Bengt Oelmann
Adaptive Noise Resilient Keyword Spotting Using One-Shot Learning
May 14, 2025Abstract:Keyword spotting (KWS) is a key component of smart devices, enabling efficient and intuitive audio interaction. However, standard KWS systems deployed on embedded devices often suffer performance degradation under real-world operating conditions. Resilient KWS systems address this issue by enabling dynamic adaptation, with applications such as adding or replacing keywords, adjusting to specific users, and improving noise robustness. However, deploying resilient, standalone KWS systems with low latency on resource-constrained devices remains challenging due to limited memory and computational resources. This study proposes a low computational approach for continuous noise adaptation of pretrained neural networks used for KWS classification, requiring only 1-shot learning and one epoch. The proposed method was assessed using two pretrained models and three real-world noise sources at signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) ranging from 24 to -3 dB. The adapted models consistently outperformed the pretrained models across all scenarios, especially at SNR $\leq$ 18 dB, achieving accuracy improvements of 4.9% to 46.0%. These results highlight the efficacy of the proposed methodology while being lightweight enough for deployment on resource-constrained devices.
On-Device Crack Segmentation for Edge Structural Health Monitoring
May 12, 2025Abstract:Crack segmentation can play a critical role in Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) by enabling accurate identification of crack size and location, which allows to monitor structural damages over time. However, deploying deep learning models for crack segmentation on resource-constrained microcontrollers presents significant challenges due to limited memory, computational power, and energy resources. To address these challenges, this study explores lightweight U-Net architectures tailored for TinyML applications, focusing on three optimization strategies: filter number reduction, network depth reduction, and the use of Depthwise Separable Convolutions (DWConv2D). Our results demonstrate that reducing convolution kernels and network depth significantly reduces RAM and Flash requirement, and inference times, albeit with some accuracy trade-offs. Specifically, by reducing the filer number to 25%, the network depth to four blocks, and utilizing depthwise convolutions, a good compromise between segmentation performance and resource consumption is achieved. This makes the network particularly suitable for low-power TinyML applications. This study not only advances TinyML-based crack segmentation but also provides the possibility for energy-autonomous edge SHM systems.
Efficient Continual Learning in Keyword Spotting using Binary Neural Networks
May 05, 2025



Abstract:Keyword spotting (KWS) is an essential function that enables interaction with ubiquitous smart devices. However, in resource-limited devices, KWS models are often static and can thus not adapt to new scenarios, such as added keywords. To overcome this problem, we propose a Continual Learning (CL) approach for KWS built on Binary Neural Networks (BNNs). The framework leverages the reduced computation and memory requirements of BNNs while incorporating techniques that enable the seamless integration of new keywords over time. This study evaluates seven CL techniques on a 16-class use case, reporting an accuracy exceeding 95% for a single additional keyword and up to 86% for four additional classes. Sensitivity to the amount of training samples in the CL phase, and differences in computational complexities are being evaluated. These evaluations demonstrate that batch-based algorithms are more sensitive to the CL dataset size, and that differences between the computational complexities are insignificant. These findings highlight the potential of developing an effective and computationally efficient technique for continuously integrating new keywords in KWS applications that is compatible with resource-constrained devices.
Survey of Quantization Techniques for On-Device Vision-based Crack Detection
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) ensures the safety and longevity of infrastructure by enabling timely damage detection. Vision-based crack detection, combined with UAVs, addresses the limitations of traditional sensor-based SHM methods but requires the deployment of efficient deep learning models on resource-constrained devices. This study evaluates two lightweight convolutional neural network models, MobileNetV1x0.25 and MobileNetV2x0.5, across TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Open Neural Network Exchange platforms using three quantization techniques: dynamic quantization, post-training quantization (PTQ), and quantization-aware training (QAT). Results show that QAT consistently achieves near-floating-point accuracy, such as an F1-score of 0.8376 for MBNV2x0.5 with Torch-QAT, while maintaining efficient resource usage. PTQ significantly reduces memory and energy consumption but suffers from accuracy loss, particularly in TensorFlow. Dynamic quantization preserves accuracy but faces deployment challenges on PyTorch. By leveraging QAT, this work enables real-time, low-power crack detection on UAVs, enhancing safety, scalability, and cost-efficiency in SHM applications, while providing insights into balancing accuracy and efficiency across different platforms for autonomous inspections.
On-device Anomaly Detection in Conveyor Belt Operations
Nov 16, 2024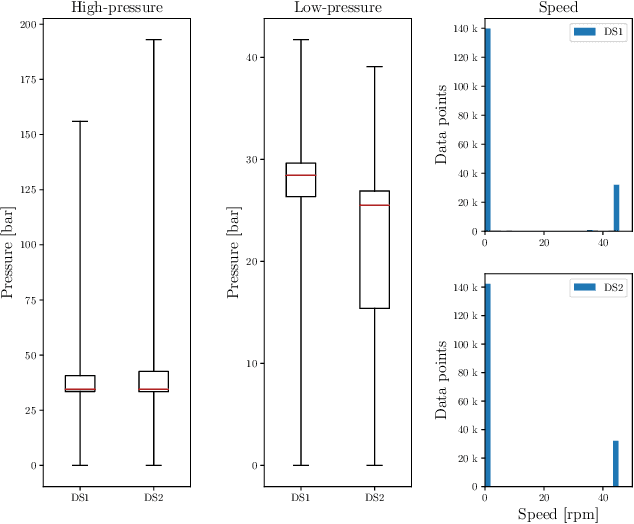
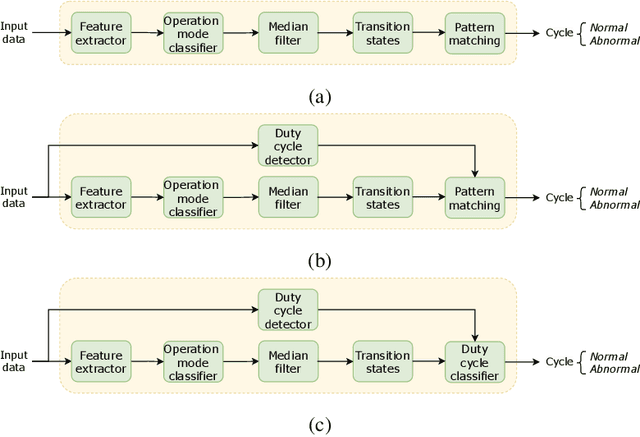
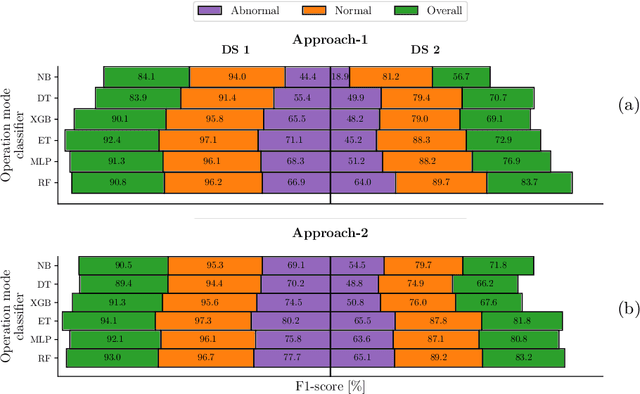
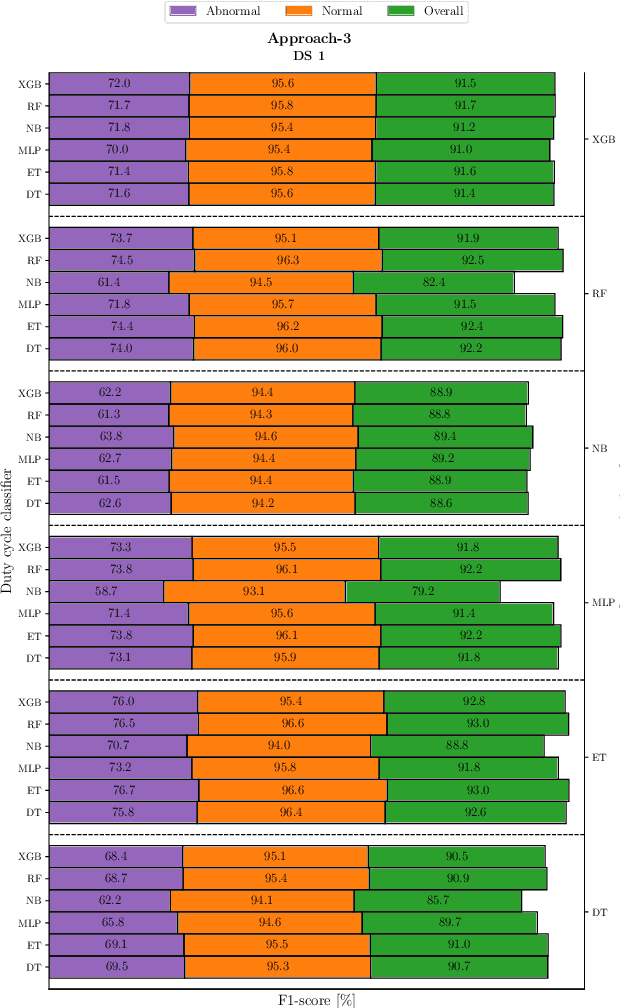
Abstract:Mining 4.0 leverages advancements in automation, digitalization, and interconnected technologies from Industry 4.0 to address the unique challenges of the mining sector, enhancing efficiency, safety, and sustainability. Conveyor belts are crucial in mining operations by enabling the continuous and efficient movement of bulk materials over long distances, which directly impacts productivity. While detecting anomalies in specific conveyor belt components, such as idlers, pulleys, and belt surfaces, has been widely studied, identifying the root causes of these failures remains critical due to factors like changing production conditions and operator errors. Continuous monitoring of mining conveyor belt work cycles for anomaly detection is still at an early stage and requires robust solutions. This study proposes two distinctive pattern recognition approaches for real-time anomaly detection in the operational cycles of mining conveyor belts, combining feature extraction, threshold-based cycle detection, and tiny machine-learning classification. Both approaches outperformed a state-of-the-art technique on two datasets for duty cycle classification in terms of F1-scores. The first approach, with 97.3% and 80.2% for normal and abnormal cycles, respectively, reaches the highest performance in the first dataset while the second approach excels on the second dataset, scoring 91.3% and 67.9%. Implemented on two low-power microcontrollers, the methods demonstrated efficient, real-time operation with energy consumption of 13.3 and 20.6 ${\mu}$J during inference. These results offer valuable insights for detecting mechanical failure sources, supporting targeted preventive maintenance, and optimizing production cycles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge