Arwa Al-Rubaian
CellOMaps: A Compact Representation for Robust Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma Growth Patterns
Jan 14, 2025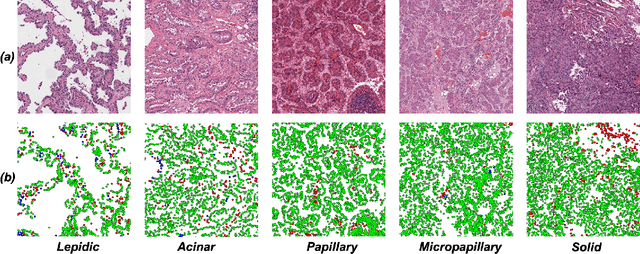



Abstract:Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is a morphologically heterogeneous disease, characterized by five primary histological growth patterns. The classification of such patterns is crucial due to their direct relation to prognosis but the high subjectivity and observer variability pose a major challenge. Although several studies have developed machine learning methods for growth pattern classification, they either only report the predominant pattern per slide or lack proper evaluation. We propose a generalizable machine learning pipeline capable of classifying lung tissue into one of the five patterns or as non-tumor. The proposed pipeline's strength lies in a novel compact Cell Organization Maps (cellOMaps) representation that captures the cellular spatial patterns from Hematoxylin and Eosin whole slide images (WSIs). The proposed pipeline provides state-of-the-art performance on LUAD growth pattern classification when evaluated on both internal unseen slides and external datasets, significantly outperforming the current approaches. In addition, our preliminary results show that the model's outputs can be used to predict patients Tumor Mutational Burden (TMB) levels.
Cell Maps Representation For Lung Adenocarcinoma Growth Patterns Classification In Whole Slide Images
Nov 27, 2023


Abstract:Lung adenocarcinoma is a morphologically heterogeneous disease, characterized by five primary histologic growth patterns. The quantity of these patterns can be related to tumor behavior and has a significant impact on patient prognosis. In this work, we propose a novel machine learning pipeline capable of classifying tissue tiles into one of the five patterns or as non-tumor, with an Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUCROC) score of 0.97. Our model's strength lies in its comprehensive consideration of cellular spatial patterns, where it first generates cell maps from Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) whole slide images (WSIs), which are then fed into a convolutional neural network classification model. Exploiting these cell maps provides the model with robust generalizability to new data, achieving approximately 30% higher accuracy on unseen test-sets compared to current state of the art approaches. The insights derived from our model can be used to predict prognosis, enhancing patient outcomes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge