Arjun Kaushik
Confidential and Protected Disease Classifier using Fully Homomorphic Encryption
May 05, 2024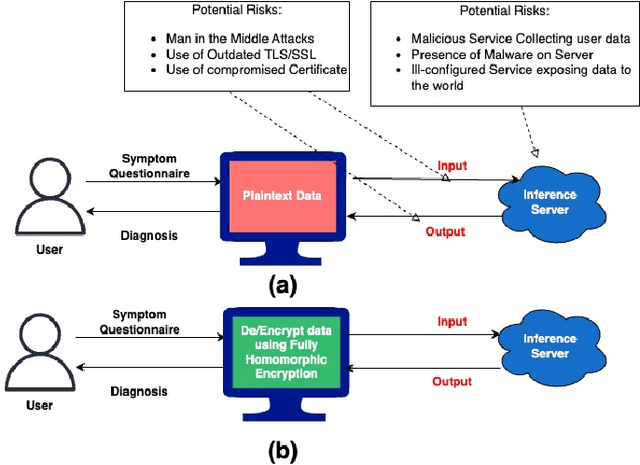
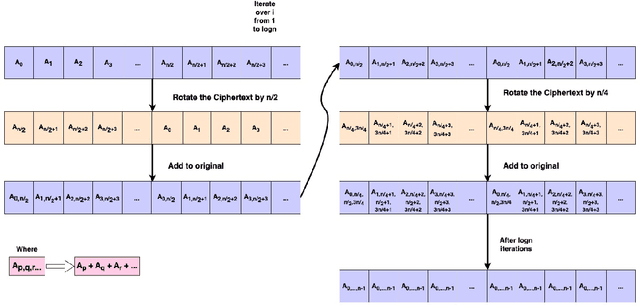
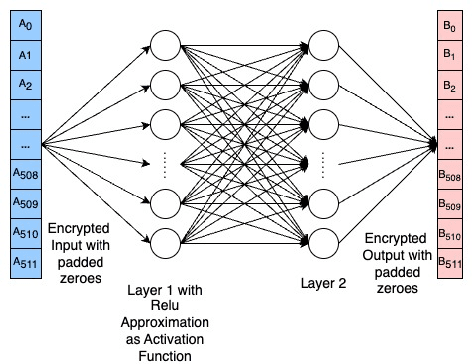
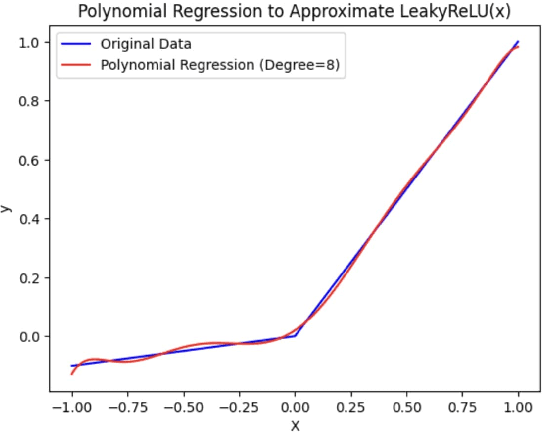
Abstract:With the rapid surge in the prevalence of Large Language Models (LLMs), individuals are increasingly turning to conversational AI for initial insights across various domains, including health-related inquiries such as disease diagnosis. Many users seek potential causes on platforms like ChatGPT or Bard before consulting a medical professional for their ailment. These platforms offer valuable benefits by streamlining the diagnosis process, alleviating the significant workload of healthcare practitioners, and saving users both time and money by avoiding unnecessary doctor visits. However, Despite the convenience of such platforms, sharing personal medical data online poses risks, including the presence of malicious platforms or potential eavesdropping by attackers. To address privacy concerns, we propose a novel framework combining FHE and Deep Learning for a secure and private diagnosis system. Operating on a question-and-answer-based model akin to an interaction with a medical practitioner, this end-to-end secure system employs Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) to handle encrypted input data. Given FHE's computational constraints, we adapt deep neural networks and activation functions to the encryted domain. Further, we also propose a faster algorithm to compute summation of ciphertext elements. Through rigorous experiments, we demonstrate the efficacy of our approach. The proposed framework achieves strict security and privacy with minimal loss in performance.
Deep Unsupervised Learning for Generalized Assignment Problems: A Case-Study of User-Association in Wireless Networks
Mar 26, 2021



Abstract:There exists many resource allocation problems in the field of wireless communications which can be formulated as the generalized assignment problems (GAP). GAP is a generic form of linear sum assignment problem (LSAP) and is more challenging to solve owing to the presence of both equality and inequality constraints. We propose a novel deep unsupervised learning (DUL) approach to solve GAP in a time-efficient manner. More specifically, we propose a new approach that facilitates to train a deep neural network (DNN) using a customized loss function. This customized loss function constitutes the objective function and penalty terms corresponding to both equality and inequality constraints. Furthermore, we propose to employ a Softmax activation function at the output of DNN along with tensor splitting which simplifies the customized loss function and guarantees to meet the equality constraint. As a case-study, we consider a typical user-association problem in a wireless network, formulate it as GAP, and consequently solve it using our proposed DUL approach. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed DUL approach provides near-optimal results with significantly lower time-complexity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge