Bernardo Aquino
Robustness against Adversarial Attacks in Neural Networks using Incremental Dissipativity
Nov 25, 2021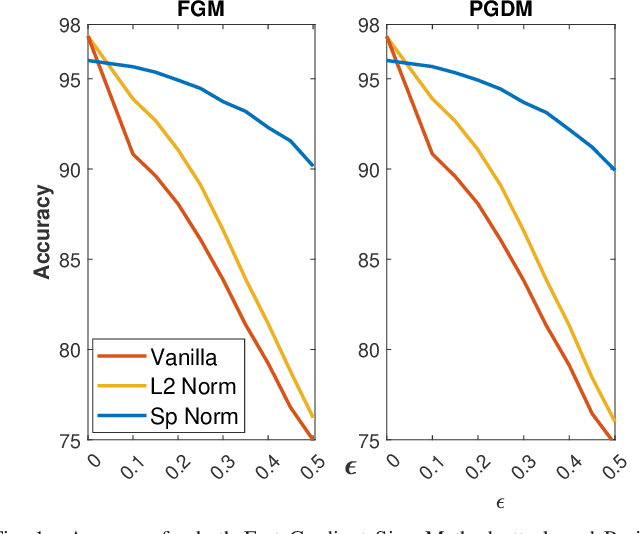
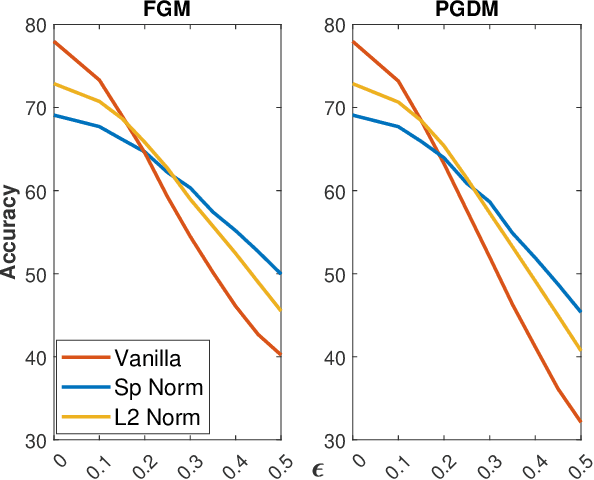
Abstract:Adversarial examples can easily degrade the classification performance in neural networks. Empirical methods for promoting robustness to such examples have been proposed, but often lack both analytical insights and formal guarantees. Recently, some robustness certificates have appeared in the literature based on system theoretic notions. This work proposes an incremental dissipativity-based robustness certificate for neural networks in the form of a linear matrix inequality for each layer. We also propose an equivalent spectral norm bound for this certificate which is scalable to neural networks with multiple layers. We demonstrate the improved performance against adversarial attacks on a feed-forward neural network trained on MNIST and an Alexnet trained using CIFAR-10.
EventGraD: Event-Triggered Communication in Parallel Machine Learning
Mar 12, 2021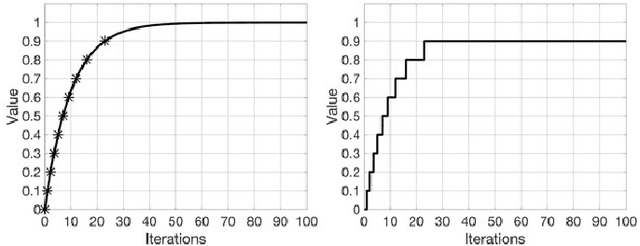
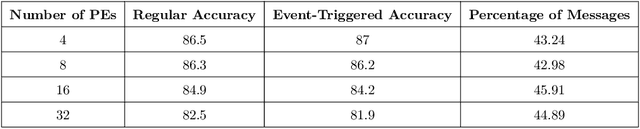
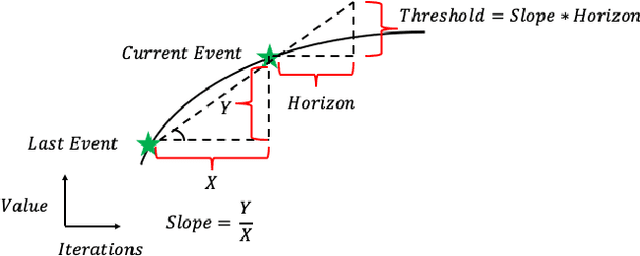
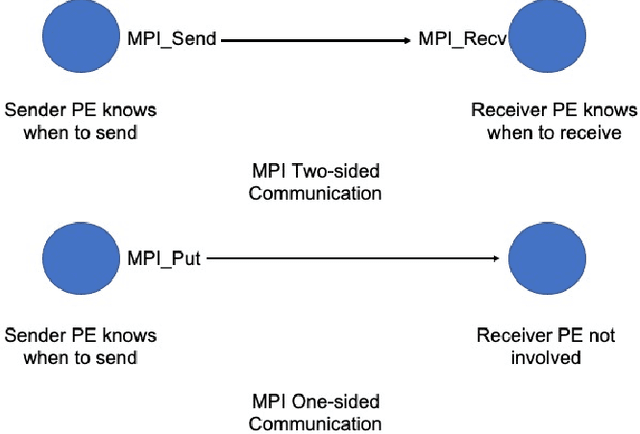
Abstract:Communication in parallel systems imposes significant overhead which often turns out to be a bottleneck in parallel machine learning. To relieve some of this overhead, in this paper, we present EventGraD - an algorithm with event-triggered communication for stochastic gradient descent in parallel machine learning. The main idea of this algorithm is to modify the requirement of communication at every iteration in standard implementations of stochastic gradient descent in parallel machine learning to communicating only when necessary at certain iterations. We provide theoretical analysis of convergence of our proposed algorithm. We also implement the proposed algorithm for data-parallel training of a popular residual neural network used for training the CIFAR-10 dataset and show that EventGraD can reduce the communication load by up to 60% while retaining the same level of accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge