Anneke von Seeger
Stein Discrepancy for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Feb 05, 2025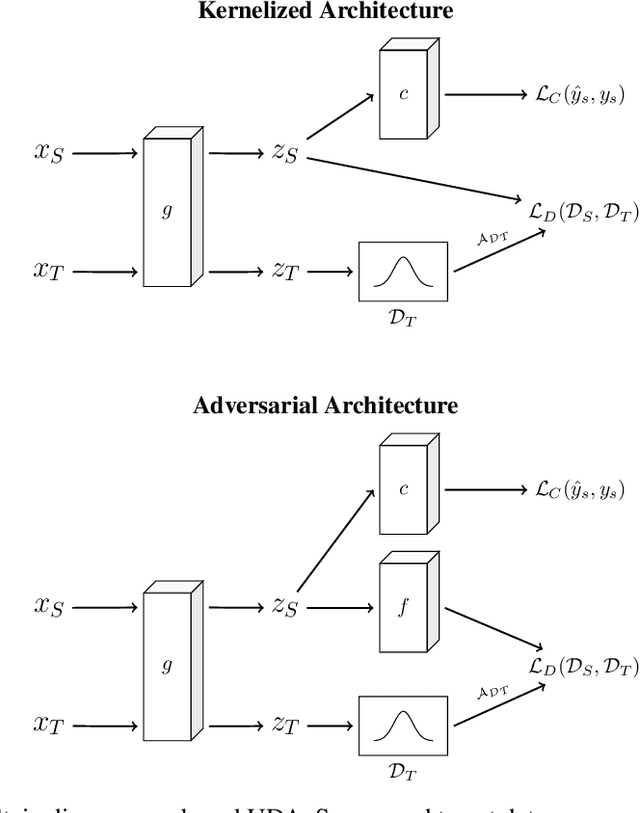
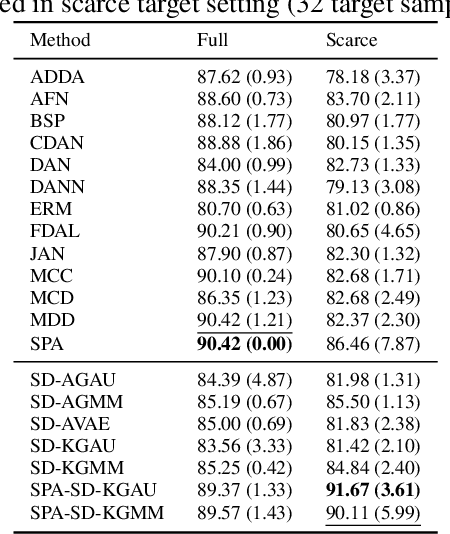
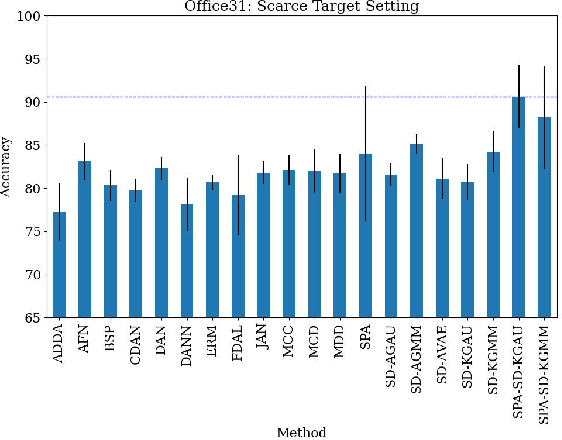
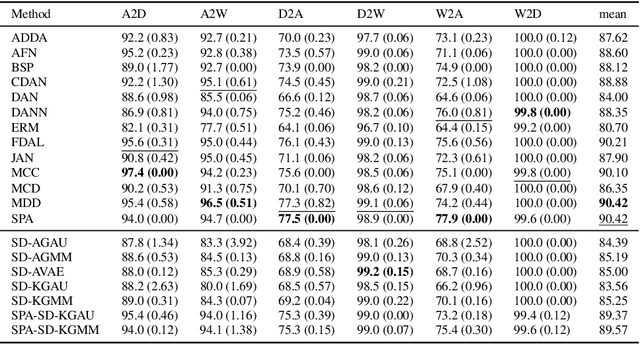
Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) leverages information from a labeled source dataset to improve accuracy on a related but unlabeled target dataset. A common approach to UDA is aligning representations from the source and target domains by minimizing the distance between their data distributions. Previous methods have employed distances such as Wasserstein distance and maximum mean discrepancy. However, these approaches are less effective when the target data is significantly scarcer than the source data. Stein discrepancy is an asymmetric distance between distributions that relies on one distribution only through its score function. In this paper, we propose a novel \ac{uda} method that uses Stein discrepancy to measure the distance between source and target domains. We develop a learning framework using both non-kernelized and kernelized Stein discrepancy. Theoretically, we derive an upper bound for the generalization error. Numerical experiments show that our method outperforms existing methods using other domain discrepancy measures when only small amounts of target data are available.
Detection of moving objects through turbulent media. Decomposition of Oscillatory vs Non-Oscillatory spatio-temporal vector fields
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we investigate how moving objects can be detected when images are impacted by atmospheric turbulence. We present a geometric spatio-temporal point of view to the problem and show that it is possible to distinguish movement due to the turbulence vs. moving objects. To perform this task, we propose an extension of 2D cartoon+texture decomposition algorithms to 3D vector fields. Our algorithm is based on curvelet spaces which permit to better characterize the movement flow geometry. We present experiments on real data which illustrate the efficiency of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge