Arijit Nag
Efficient Continual Pre-training of LLMs for Low-resource Languages
Dec 13, 2024Abstract:Open-source Large Language models (OsLLMs) propel the democratization of natural language research by giving the flexibility to augment or update model parameters for performance improvement. Nevertheless, like proprietary LLMs, Os-LLMs offer poorer performance on low-resource languages (LRLs) than high-resource languages (HRLs), owing to smaller amounts of training data and underrepresented vocabulary. On the other hand, continual pre-training (CPT) with large amounts of language-specific data is a costly proposition in terms of data acquisition and computational resources. Our goal is to drastically reduce CPT cost. To that end, we first develop a new algorithm to select a subset of texts from a larger corpus. We show the effectiveness of our technique using very little CPT data. In search of further improvement, we design a new algorithm to select tokens to include in the LLM vocabulary. We experiment with the recent Llama-3 model and nine Indian languages with diverse scripts and extent of resource availability. For evaluation, we use IndicGenBench, a generation task benchmark dataset for Indic languages. We experiment with various CPT corpora and augmented vocabulary size and offer insights across language families.
Cost-Performance Optimization for Processing Low-Resource Language Tasks Using Commercial LLMs
Mar 08, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit impressive zero/few-shot inference and generation quality for high-resource languages(HRLs). A few of them have been trained in low-resource languages (LRLs) and give decent performance. Owing to the prohibitive costs of training LLMs, they are usually used as a network service, with the client charged by the count of input and output tokens. The number of tokens strongly depends on the script and language, as well as the LLM's sub-word vocabulary. We show that LRLs are at a pricing disadvantage, because the well-known LLMs produce more tokens for LRLs than HRLs. This is because most currently popular LLMs are optimized for HRL vocabularies. Our objective is to level the playing field: reduce the cost of processing LRLs in contemporary LLMs while ensuring that predictive and generative qualities are not compromised. As means to reduce the number of tokens processed by the LLM, we consider code-mixing, translation, and transliteration of LRLs to HRLs. We perform an extensive study using the IndicXTREME dataset, covering 15 Indian languages, while using GPT-4 (one of the costliest LLM services released so far) as a commercial LLM. We observe and analyze interesting patterns involving token count, cost,and quality across a multitude of languages and tasks. We show that choosing the best policy to interact with the LLM can reduce cost by 90% while giving better or comparable performance, compared to communicating with the LLM in the original LRL.
A Data Bootstrapping Recipe for Low Resource Multilingual Relation Classification
Oct 18, 2021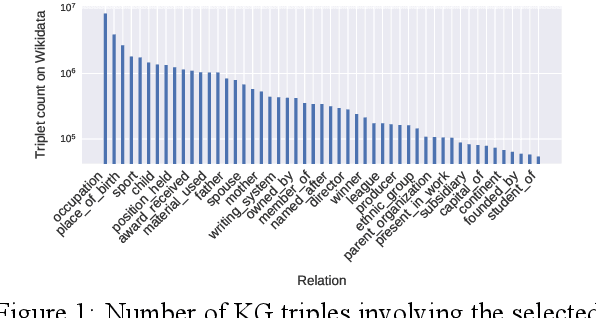
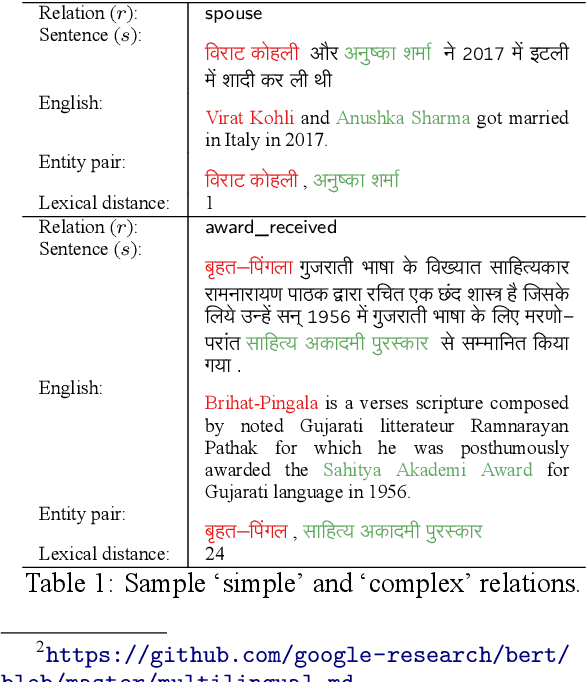
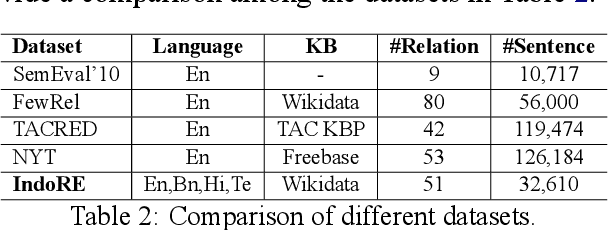
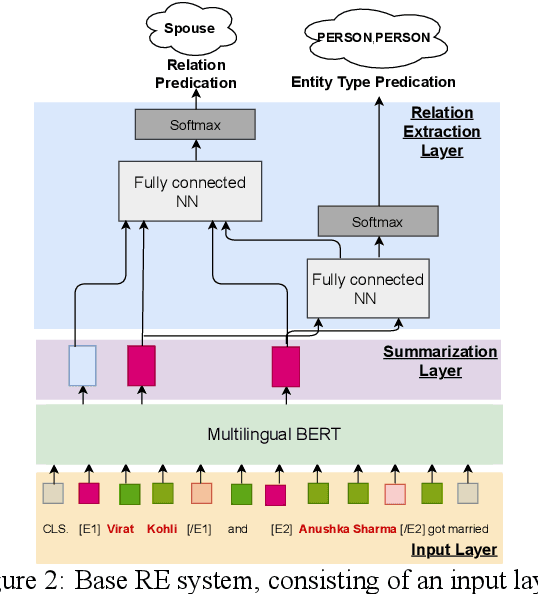
Abstract:Relation classification (sometimes called 'extraction') requires trustworthy datasets for fine-tuning large language models, as well as for evaluation. Data collection is challenging for Indian languages, because they are syntactically and morphologically diverse, as well as different from resource-rich languages like English. Despite recent interest in deep generative models for Indian languages, relation classification is still not well served by public data sets. In response, we present IndoRE, a dataset with 21K entity and relation tagged gold sentences in three Indian languages, plus English. We start with a multilingual BERT (mBERT) based system that captures entity span positions and type information and provides competitive monolingual relation classification. Using this system, we explore and compare transfer mechanisms between languages. In particular, we study the accuracy efficiency tradeoff between expensive gold instances vs. translated and aligned 'silver' instances. We release the dataset for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge