Benoît Grossin
A synthetic dataset of French electric load curves with temperature conditioning
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:The undergoing energy transition is causing behavioral changes in electricity use, e.g. with self-consumption of local generation, or flexibility services for demand control. To better understand these changes and the challenges they induce, accessing individual smart meter data is crucial. Yet this is personal data under the European GDPR. A widespread use of such data requires thus to create synthetic realistic and privacy-preserving samples. This paper introduces a new synthetic load curve dataset generated by conditional latent diffusion. We also provide the contracted power, time-of-use plan and local temperature used for generation. Fidelity, utility and privacy of the dataset are thoroughly evaluated, demonstrating its good quality and thereby supporting its interest for energy modeling applications.
Autoencoder-based time series clustering with energy applications
Feb 10, 2020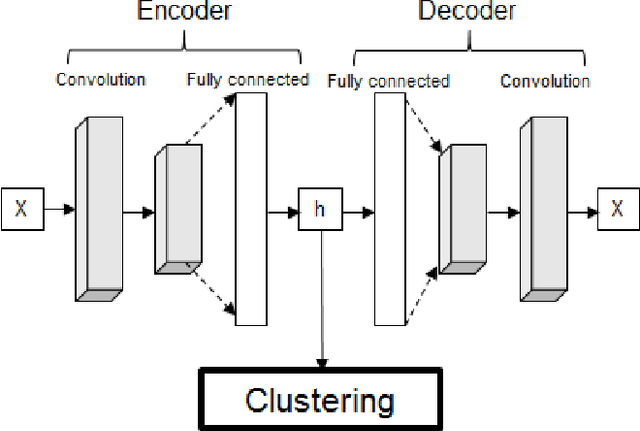
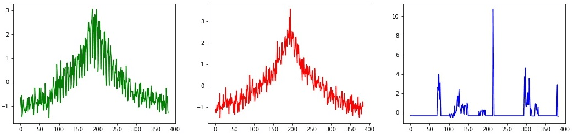
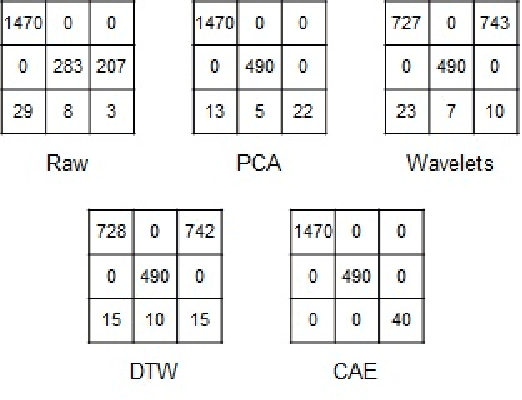
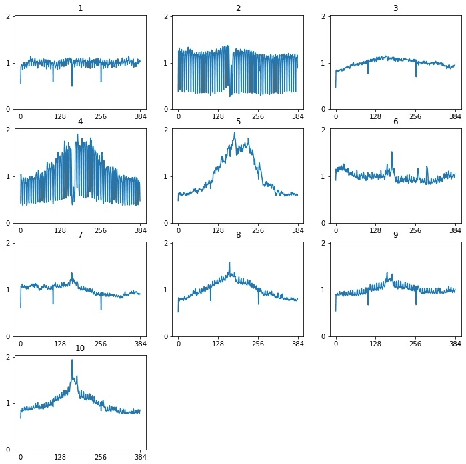
Abstract:Time series clustering is a challenging task due to the specific nature of the data. Classical approaches do not perform well and need to be adapted either through a new distance measure or a data transformation. In this paper we investigate the combination of a convolutional autoencoder and a k-medoids algorithm to perfom time series clustering. The convolutional autoencoder allows to extract meaningful features and reduce the dimension of the data, leading to an improvement of the subsequent clustering. Using simulation and energy related data to validate the approach, experimental results show that the clustering is robust to outliers thus leading to finer clusters than with standard methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge