Anton Vakhrushev
SketchBoost: Fast Gradient Boosted Decision Tree for Multioutput Problems
Nov 23, 2022Abstract:Gradient Boosted Decision Tree (GBDT) is a widely-used machine learning algorithm that has been shown to achieve state-of-the-art results on many standard data science problems. We are interested in its application to multioutput problems when the output is highly multidimensional. Although there are highly effective GBDT implementations, their scalability to such problems is still unsatisfactory. In this paper, we propose novel methods aiming to accelerate the training process of GBDT in the multioutput scenario. The idea behind these methods lies in the approximate computation of a scoring function used to find the best split of decision trees. These methods are implemented in SketchBoost, which itself is integrated into our easily customizable Python-based GPU implementation of GBDT called Py-Boost. Our numerical study demonstrates that SketchBoost speeds up the training process of GBDT by up to over 40 times while achieving comparable or even better performance.
LightAutoML: AutoML Solution for a Large Financial Services Ecosystem
Sep 03, 2021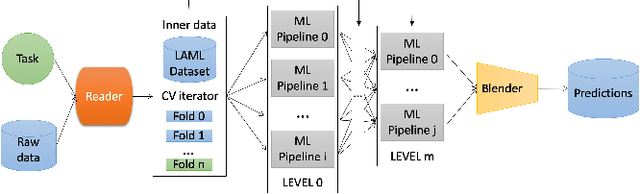

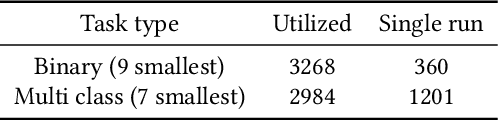
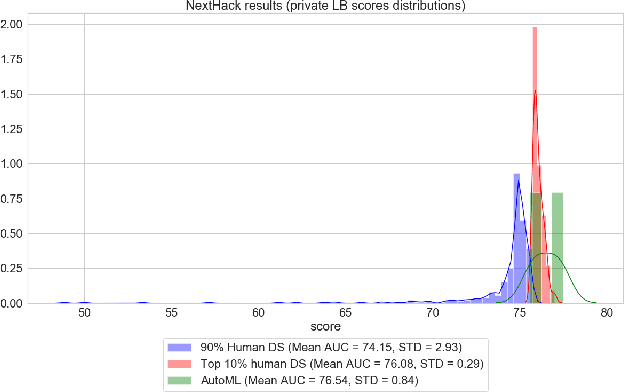
Abstract:We present an AutoML system called LightAutoML developed for a large European financial services company and its ecosystem satisfying the set of idiosyncratic requirements that this ecosystem has for AutoML solutions. Our framework was piloted and deployed in numerous applications and performed at the level of the experienced data scientists while building high-quality ML models significantly faster than these data scientists. We also compare the performance of our system with various general-purpose open source AutoML solutions and show that it performs better for most of the ecosystem and OpenML problems. We also present the lessons that we learned while developing the AutoML system and moving it into production.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge