Ayca Özcelikkale
Communication Trade-offs in Federated Learning of Spiking Neural Networks
Feb 27, 2023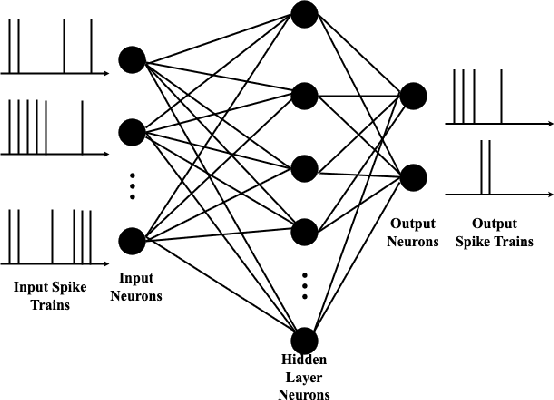
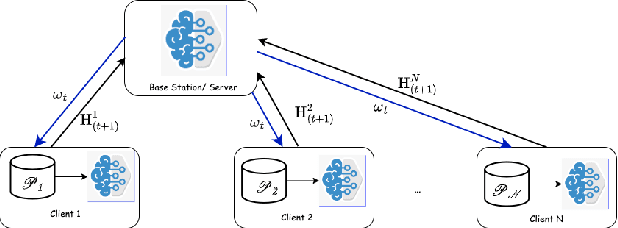
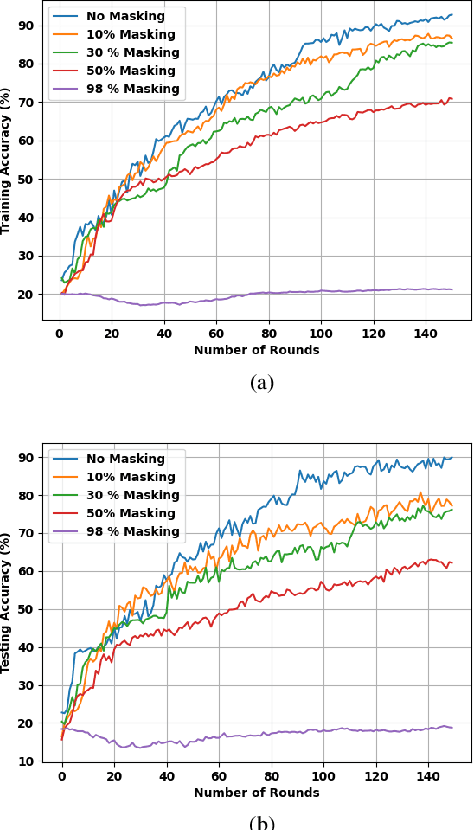
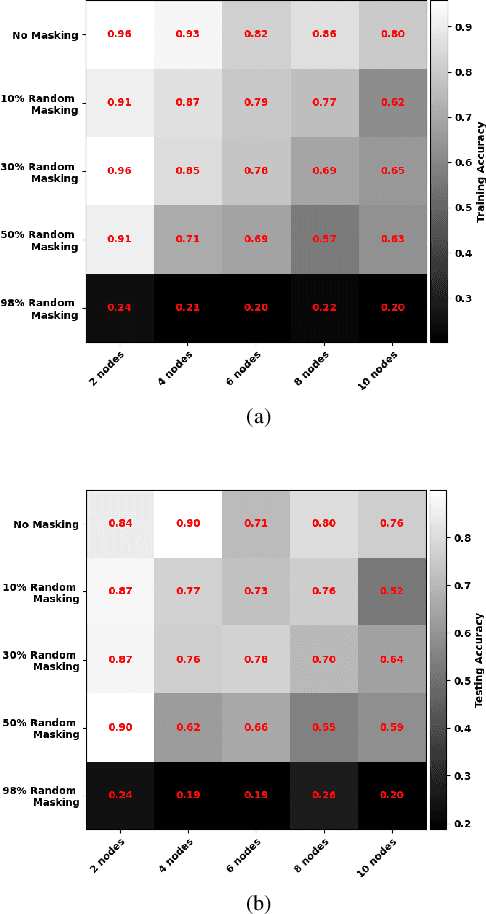
Abstract:Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) are biologically inspired alternatives to conventional Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs). Despite promising preliminary results, the trade-offs in the training of SNNs in a distributed scheme are not well understood. Here, we consider SNNs in a federated learning setting where a high-quality global model is created by aggregating multiple local models from the clients without sharing any data. We investigate federated learning for training multiple SNNs at clients when two mechanisms reduce the uplink communication cost: i) random masking of the model updates sent from the clients to the server; and ii) client dropouts where some clients do not send their updates to the server. We evaluated the performance of the SNNs using a subset of the Spiking Heidelberg digits (SHD) dataset. The results show that a trade-off between the random masking and the client drop probabilities is crucial to obtain a satisfactory performance for a fixed number of clients.
Double Descent in Random Feature Models: Precise Asymptotic Analysis for General Convex Regularization
Apr 06, 2022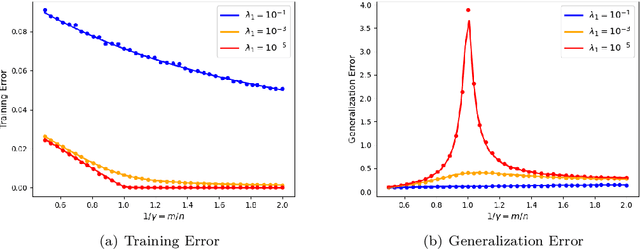
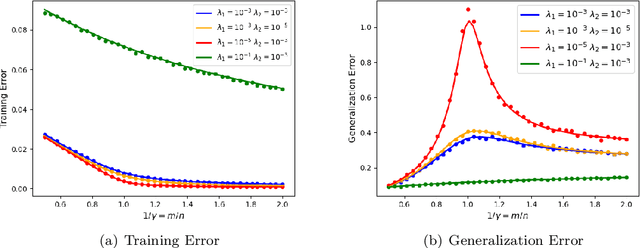
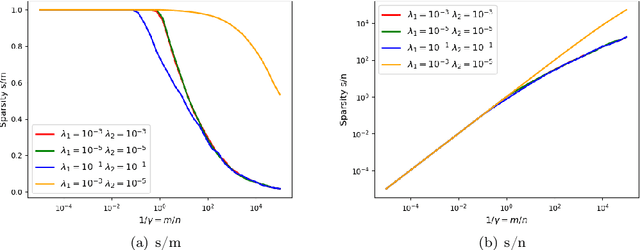
Abstract:We prove rigorous results on the double descent phenomenon in random features (RF) model by employing the powerful Convex Gaussian Min-Max Theorem (CGMT) in a novel multi-level manner. Using this technique, we provide precise asymptotic expressions for the generalization of RF regression under a broad class of convex regularization terms including arbitrary separable functions. We further compute our results for the combination of $\ell_1$ and $\ell_2$ regularization case, known as elastic net, and present numerical studies about it. We numerically demonstrate the predictive capacity of our framework, and show experimentally that the predicted test error is accurate even in the non-asymptotic regime.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge