Ashok Krishnamurthy
Early Fusion of Features for Semantic Segmentation
Feb 08, 2024

Abstract:This paper introduces a novel segmentation framework that integrates a classifier network with a reverse HRNet architecture for efficient image segmentation. Our approach utilizes a ResNet-50 backbone, pretrained in a semi-supervised manner, to generate feature maps at various scales. These maps are then processed by a reverse HRNet, which is adapted to handle varying channel dimensions through 1x1 convolutions, to produce the final segmentation output. We strategically avoid fine-tuning the backbone network to minimize memory consumption during training. Our methodology is rigorously tested across several benchmark datasets including Mapillary Vistas, Cityscapes, CamVid, COCO, and PASCAL-VOC2012, employing metrics such as pixel accuracy and mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) to evaluate segmentation performance. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed model in achieving high segmentation accuracy, indicating its potential for various applications in image analysis. By leveraging the strengths of both the ResNet-50 and reverse HRNet within a unified framework, we present a robust solution to the challenges of image segmentation.
A Framework for Estimating Long Term Driver Behavior
Jul 11, 2016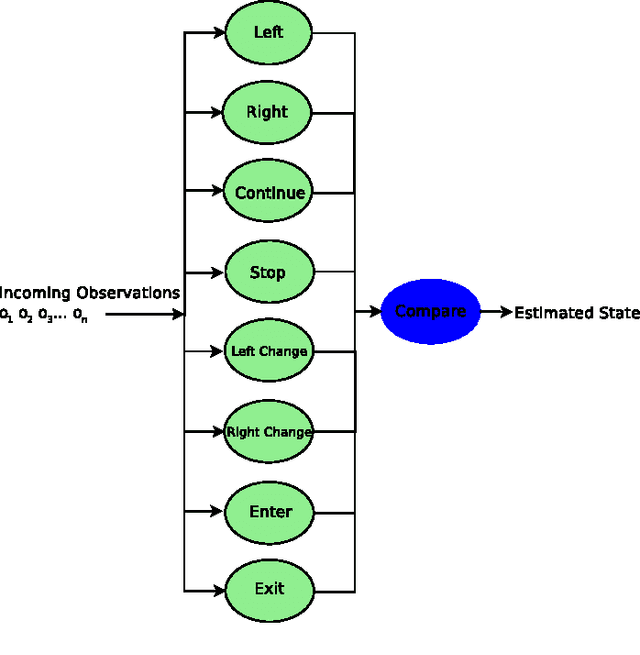
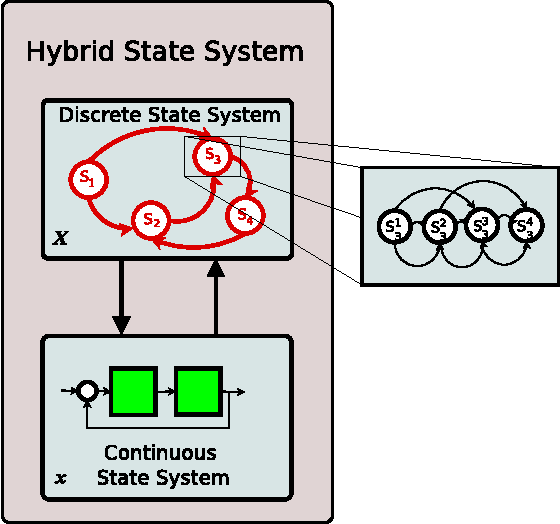
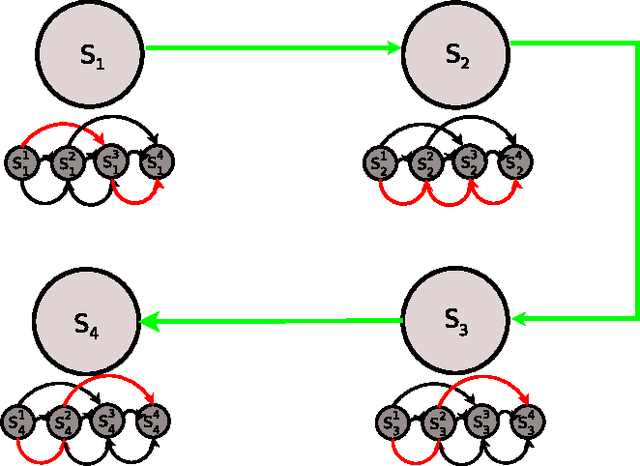

Abstract:The authors present a cyber-physical systems study on the estimation of driver behavior in autonomous vehicles and vehicle safety systems. Extending upon previous work, the approach described is suitable for the long term estimation and tracking of autonomous vehicle behavior. The proposed system makes use of a previously defined Hybrid State System and Hidden Markov Model (HSS+HMM) system which has provided good results for driver behavior estimation. The HSS+HMM system utilizes the hybrid characteristics of decision-behavior coupling of many systems such as the driver and the vehicle, uses Kalman Filter estimates of observable parameters to track the instantaneous continuous state, and estimates the most likely driver state. The HSS+HMM system is encompassed in a HSS structure and inter-system connectivity is determined by using Signal Processing and Pattern Recognition techniques. The proposed method is suitable for scenarios that involve unknown decisions of other individuals, such as lane changes or intersection precedence/access. The long term driver behavior estimation system involves an extended HSS+HMM structure that is capable of including external information in the estimation process. Through the grafting and pruning of metastates, the HSS+HMM system can be dynamically updated to best represent driver choices given external information. Three application examples are also provided to elucidate the theoretical system.
A Hands-on Education Program on Cyber Physical Systems for High School Students
Aug 03, 2014
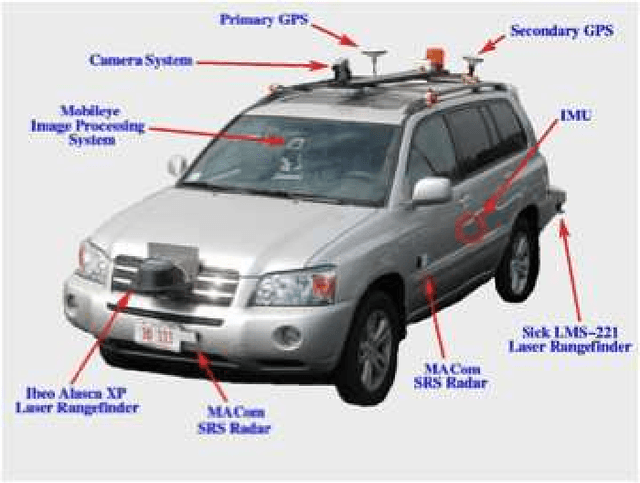

Abstract:Cyber Physical Systems (CPS) are the conjoining of an entities' physical and computational elements. The development of a typical CPS system follows a sequence from conceptual modeling, testing in simulated (virtual) worlds, testing in controlled (possibly laboratory) environments and finally deployment. Throughout each (repeatable) stage, the behavior of the physical entities, the sensing and situation assessment, and the computation and control options have to be understood and carefully represented through abstraction. The CPS Group at the Ohio State University, as part of an NSF funded CPS project on "Autonomous Driving in Mixed Environments", has been developing CPS related educational activities at the K-12, undergraduate and graduate levels. The aim of these educational activities is to train students in the principles and design issues in CPS and to broaden the participation in science and engineering. The project team has a strong commitment to impact STEM education across the entire K-20 community. In this paper, we focus on the K-12 community and present a two-week Summer Program for high school juniors and seniors that introduces them to the principles of CPS design and walks them through several of the design steps. We also provide an online repository that aids CPS researchers in providing a similar educational experience.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge