Artem Dementyev
PhaseCoder: Microphone Geometry-Agnostic Spatial Audio Understanding for Multimodal LLMs
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Current multimodal LLMs process audio as a mono stream, ignoring the rich spatial information essential for embodied AI. Existing spatial audio models, conversely, are constrained to fixed microphone geometries, preventing deployment across diverse devices. We present PhaseCoder, a transformer-only spatial audio encoder that is agnostic to microphone geometry. PhaseCoder takes raw multichannel audio and microphone coordinates as inputs to perform localization and produces robust spatial embeddings. We demonstrate that Gemma 3n LLM can be fine-tuned to reason over "Spatial Audio Tokens" produced by PhaseCoder. We show our encoder achieves state-of-the-art results on microphone-invariant localization benchmarks and, for the first time, enables an LLM to perform complex spatial reasoning and targeted transcription tasks from an arbitrary microphone array.
Towards sub-millisecond latency real-time speech enhancement models on hearables
Sep 26, 2024

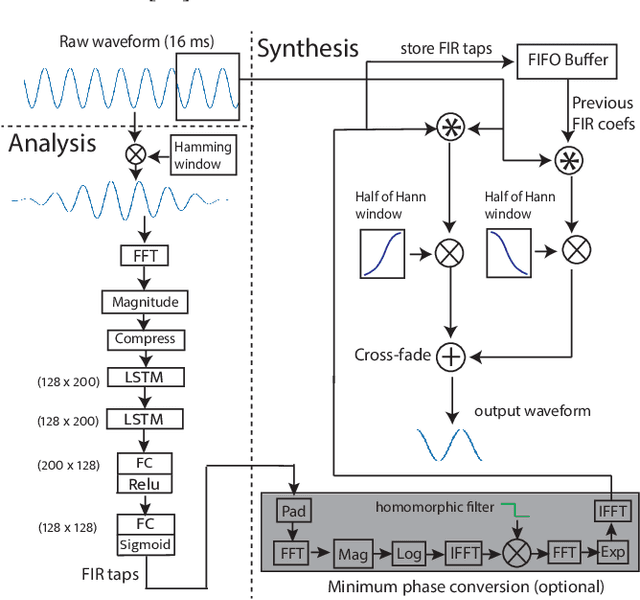
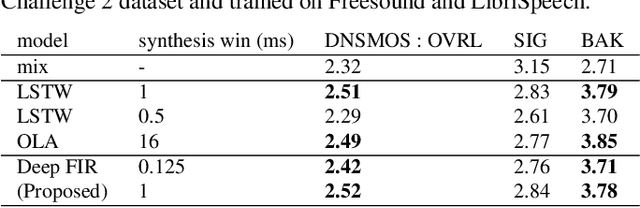
Abstract:Low latency models are critical for real-time speech enhancement applications, such as hearing aids and hearables. However, the sub-millisecond latency space for resource-constrained hearables remains underexplored. We demonstrate speech enhancement using a computationally efficient minimum-phase FIR filter, enabling sample-by-sample processing to achieve mean algorithmic latency of 0.32 ms to 1.25 ms. With a single microphone, we observe a mean SI-SDRi of 4.1 dB. The approach shows generalization with a DNSMOS increase of 0.2 on unseen audio recordings. We use a lightweight LSTM-based model of 644k parameters to generate FIR taps. We benchmark that our system can run on low-power DSP with 388 MIPS and mean end-to-end latency of 3.35 ms. We provide a comparison with baseline low-latency spectral masking techniques. We hope this work will enable a better understanding of latency and can be used to improve the comfort and usability of hearables.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge