Bekir Z Demiray
EfficientTempNet: Temporal Super-Resolution of Radar Rainfall
Mar 09, 2023Abstract:Rainfall data collected by various remote sensing instruments such as radars or satellites has different space-time resolutions. This study aims to improve the temporal resolution of radar rainfall products to help with more accurate climate change modeling and studies. In this direction, we introduce a solution based on EfficientNetV2, namely EfficientTempNet, to increase the temporal resolution of radar-based rainfall products from 10 minutes to 5 minutes. We tested EfficientRainNet over a dataset for the state of Iowa, US, and compared its performance to three different baselines to show that EfficientTempNet presents a viable option for better climate change monitoring.
DEM Super-Resolution with EfficientNetV2
Sep 20, 2021
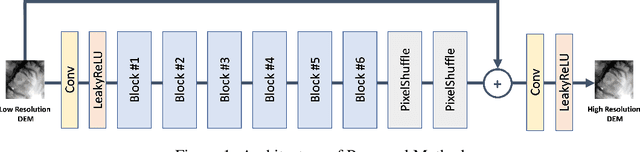
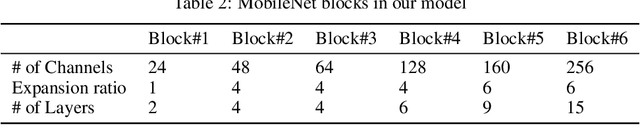
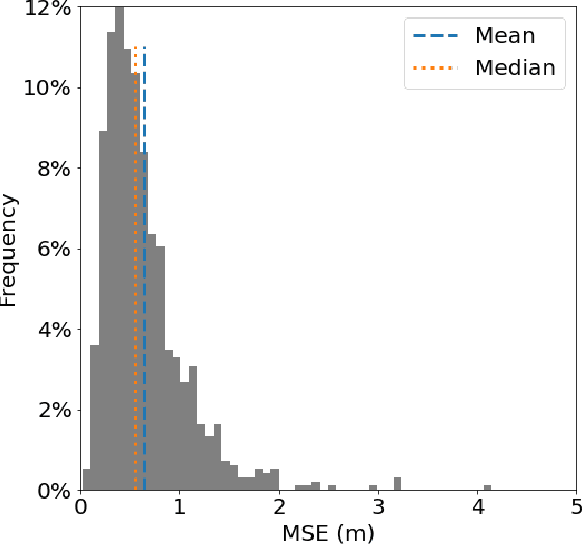
Abstract:Efficient climate change monitoring and modeling rely on high-quality geospatial and environmental datasets. Due to limitations in technical capabilities or resources, the acquisition of high-quality data for many environmental disciplines is costly. Digital Elevation Model (DEM) datasets are such examples whereas their low-resolution versions are widely available, high-resolution ones are scarce. In an effort to rectify this problem, we propose and assess an EfficientNetV2 based model. The proposed model increases the spatial resolution of DEMs up to 16times without additional information.
D-SRGAN: DEM Super-Resolution with Generative Adversarial Networks
Apr 16, 2020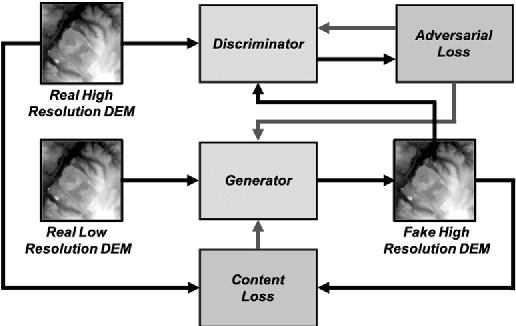
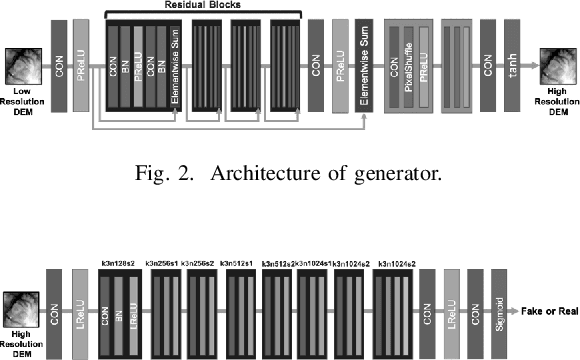
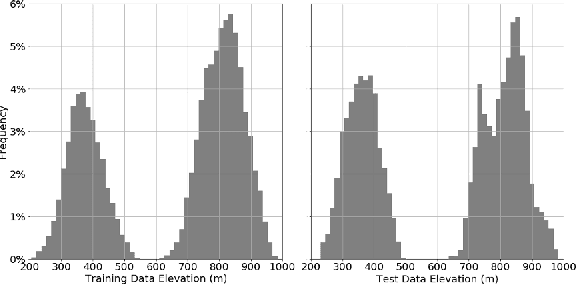

Abstract:LIDAR (light detection and ranging) is an optical remote-sensing technique that measures the distance between sensor and object, and the reflected energy from the object. Over the years, LIDAR data has been used as the primary source of Digital Elevation Models (DEMs). DEMs have been used in a variety of applications like road extraction, hydrological modeling, flood mapping, and surface analysis. A number of studies in flooding suggest the usage of high-resolution DEMs as inputs in the applications improve the overall reliability and accuracy. Despite the importance of high-resolution DEM, many areas in the United States and the world do not have access to high-resolution DEM due to technological limitations or the cost of the data collection. With recent development in Graphical Processing Units (GPU) and novel algorithms, deep learning techniques have become attractive to researchers for their performance in learning features from high-resolution datasets. Numerous new methods have been proposed such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to create intelligent models that correct and augment large-scale datasets. In this paper, a GAN based model is developed and evaluated, inspired by single image super-resolution methods, to increase the spatial resolution of a given DEM dataset up to 4 times without additional information related to data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge