Barbara A. Han
Towards Interpreting Zoonotic Potential of Betacoronavirus Sequences With Attention
Aug 18, 2021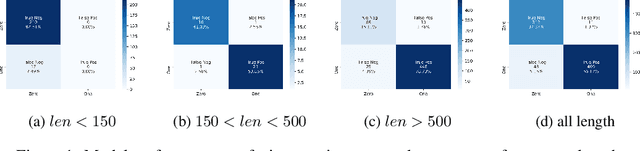
Abstract:Current methods for viral discovery target evolutionarily conserved proteins that accurately identify virus families but remain unable to distinguish the zoonotic potential of newly discovered viruses. Here, we apply an attention-enhanced long-short-term memory (LSTM) deep neural net classifier to a highly conserved viral protein target to predict zoonotic potential across betacoronaviruses. The classifier performs with a 94% accuracy. Analysis and visualization of attention at the sequence and structure-level features indicate possible association between important protein-protein interactions governing viral replication in zoonotic betacoronaviruses and zoonotic transmission.
Formal Concept Analysis of Rodent Carriers of Zoonotic Disease
Aug 25, 2016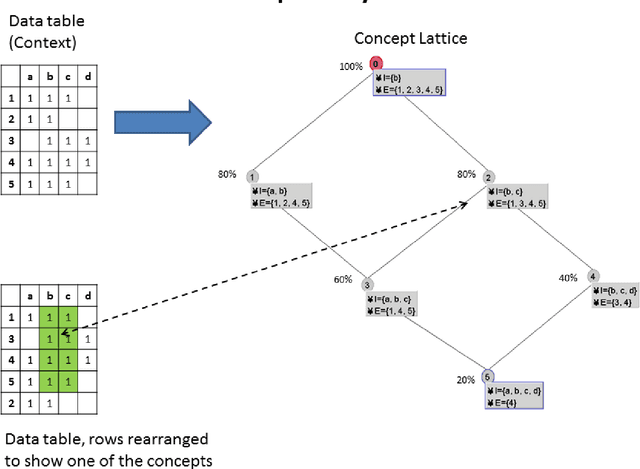
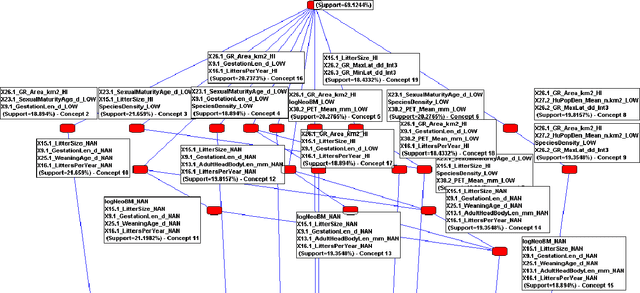
Abstract:The technique of Formal Concept Analysis is applied to a dataset describing the traits of rodents, with the goal of identifying zoonotic disease carriers,or those species carrying infections that can spillover to cause human disease. The concepts identified among these species together provide rules-of-thumb about the intrinsic biological features of rodents that carry zoonotic diseases, and offer utility for better targeting field surveillance efforts in the search for novel disease carriers in the wild.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge