Axel Andersson
Transcriptome-supervised classification of tissue morphology using deep learning
Dec 07, 2023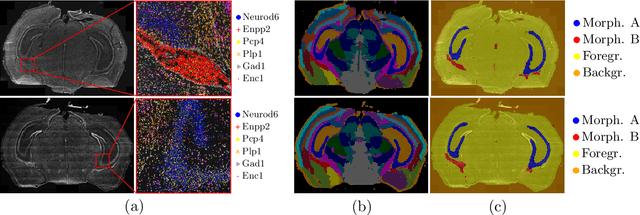
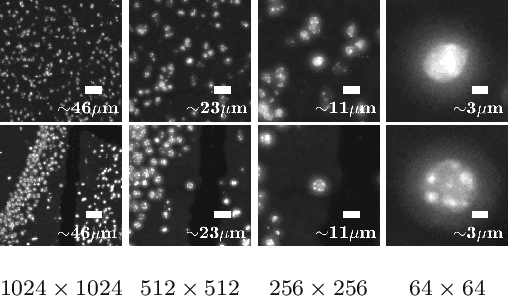
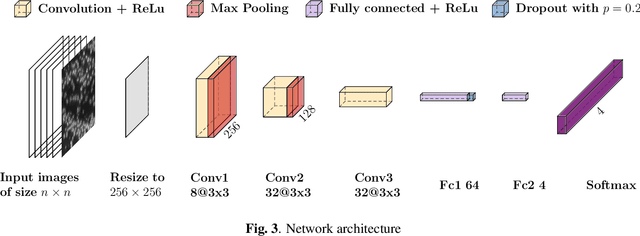
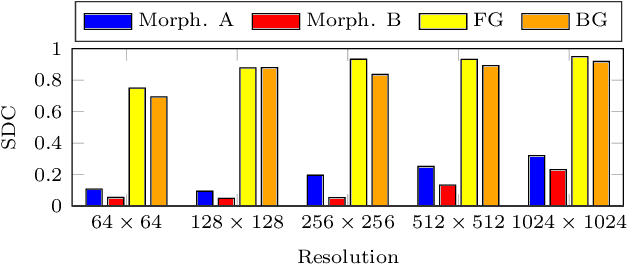
Abstract:Deep learning has proven to successfully learn variations in tissue and cell morphology. Training of such models typically relies on expensive manual annotations. Here we conjecture that spatially resolved gene expression, e.i., the transcriptome, can be used as an alternative to manual annotations. In particular, we trained five convolutional neural networks with patches of different size extracted from locations defined by spatially resolved gene expression. The network is trained to classify tissue morphology related to two different genes, general tissue, as well as background, on an image of fluorescence stained nuclei in a mouse brain coronal section. Performance is evaluated on an independent tissue section from a different mouse brain, reaching an average Dice score of 0.51. Results may indicate that novel techniques for spatially resolved transcriptomics together with deep learning may provide a unique and unbiased way to find genotype-phenotype relationships.
* Accepted for publication at IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2020
End-to-end Multiple Instance Learning with Gradient Accumulation
Mar 08, 2022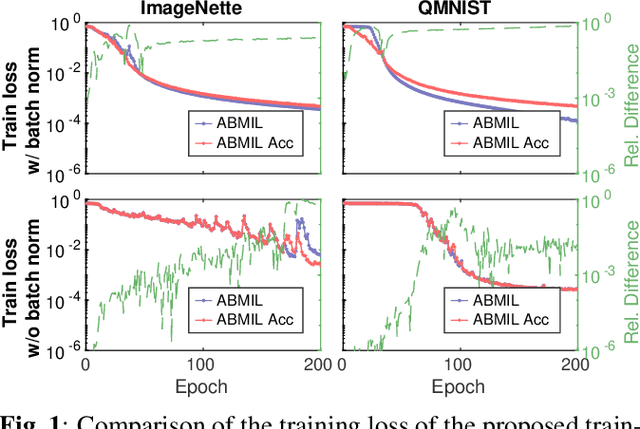
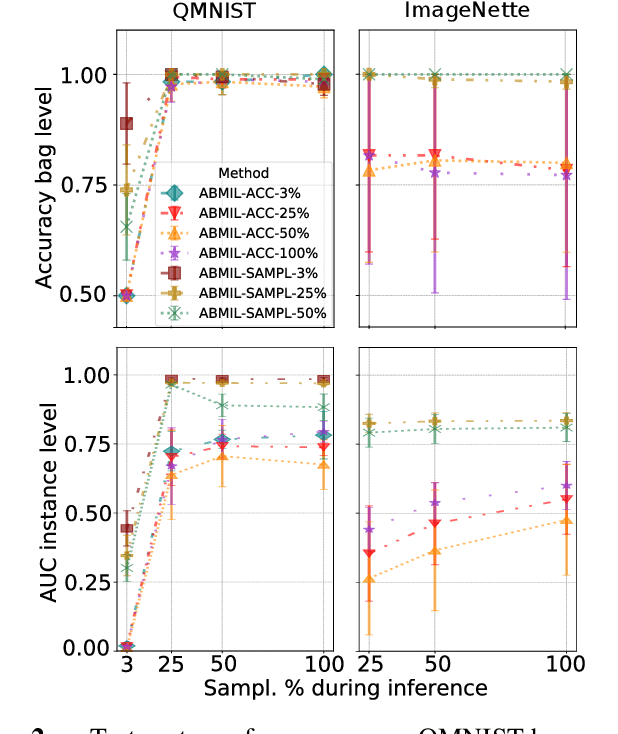
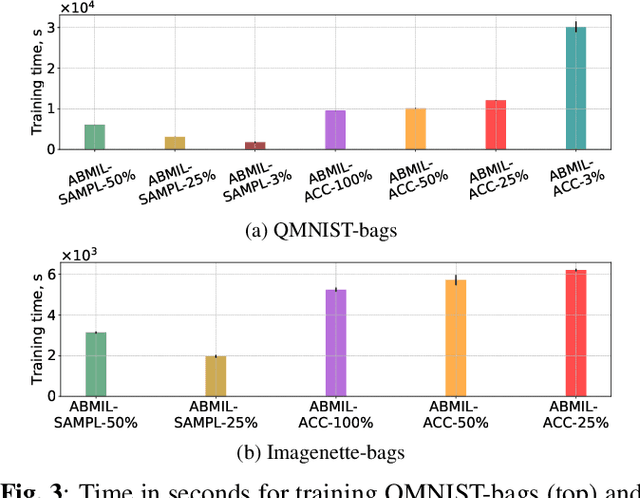
Abstract:Being able to learn on weakly labeled data, and provide interpretability, are two of the main reasons why attention-based deep multiple instance learning (ABMIL) methods have become particularly popular for classification of histopathological images. Such image data usually come in the form of gigapixel-sized whole-slide-images (WSI) that are cropped into smaller patches (instances). However, the sheer size of the data makes training of ABMIL models challenging. All the instances from one WSI cannot be processed at once by conventional GPUs. Existing solutions compromise training by relying on pre-trained models, strategic sampling or selection of instances, or self-supervised learning. We propose a training strategy based on gradient accumulation that enables direct end-to-end training of ABMIL models without being limited by GPU memory. We conduct experiments on both QMNIST and Imagenette to investigate the performance and training time, and compare with the conventional memory-expensive baseline and a recent sampled-based approach. This memory-efficient approach, although slower, reaches performance indistinguishable from the memory-expensive baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge