Aunabil Chakma
Structured Semantic Information Helps Retrieve Better Examples for In-Context Learning in Few-Shot Relation Extraction
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:This paper presents several strategies to automatically obtain additional examples for in-context learning of one-shot relation extraction. Specifically, we introduce a novel strategy for example selection, in which new examples are selected based on the similarity of their underlying syntactic-semantic structure to the provided one-shot example. We show that this method results in complementary word choices and sentence structures when compared to LLM-generated examples. When these strategies are combined, the resulting hybrid system achieves a more holistic picture of the relations of interest than either method alone. Our framework transfers well across datasets (FS-TACRED and FS-FewRel) and LLM families (Qwen and Gemma). Overall, our hybrid selection method consistently outperforms alternative strategies and achieves state-of-the-art performance on FS-TACRED and strong gains on a customized FewRel subset.
ChakmaNMT: A Low-resource Machine Translation On Chakma Language
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:The geopolitical division between the indigenous Chakma population and mainstream Bangladesh creates a significant cultural and linguistic gap, as the Chakma community, mostly residing in the hill tracts of Bangladesh, maintains distinct cultural traditions and language. Developing a Machine Translation (MT) model or Chakma to Bangla could play a crucial role in alleviating this cultural-linguistic divide. Thus, we have worked on MT between CCP-BN(Chakma-Bangla) by introducing a novel dataset of 15,021 parallel samples and 42,783 monolingual samples of the Chakma Language. Moreover, we introduce a small set for Benchmarking containing 600 parallel samples between Chakma, Bangla, and English. We ran traditional and state-of-the-art models in NLP on the training set, where fine-tuning BanglaT5 with back-translation using transliteration of Chakma achieved the highest BLEU score of 17.8 and 4.41 in CCP-BN and BN-CCP respectively on the Benchmark Dataset. As far as we know, this is the first-ever work on MT for the Chakma Language. Hopefully, this research will help to bridge the gap in linguistic resources and contribute to preserving endangered languages. Our dataset link and codes will be published soon.
LowResource at BLP-2023 Task 2: Leveraging BanglaBert for Low Resource Sentiment Analysis of Bangla Language
Nov 21, 2023
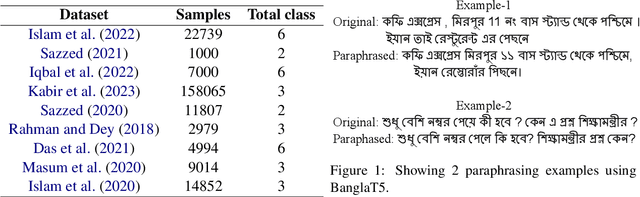
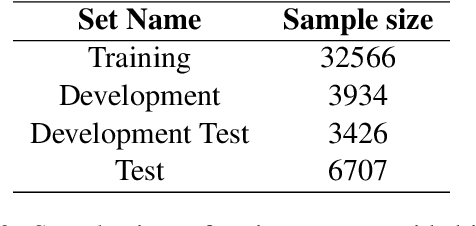
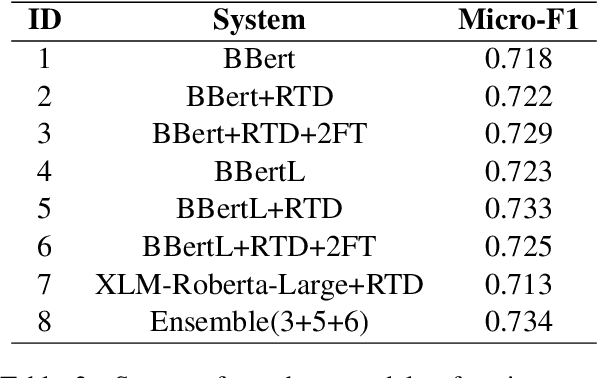
Abstract:This paper describes the system of the LowResource Team for Task 2 of BLP-2023, which involves conducting sentiment analysis on a dataset composed of public posts and comments from diverse social media platforms. Our primary aim is to utilize BanglaBert, a BERT model pre-trained on a large Bangla corpus, using various strategies including fine-tuning, dropping random tokens, and using several external datasets. Our final model is an ensemble of the three best BanglaBert variations. Our system has achieved overall 3rd in the Test Set among 30 participating teams with a score of 0.718. Additionally, we discuss the promising systems that didn't perform well namely task-adaptive pertaining and paraphrasing using BanglaT5. Training codes and external datasets which are used for our system are publicly available at https://github.com/Aunabil4602/bnlp-workshop-task2-2023
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge