Andréa Carneiro Linhares
A Multilingual Study of Multi-Sentence Compression using Word Vertex-Labeled Graphs and Integer Linear Programming
Apr 09, 2020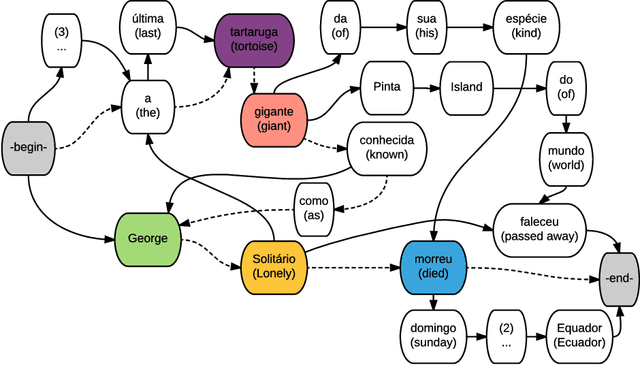
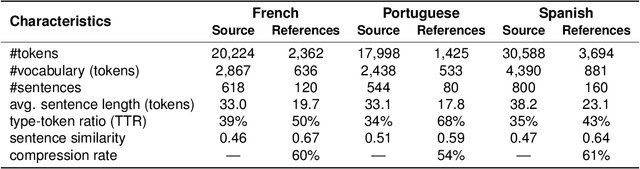
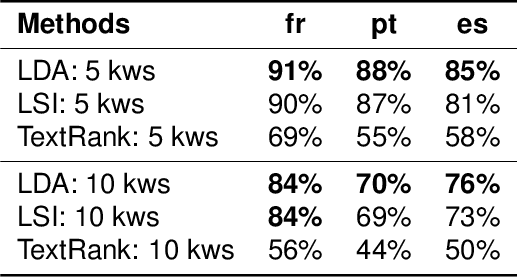
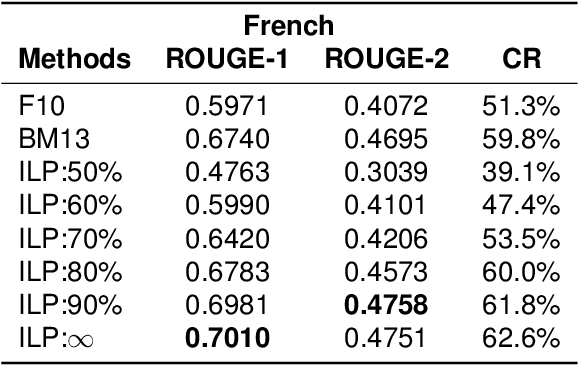
Abstract:Multi-Sentence Compression (MSC) aims to generate a short sentence with the key information from a cluster of similar sentences. MSC enables summarization and question-answering systems to generate outputs combining fully formed sentences from one or several documents. This paper describes an Integer Linear Programming method for MSC using a vertex-labeled graph to select different keywords, with the goal of generating more informative sentences while maintaining their grammaticality. Our system is of good quality and outperforms the state of the art for evaluations led on news datasets in three languages: French, Portuguese and Spanish. We led both automatic and manual evaluations to determine the informativeness and the grammaticality of compressions for each dataset. In additional tests, which take advantage of the fact that the length of compressions can be modulated, we still improve ROUGE scores with shorter output sentences.
* Preprint version
Automatic Discourse Segmentation: an evaluation in French
Feb 10, 2020
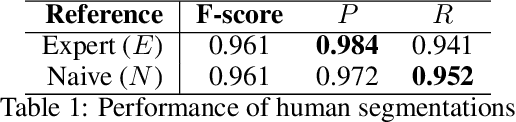
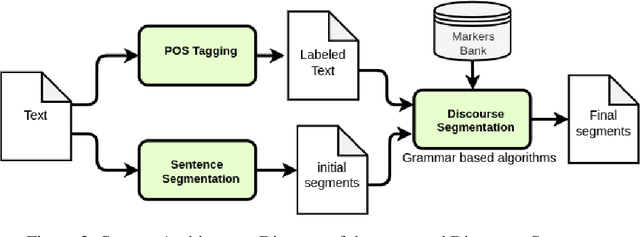
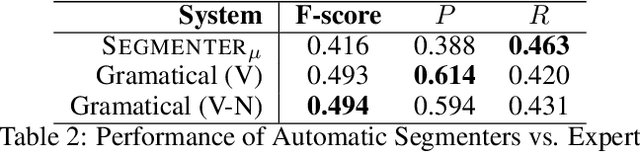
Abstract:In this article, we describe some discursive segmentation methods as well as a preliminary evaluation of the segmentation quality. Although our experiment were carried for documents in French, we have developed three discursive segmentation models solely based on resources simultaneously available in several languages: marker lists and a statistic POS labeling. We have also carried out automatic evaluations of these systems against the Annodis corpus, which is a manually annotated reference. The results obtained are very encouraging.
Predicting the Semantic Textual Similarity with Siamese CNN and LSTM
Oct 24, 2018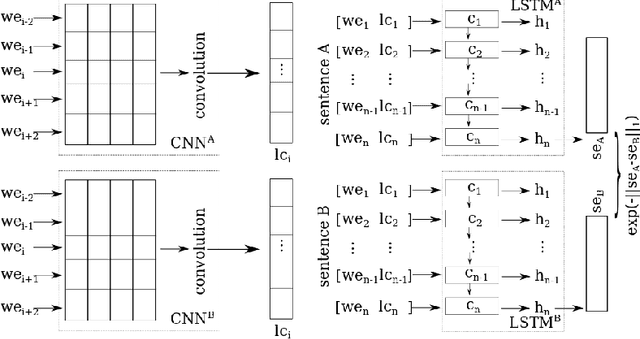
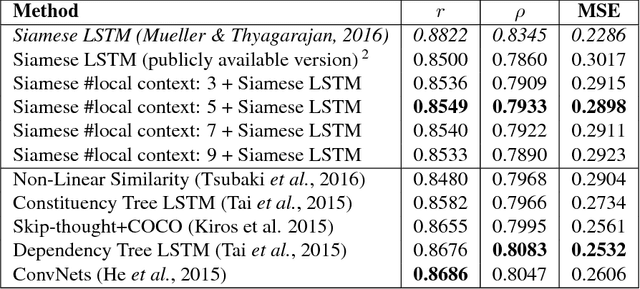
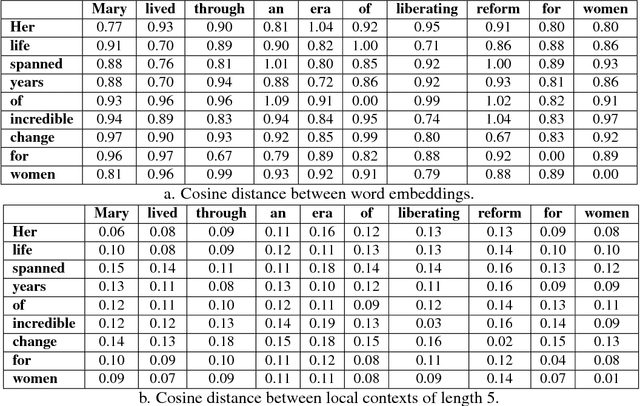
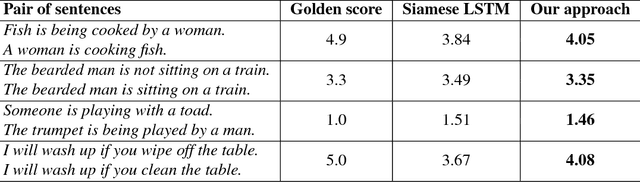
Abstract:Semantic Textual Similarity (STS) is the basis of many applications in Natural Language Processing (NLP). Our system combines convolution and recurrent neural networks to measure the semantic similarity of sentences. It uses a convolution network to take account of the local context of words and an LSTM to consider the global context of sentences. This combination of networks helps to preserve the relevant information of sentences and improves the calculation of the similarity between sentences. Our model has achieved good results and is competitive with the best state-of-the-art systems.
Métodos de Otimização Combinatória Aplicados ao Problema de Compressão MultiFrases
Mar 19, 2017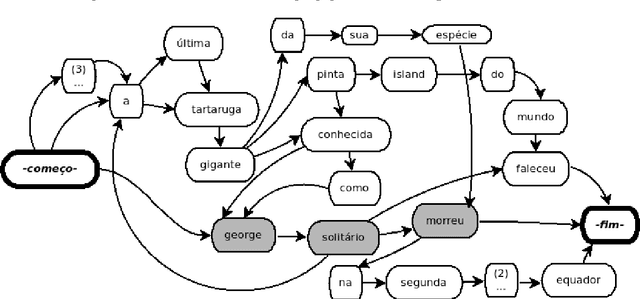


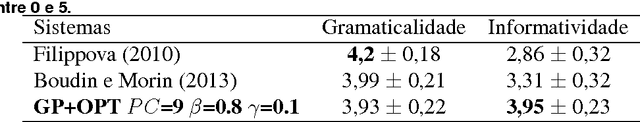
Abstract:The Internet has led to a dramatic increase in the amount of available information. In this context, reading and understanding this flow of information have become costly tasks. In the last years, to assist people to understand textual data, various Natural Language Processing (NLP) applications based on Combinatorial Optimization have been devised. However, for Multi-Sentences Compression (MSC), method which reduces the sentence length without removing core information, the insertion of optimization methods requires further study to improve the performance of MSC. This article describes a method for MSC using Combinatorial Optimization and Graph Theory to generate more informative sentences while maintaining their grammaticality. An experiment led on a corpus of 40 clusters of sentences shows that our system has achieved a very good quality and is better than the state-of-the-art.
LIA-RAG: a system based on graphs and divergence of probabilities applied to Speech-To-Text Summarization
Jan 26, 2016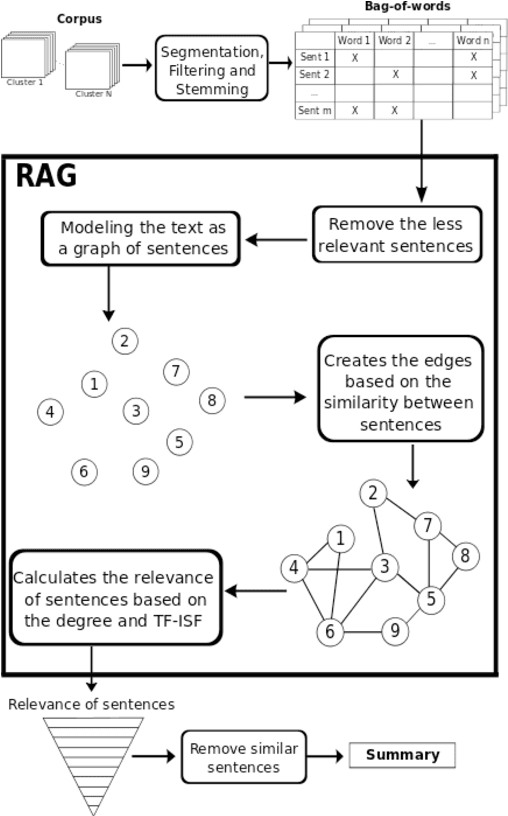
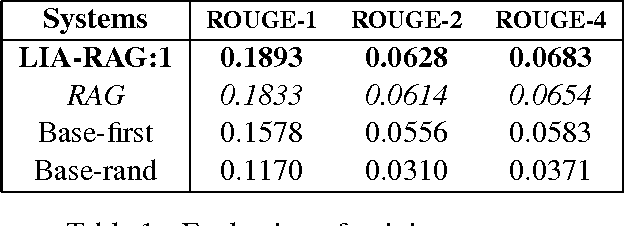
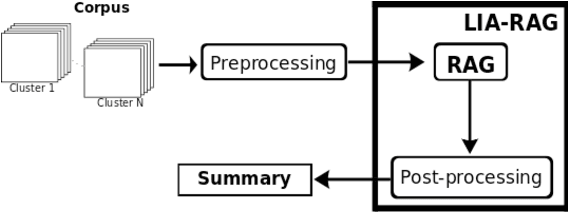

Abstract:This paper aims to introduces a new algorithm for automatic speech-to-text summarization based on statistical divergences of probabilities and graphs. The input is a text from speech conversations with noise, and the output a compact text summary. Our results, on the pilot task CCCS Multiling 2015 French corpus are very encouraging
Optimisation using Natural Language Processing: Personalized Tour Recommendation for Museums
Jan 06, 2015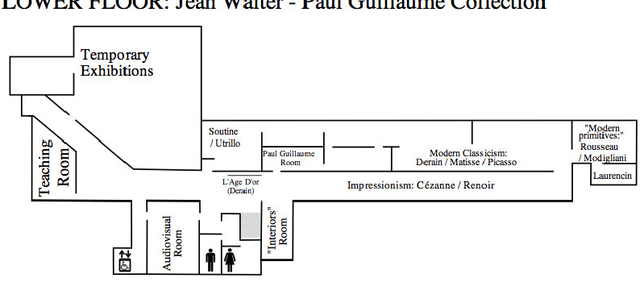
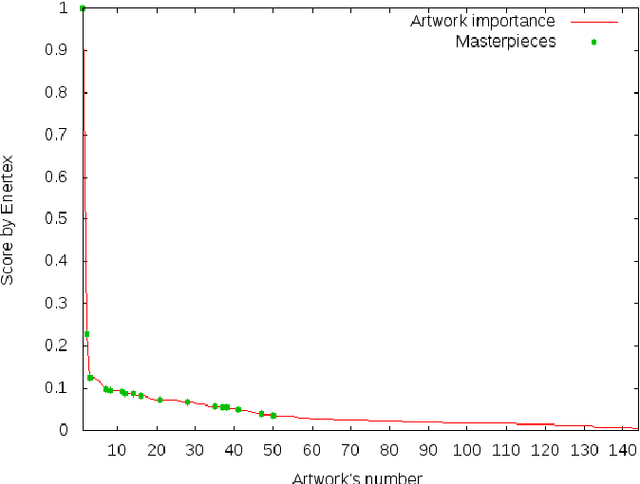
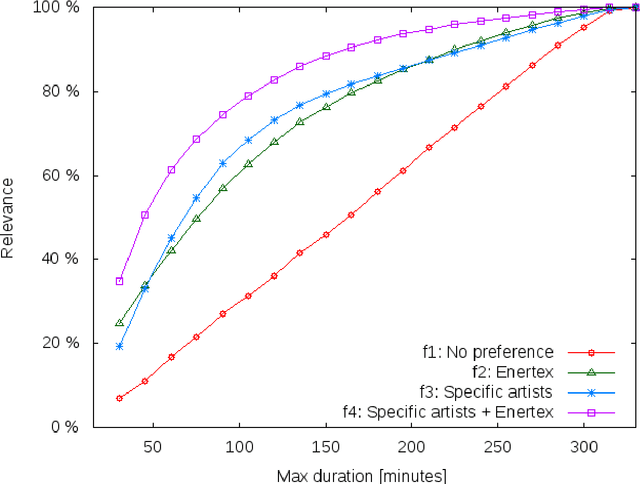
Abstract:This paper proposes a new method to provide personalized tour recommendation for museum visits. It combines an optimization of preference criteria of visitors with an automatic extraction of artwork importance from museum information based on Natural Language Processing using textual energy. This project includes researchers from computer and social sciences. Some results are obtained with numerical experiments. They show that our model clearly improves the satisfaction of the visitor who follows the proposed tour. This work foreshadows some interesting outcomes and applications about on-demand personalized visit of museums in a very near future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge