Anton Bolychev
Multi-CALF: A Policy Combination Approach with Statistical Guarantees
May 18, 2025Abstract:We introduce Multi-CALF, an algorithm that intelligently combines reinforcement learning policies based on their relative value improvements. Our approach integrates a standard RL policy with a theoretically-backed alternative policy, inheriting formal stability guarantees while often achieving better performance than either policy individually. We prove that our combined policy converges to a specified goal set with known probability and provide precise bounds on maximum deviation and convergence time. Empirical validation on control tasks demonstrates enhanced performance while maintaining stability guarantees.
A universal policy wrapper with guarantees
May 18, 2025Abstract:We introduce a universal policy wrapper for reinforcement learning agents that ensures formal goal-reaching guarantees. In contrast to standard reinforcement learning algorithms that excel in performance but lack rigorous safety assurances, our wrapper selectively switches between a high-performing base policy -- derived from any existing RL method -- and a fallback policy with known convergence properties. Base policy's value function supervises this switching process, determining when the fallback policy should override the base policy to ensure the system remains on a stable path. The analysis proves that our wrapper inherits the fallback policy's goal-reaching guarantees while preserving or improving upon the performance of the base policy. Notably, it operates without needing additional system knowledge or online constrained optimization, making it readily deployable across diverse reinforcement learning architectures and tasks.
Critic as Lyapunov function (CALF): a model-free, stability-ensuring agent
Sep 15, 2024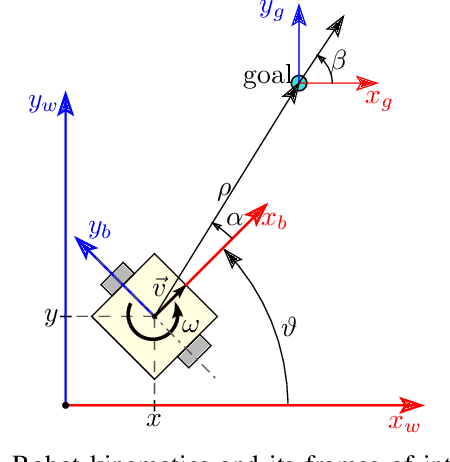
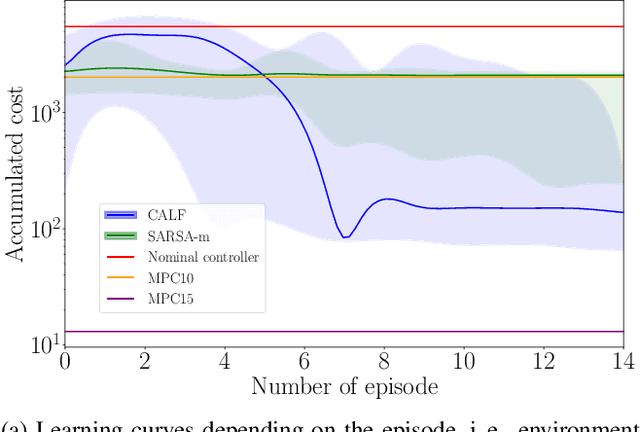
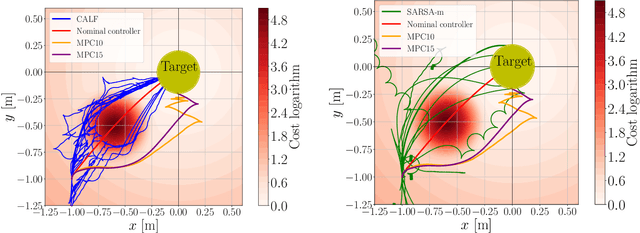
Abstract:This work presents and showcases a novel reinforcement learning agent called Critic As Lyapunov Function (CALF) which is model-free and ensures online environment, in other words, dynamical system stabilization. Online means that in each learning episode, the said environment is stabilized. This, as demonstrated in a case study with a mobile robot simulator, greatly improves the overall learning performance. The base actor-critic scheme of CALF is analogous to SARSA. The latter did not show any success in reaching the target in our studies. However, a modified version thereof, called SARSA-m here, did succeed in some learning scenarios. Still, CALF greatly outperformed the said approach. CALF was also demonstrated to improve a nominal stabilizer provided to it. In summary, the presented agent may be considered a viable approach to fusing classical control with reinforcement learning. Its concurrent approaches are mostly either offline or model-based, like, for instance, those that fuse model-predictive control into the agent.
An approach to improve agent learning via guaranteeing goal reaching in all episodes
May 29, 2024Abstract:Reinforcement learning is commonly concerned with problems of maximizing accumulated rewards in Markov decision processes. Oftentimes, a certain goal state or a subset of the state space attain maximal reward. In such a case, the environment may be considered solved when the goal is reached. Whereas numerous techniques, learning or non-learning based, exist for solving environments, doing so optimally is the biggest challenge. Say, one may choose a reward rate which penalizes the action effort. Reinforcement learning is currently among the most actively developed frameworks for solving environments optimally by virtue of maximizing accumulated reward, in other words, returns. Yet, tuning agents is a notoriously hard task as reported in a series of works. Our aim here is to help the agent learn a near-optimal policy efficiently while ensuring a goal reaching property of some basis policy that merely solves the environment. We suggest an algorithm, which is fairly flexible, and can be used to augment practically any agent as long as it comprises of a critic. A formal proof of a goal reaching property is provided. Simulation experiments on six problems under five agents, including the benchmarked one, provided an empirical evidence that the learning can indeed be boosted while ensuring goal reaching property.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge