Anuradha Kar
MLGaze: Machine Learning-Based Analysis of Gaze Error Patterns in Consumer Eye Tracking Systems
May 07, 2020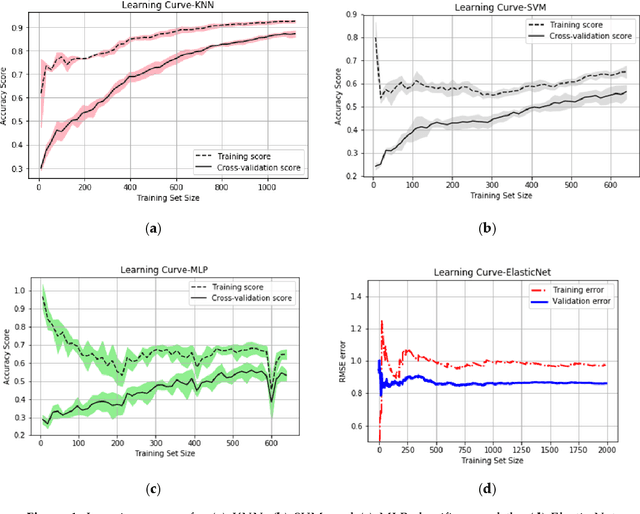
Abstract:Analyzing the gaze accuracy characteristics of an eye tracker is a critical task as its gaze data is frequently affected by non-ideal operating conditions in various consumer eye tracking applications. In this study, gaze error patterns produced by a commercial eye tracking device were studied with the help of machine learning algorithms, such as classifiers and regression models. Gaze data were collected from a group of participants under multiple conditions that commonly affect eye trackers operating on desktop and handheld platforms. These conditions (referred here as error sources) include user distance, head pose, and eye-tracker pose variations, and the collected gaze data were used to train the classifier and regression models. It was seen that while the impact of the different error sources on gaze data characteristics were nearly impossible to distinguish by visual inspection or from data statistics, machine learning models were successful in identifying the impact of the different error sources and predicting the variability in gaze error levels due to these conditions. The objective of this study was to investigate the efficacy of machine learning methods towards the detection and prediction of gaze error patterns, which would enable an in-depth understanding of the data quality and reliability of eye trackers under unconstrained operating conditions. Coding resources for all the machine learning methods adopted in this study were included in an open repository named MLGaze to allow researchers to replicate the principles presented here using data from their own eye trackers.
Efficient CNN Implementation for Eye-Gaze Estimation on Low-Power/Low-Quality Consumer Imaging Systems
Jun 28, 2018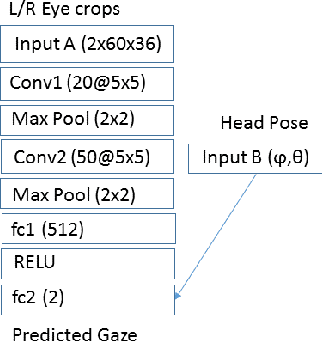
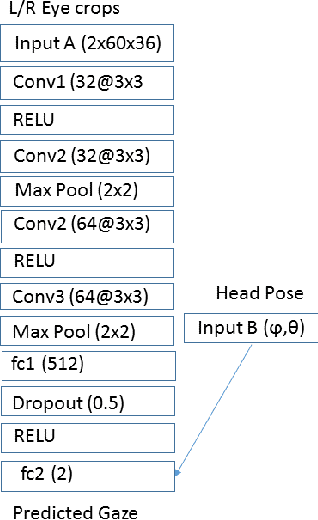
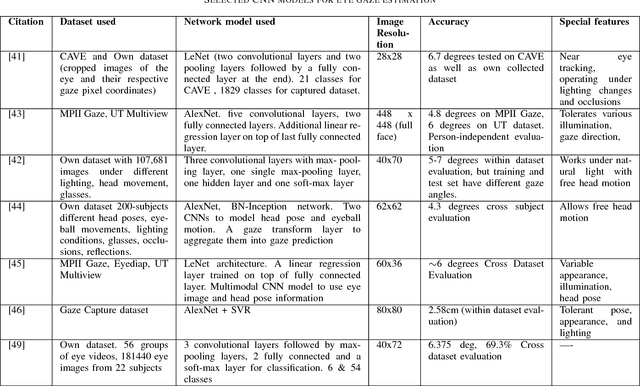
Abstract:Accurate and efficient eye gaze estimation is important for emerging consumer electronic systems such as driver monitoring systems and novel user interfaces. Such systems are required to operate reliably in difficult, unconstrained environments with low power consumption and at minimal cost. In this paper a new hardware friendly, convolutional neural network model with minimal computational requirements is introduced and assessed for efficient appearance-based gaze estimation. The model is tested and compared against existing appearance based CNN approaches, achieving better eye gaze accuracy with significantly fewer computational requirements. A brief updated literature review is also provided.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge