Arman Pourghorban
Target Defense against Periodically Arriving Intruders
Mar 09, 2023Abstract:We consider a variant of pursuit-evasion games where a single defender is tasked to defend a static target from a sequence of periodically arriving intruders. The intruders' objective is to breach the boundary of a circular target without being captured and the defender's objective is to capture as many intruders as possible. At the beginning of each period, a new intruder appears at a random location on the perimeter of a fixed circle surrounding the target and moves radially towards the target center to breach the target. The intruders are slower in speed compared to the defender and they have their own sensing footprint through which they can perfectly detect the defender if it is within their sensing range. Considering the speed and sensing limitations of the agents, we analyze the entire game by dividing it into partial information and full information phases. We address the defender's capturability using the notions of engagement surface and capture circle. We develop and analyze three efficient strategies for the defender and derive a lower bound on the capture fraction. Finally, we conduct a series of simulations and numerical experiments to compare and contrast the three proposed approaches.
Target Defense against Sequentially Arriving Intruders
Dec 13, 2022

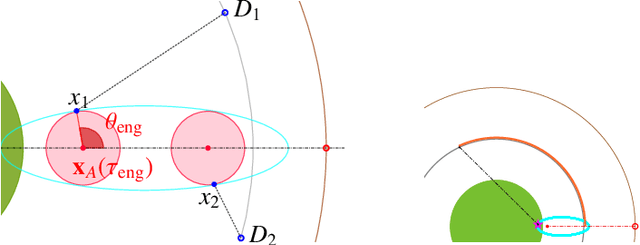

Abstract:We consider a variant of the target defense problem where a single defender is tasked to capture a sequence of incoming intruders. The intruders' objective is to breach the target boundary without being captured by the defender. As soon as the current intruder breaches the target or gets captured by the defender, the next intruder appears at a random location on a fixed circle surrounding the target. Therefore, the defender's final location at the end of the current game becomes its initial location for the next game. Thus, the players pick strategies that are advantageous for the current as well as for the future games. Depending on the information available to the players, each game is divided into two phases: partial information and full information phase. Under some assumptions on the sensing and speed capabilities, we analyze the agents' strategies in both phases. We derive equilibrium strategies for both the players to optimize the capture percentage using the notions of engagement surface and capture circle. We quantify the percentage of capture for both finite and infinite sequences of incoming intruders.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge