Asma Dachraoui
ml_edm package: a Python toolkit for Machine Learning based Early Decision Making
Aug 23, 2024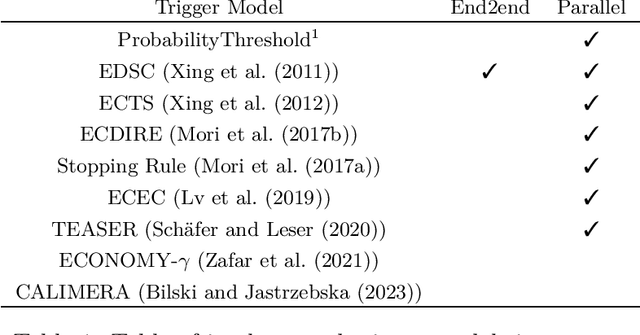
Abstract:\texttt{ml\_edm} is a Python 3 library, designed for early decision making of any learning tasks involving temporal/sequential data. The package is also modular, providing researchers an easy way to implement their own triggering strategy for classification, regression or any machine learning task. As of now, many Early Classification of Time Series (ECTS) state-of-the-art algorithms, are efficiently implemented in the library leveraging parallel computation. The syntax follows the one introduce in \texttt{scikit-learn}, making estimators and pipelines compatible with \texttt{ml\_edm}. This software is distributed over the BSD-3-Clause license, source code can be found at \url{https://github.com/ML-EDM/ml_edm}.
Early Classification of Time Series. Cost-based Optimization Criterion and Algorithms
May 20, 2020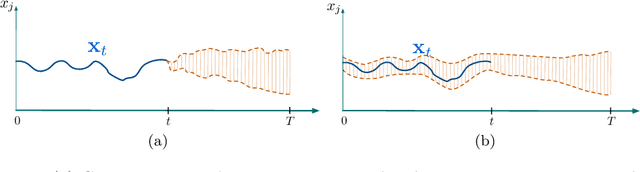
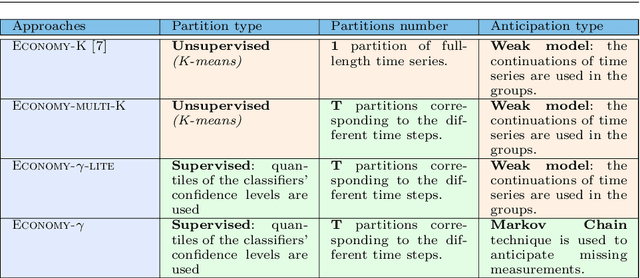
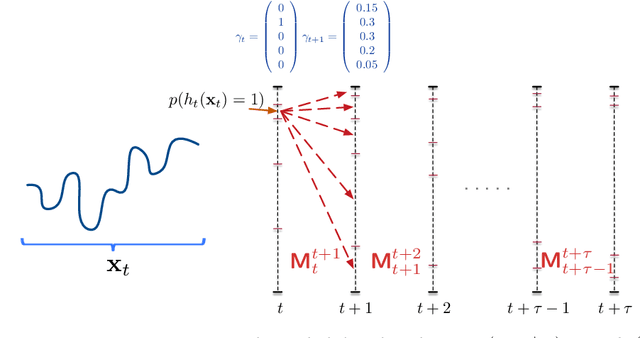
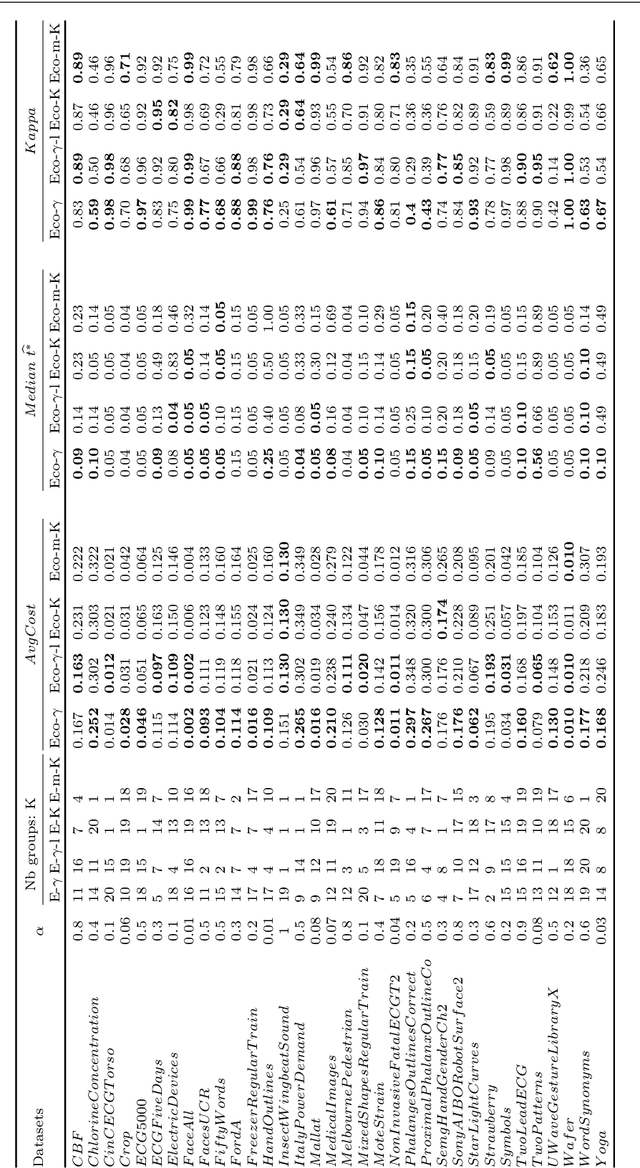
Abstract:An increasing number of applications require to recognize the class of an incoming time series as quickly as possible without unduly compromising the accuracy of the prediction. In this paper, we put forward a new optimization criterion which takes into account both the cost of misclassification and the cost of delaying the decision. Based on this optimization criterion, we derived a family of non-myopic algorithms which try to anticipate the expected future gain in information in balance with the cost of waiting. In one class of algorithms, unsupervised-based, the expectations use the clustering of time series, while in a second class, supervised-based, time series are grouped according to the confidence level of the classifier used to label them. Extensive experiments carried out on real data sets using a large range of delay cost functions show that the presented algorithms are able to satisfactorily solving the earliness vs. accuracy trade-off, with the supervised-based approaches faring better than the unsupervised-based ones. In addition, all these methods perform better in a wide variety of conditions than a state of the art method based on a myopic strategy which is recognized as very competitive.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge