Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Bing Cai Kok
Getting to Know One Another: Calibrating Intent, Capabilities and Trust for Human-Robot Collaboration
Aug 03, 2020Figures and Tables: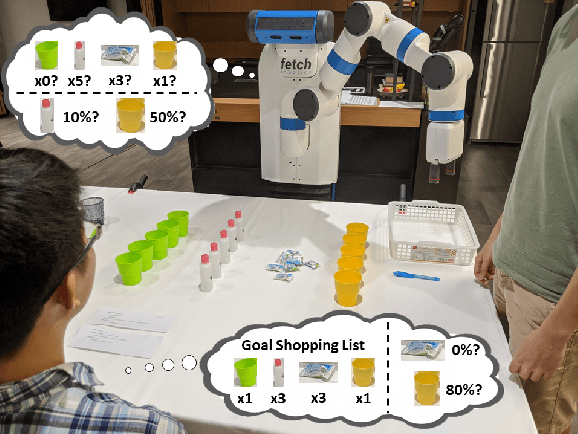
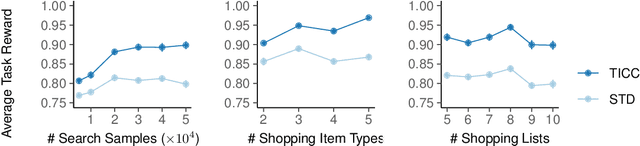
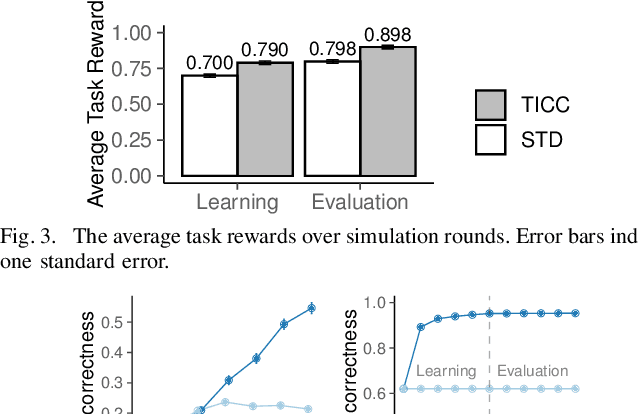





Abstract:Common experience suggests that agents who know each other well are better able to work together. In this work, we address the problem of calibrating intention and capabilities in human-robot collaboration. In particular, we focus on scenarios where the robot is attempting to assist a human who is unable to directly communicate her intent. Moreover, both agents may have differing capabilities that are unknown to one another. We adopt a decision-theoretic approach and propose the TICC-POMDP for modeling this setting, with an associated online solver. Experiments show our approach leads to better team performance both in simulation and in a real-world study with human subjects.
* IROS 2020
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge