminent threat or appear as target zones to be accessed for further investigation to identify any occluded objects. Only certain occluding items belonging to certain semantic classes can give rise to CGLs. This fact was overlooked by Saha et al. and no attempts were made to utilize semantic class information, which is crucial for CGL detection. In this paper, we propose a multitask-learning-based approach to achieve 2 goals - i) extraction of features having semantic class information; ii) robust training of the common encoder, exploiting large standard annotated datasets as training set for the auxiliary task (semantic segmentation). To explicitly incorporate class information in the features extracted by the encoder, we have further employed attention mechanism in a novel manner. We have also proposed a better evaluation metric for CGL detection that gives more weightage to recognition rather than precise localization. Experimental evaluations performed on the CGL dataset, demonstrate a significant increase in performance of about 3% to 14% mIoU and 3% to 16% DaR on split 1, and 1% mIoU and 1% to 2% DaR on split 2 over SOTA, serving as a testimony to the superiority of our approach.
Catch Me if You Can: A Novel Task for Detection of Covert Geo-Locations
Feb 05, 2022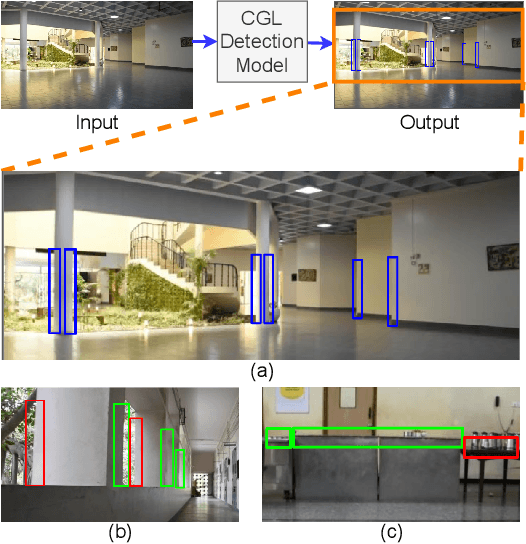
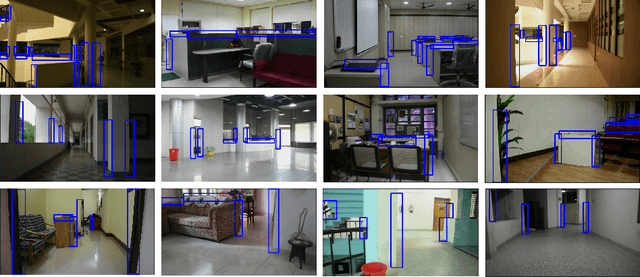

Abstract:Most visual scene understanding tasks in the field of computer vision involve identification of the objects present in the scene. Image regions like hideouts, turns, & other obscured regions of the scene also contain crucial information, for specific surveillance tasks. Task proposed in this paper involves the design of an intelligent visual aid for identification of such locations in an image, which has either the potential to create an imminent threat from an adversary or appear as the target zones needing further investigation. Covert places (CGL) for hiding behind an occluding object are concealed 3D locations, not detectable from the viewpoint (camera). Hence this involves delineating specific image regions around the projections of outer boundary of the occluding objects, as places to be accessed around the potential hideouts. CGL detection finds applications in military counter-insurgency operations, surveillance with path planning for an exploratory robot. Given an RGB image, the goal is to identify all CGLs in the 2D scene. Identification of such regions would require knowledge about the 3D boundaries of obscuring items (pillars, furniture), their spatial location with respect to the neighboring regions of the scene. We propose this as a novel task, termed Covert Geo-Location (CGL) Detection. Classification of any region of an image as a CGL (as boundary sub-segments of an occluding object that conceals the hideout) requires examining the 3D relation between boundaries of occluding objects and their neighborhoods & surroundings. Our method successfully extracts relevant depth features from a single RGB image and quantitatively yields significant improvement over existing object detection and segmentation models adapted and trained for CGL detection. We also introduce a novel hand-annotated CGL detection dataset containing 1.5K real-world images for experimentation.
Stutter Diagnosis and Therapy System Based on Deep Learning
Jul 13, 2020


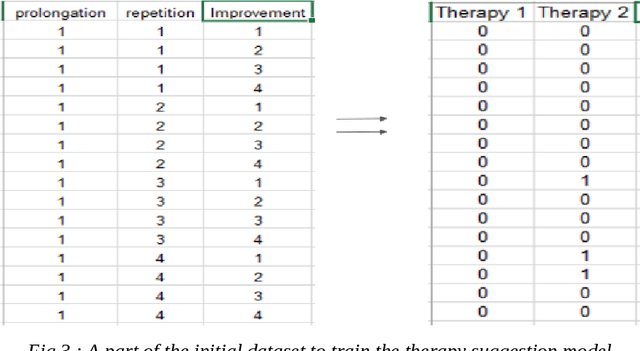
Abstract:Stuttering, also called stammering, is a communication disorder that breaks the continuity of the speech. This program of work is an attempt to develop automatic recognition procedures to assess stuttered dysfluencies and use these assessments to filter out speech therapies for an individual. Stuttering may be in the form of repetitions, prolongations or abnormal stoppages of sounds and syllables. Our system aims to help stutterers by diagnosing the severity and type of stutter and also by suggesting appropriate therapies for practice by learning the correlation between stutter descriptors and the effectiveness of speech therapies on them. This paper focuses on the implementation of a stutter diagnosis agent using Gated Recurrent CNN on MFCC audio features and therapy recommendation agent using SVM. It also presents the results obtained and various key findings of the system developed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge