Andreas Siebert
PerCoV2: Improved Ultra-Low Bit-Rate Perceptual Image Compression with Implicit Hierarchical Masked Image Modeling
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:We introduce PerCoV2, a novel and open ultra-low bit-rate perceptual image compression system designed for bandwidth- and storage-constrained applications. Building upon prior work by Careil et al., PerCoV2 extends the original formulation to the Stable Diffusion 3 ecosystem and enhances entropy coding efficiency by explicitly modeling the discrete hyper-latent image distribution. To this end, we conduct a comprehensive comparison of recent autoregressive methods (VAR and MaskGIT) for entropy modeling and evaluate our approach on the large-scale MSCOCO-30k benchmark. Compared to previous work, PerCoV2 (i) achieves higher image fidelity at even lower bit-rates while maintaining competitive perceptual quality, (ii) features a hybrid generation mode for further bit-rate savings, and (iii) is built solely on public components. Code and trained models will be released at https://github.com/Nikolai10/PerCoV2.
PerCo (SD): Open Perceptual Compression
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:We introduce PerCo (SD), a perceptual image compression method based on Stable Diffusion v2.1, targeting the ultra-low bit range. PerCo (SD) serves as an open and competitive alternative to the state-of-the-art method PerCo, which relies on a proprietary variant of GLIDE and remains closed to the public. In this work, we review the theoretical foundations, discuss key engineering decisions in adapting PerCo to the Stable Diffusion ecosystem, and provide a comprehensive comparison, both quantitatively and qualitatively. On the MSCOCO-30k dataset, PerCo (SD) demonstrates improved perceptual characteristics at the cost of higher distortion. We partly attribute this gap to the different model capacities being used (866M vs. 1.4B). We hope our work contributes to a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms and paves the way for future advancements in the field. Code and trained models will be released at https://github.com/Nikolai10/PerCo.
EGIC: Enhanced Low-Bit-Rate Generative Image Compression Guided by Semantic Segmentation
Sep 06, 2023Abstract:We introduce EGIC, a novel generative image compression method that allows traversing the distortion-perception curve efficiently from a single model. Specifically, we propose an implicitly encoded variant of image interpolation that predicts the residual between a MSE-optimized and GAN-optimized decoder output. On the receiver side, the user can then control the impact of the residual on the GAN-based reconstruction. Together with improved GAN-based building blocks, EGIC outperforms a wide-variety of perception-oriented and distortion-oriented baselines, including HiFiC, MRIC and DIRAC, while performing almost on par with VTM-20.0 on the distortion end. EGIC is simple to implement, very lightweight (e.g. 0.18x model parameters compared to HiFiC) and provides excellent interpolation characteristics, which makes it a promising candidate for practical applications targeting the low bit range.
Differential Invariants under Gamma Correction
Mar 26, 2000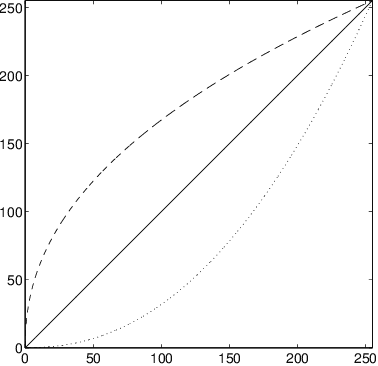
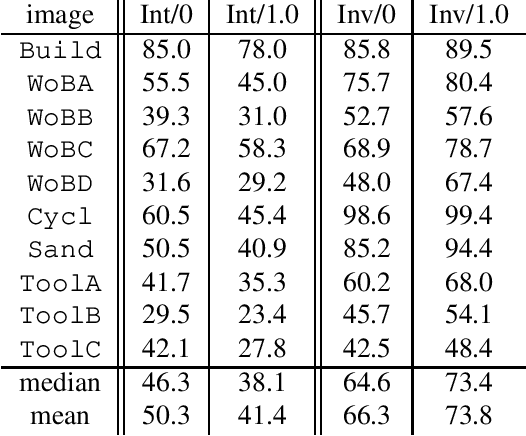
Abstract:This paper presents invariants under gamma correction and similarity transformations. The invariants are local features based on differentials which are implemented using derivatives of the Gaussian. The use of the proposed invariant representation is shown to yield improved correlation results in a template matching scenario.
* 8 pages, 12 figures
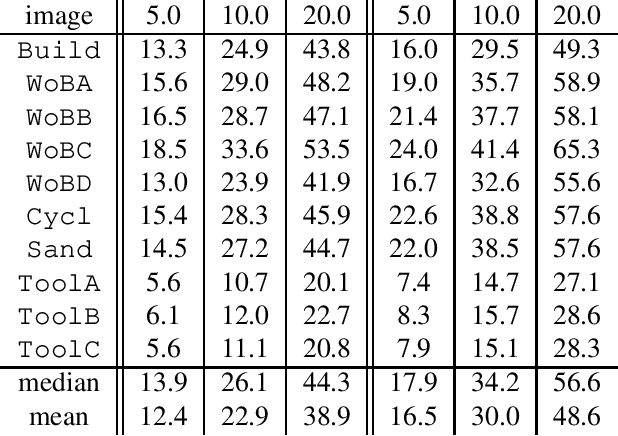
A Differential Invariant for Zooming
Aug 26, 1999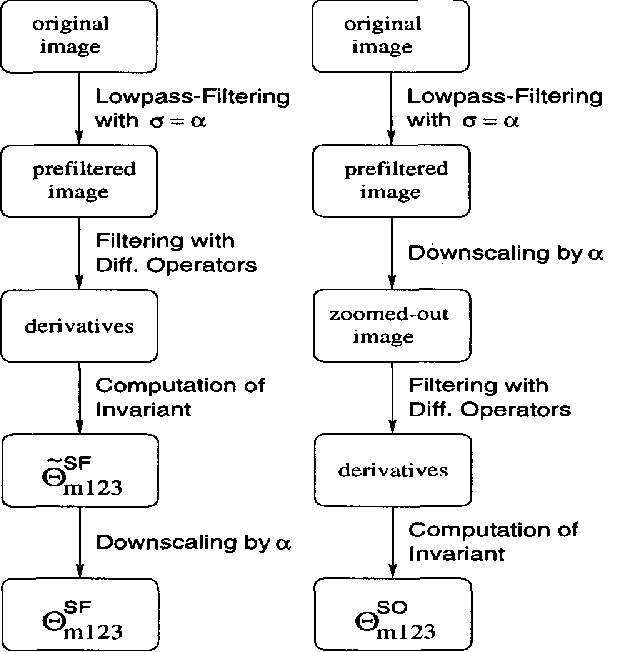
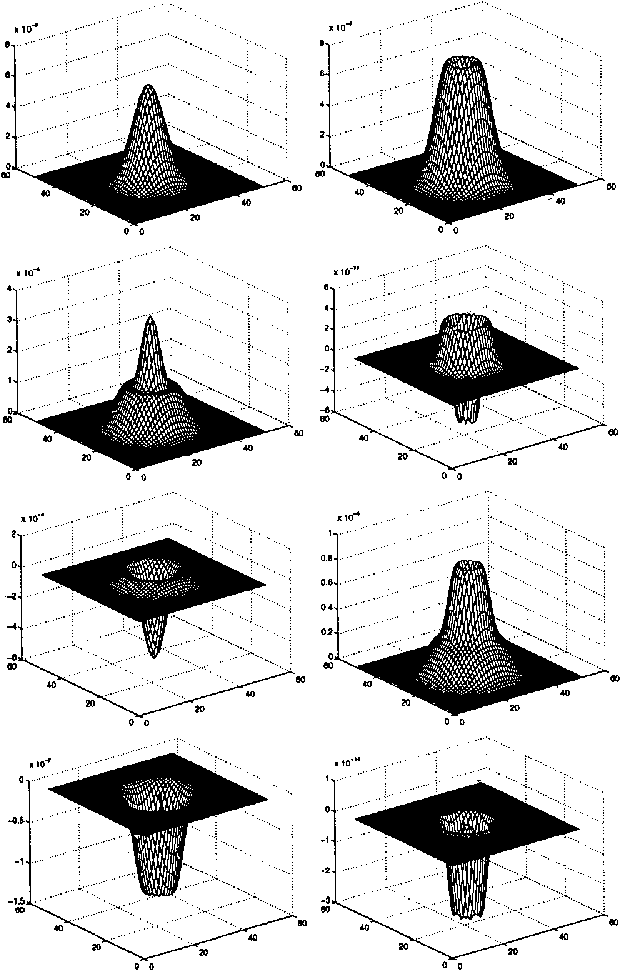
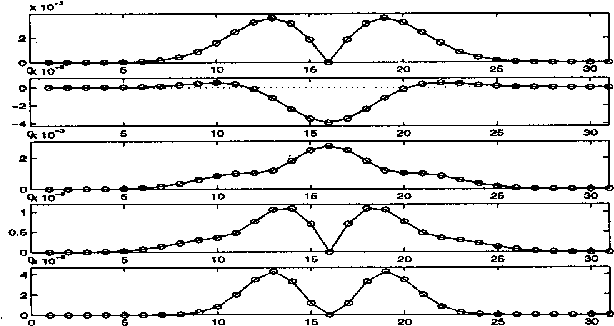
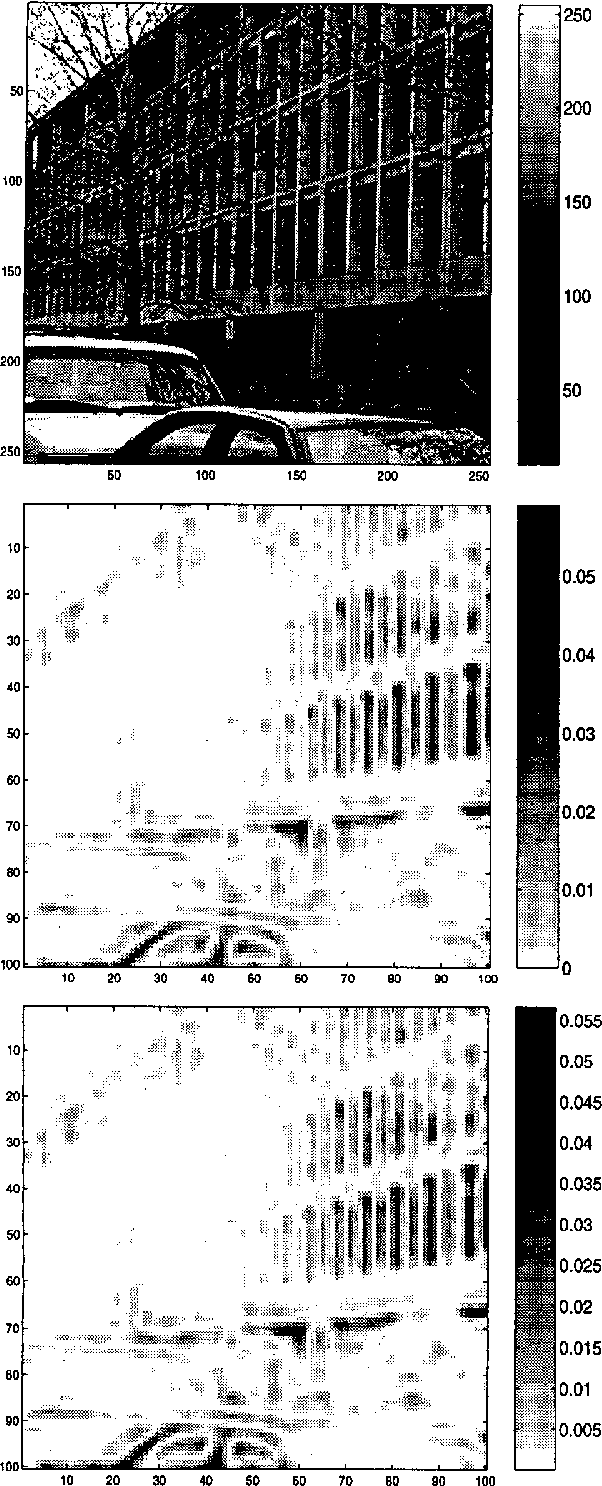
Abstract:This paper presents an invariant under scaling and linear brightness change. The invariant is based on differentials and therefore is a local feature. Rotationally invariant 2-d differential Gaussian operators up to third order are proposed for the implementation of the invariant. The performance is analyzed by simulating a camera zoom-out.
* 5 pages, 7 figures
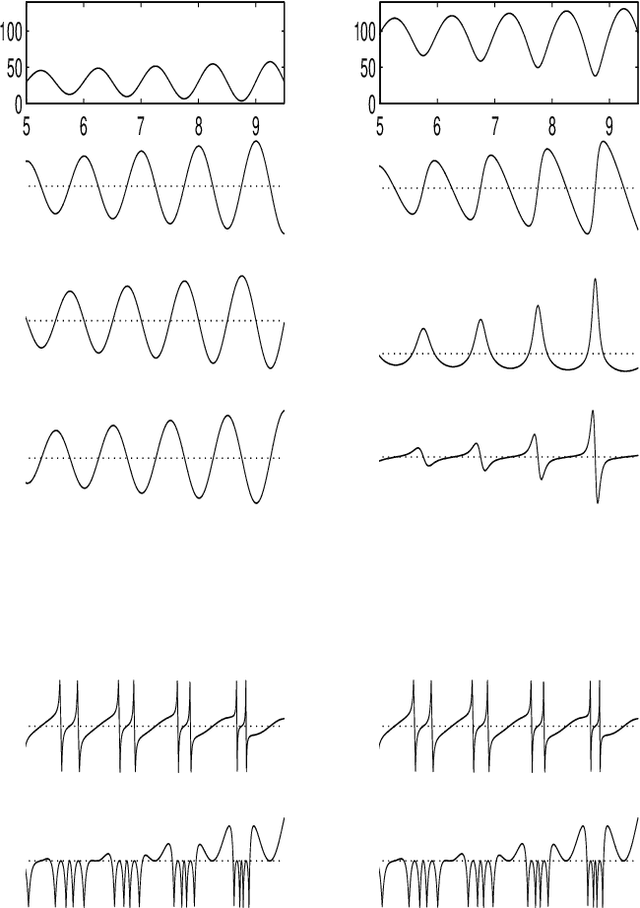
A Linear Shift Invariant Multiscale Transform
Oct 02, 1998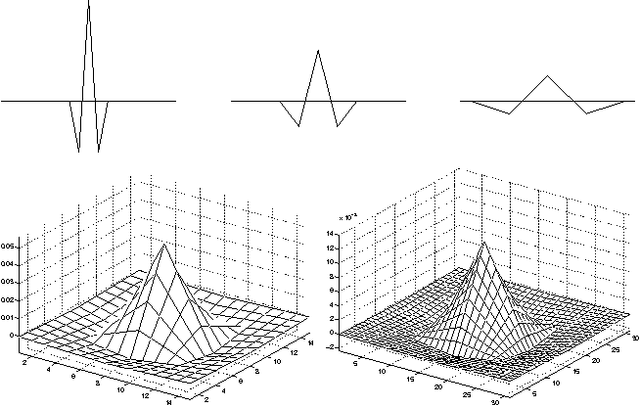
Abstract:This paper presents a multiscale decomposition algorithm. Unlike standard wavelet transforms, the proposed operator is both linear and shift invariant. The central idea is to obtain shift invariance by averaging the aligned wavelet transform projections over all circular shifts of the signal. It is shown how the same transform can be obtained by a linear filter bank.
* 4 pages, 5 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge