Andri Pranolo
Comparative Analysis of Image Enhancement Techniques for Brain Tumor Segmentation: Contrast, Histogram, and Hybrid Approaches
Apr 08, 2024

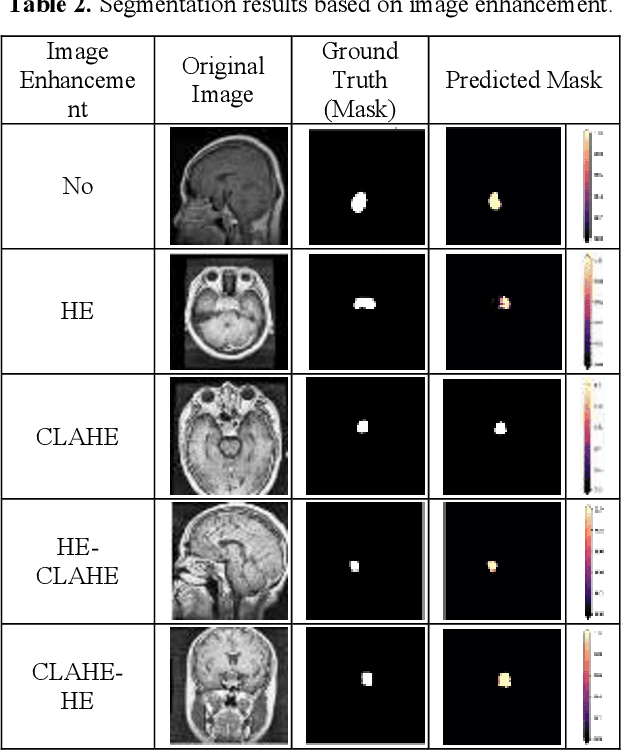
Abstract:This study systematically investigates the impact of image enhancement techniques on Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based Brain Tumor Segmentation, focusing on Histogram Equalization (HE), Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE), and their hybrid variations. Employing the U-Net architecture on a dataset of 3064 Brain MRI images, the research delves into preprocessing steps, including resizing and enhancement, to optimize segmentation accuracy. A detailed analysis of the CNN-based U-Net architecture, training, and validation processes is provided. The comparative analysis, utilizing metrics such as Accuracy, Loss, MSE, IoU, and DSC, reveals that the hybrid approach CLAHE-HE consistently outperforms others. Results highlight its superior accuracy (0.9982, 0.9939, 0.9936 for training, testing, and validation, respectively) and robust segmentation overlap, with Jaccard values of 0.9862, 0.9847, and 0.9864, and Dice values of 0.993, 0.9923, and 0.9932 for the same phases, emphasizing its potential in neuro-oncological applications. The study concludes with a call for refinement in segmentation methodologies to further enhance diagnostic precision and treatment planning in neuro-oncology.
* 9 Pages, & Figures, 2 Tables, International Conference on Computer Science Electronics and Information (ICCSEI 2023)
Nondestructive chicken egg fertility detection using CNN-transfer learning algorithms
Sep 28, 2023Abstract:This study explored the application of CNN-Transfer Learning for nondestructive chicken egg fertility detection for precision poultry hatchery practices. Four models, VGG16, ResNet50, InceptionNet, and MobileNet, were trained and evaluated on a dataset (200 single egg images) using augmented images (rotation, flip, scale, translation, and reflection). Although the training results demonstrated that all models achieved high accuracy, indicating their ability to accurately learn and classify chicken eggs' fertility state, when evaluated on the testing set, variations in accuracy and performance were observed. InceptionNet exhibited the best overall performance, accurately classifying fertile and non-fertile eggs. It demonstrated excellent performance in both training and testing sets in all parameters of the evaluation metrics. In testing set, it achieved an accuracy of 0.98, a sensitivity of 1 for detecting fertile eggs, and a specificity of 0.96 for identifying non-fertile eggs. The higher performance is attributed to its unique architecture efficiently capturing features at different scales leading to improved accuracy and robustness. Further optimization and fine-tuning of the models might necessary to address the limitations in accurately detecting fertile and non-fertile eggs in case of other models. This study highlighted the potential of CNN-Transfer Learning for nondestructive fertility detection and emphasizes the need for further research to enhance the models' capabilities and ensure accurate classification.
* 18 pages, 9 figures, 1 table, journal article published
Optimized Three Deep Learning Models Based-PSO Hyperparameters for Beijing PM2.5 Prediction
Jun 10, 2023Abstract:Deep learning is a machine learning approach that produces excellent performance in various applications, including natural language processing, image identification, and forecasting. Deep learning network performance depends on the hyperparameter settings. This research attempts to optimize the deep learning architecture of Long short term memory (LSTM), Convolutional neural network (CNN), and Multilayer perceptron (MLP) for forecasting tasks using Particle swarm optimization (PSO), a swarm intelligence-based metaheuristic optimization methodology: Proposed M-1 (PSO-LSTM), M-2 (PSO-CNN), and M-3 (PSO-MLP). Beijing PM2.5 datasets was analyzed to measure the performance of the proposed models. PM2.5 as a target variable was affected by dew point, pressure, temperature, cumulated wind speed, hours of snow, and hours of rain. The deep learning network inputs consist of three different scenarios: daily, weekly, and monthly. The results show that the proposed M-1 with three hidden layers produces the best results of RMSE and MAPE compared to the proposed M-2, M-3, and all the baselines. A recommendation for air pollution management could be generated by using these optimized models
* Volume 5 (1): 53-66
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge