Anatoly Shalyto
New Arabic Medical Dataset for Diseases Classification
Jul 05, 2021
Abstract:The Arabic language suffers from a great shortage of datasets suitable for training deep learning models, and the existing ones include general non-specialized classifications. In this work, we introduce a new Arab medical dataset, which includes two thousand medical documents collected from several Arabic medical websites, in addition to the Arab Medical Encyclopedia. The dataset was built for the task of classifying texts and includes 10 classes (Blood, Bone, Cardiovascular, Ear, Endocrine, Eye, Gastrointestinal, Immune, Liver and Nephrological) diseases. Experiments on the dataset were performed by fine-tuning three pre-trained models: BERT from Google, Arabert that based on BERT with large Arabic corpus, and AraBioNER that based on Arabert with Arabic medical corpus.
Reinforcement-based Simultaneous Algorithm and its Hyperparameters Selection
Nov 07, 2016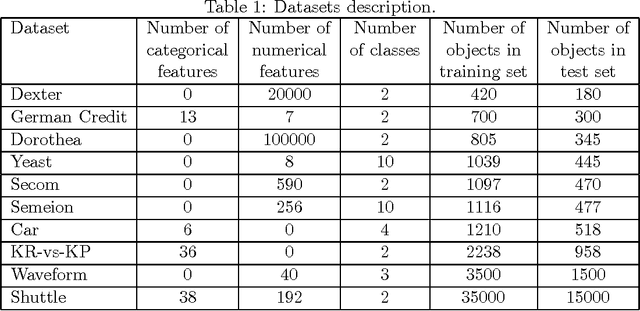
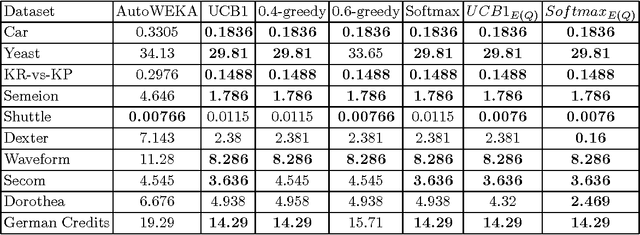
Abstract:Many algorithms for data analysis exist, especially for classification problems. To solve a data analysis problem, a proper algorithm should be chosen, and also its hyperparameters should be selected. In this paper, we present a new method for the simultaneous selection of an algorithm and its hyperparameters. In order to do so, we reduced this problem to the multi-armed bandit problem. We consider an algorithm as an arm and algorithm hyperparameters search during a fixed time as the corresponding arm play. We also suggest a problem-specific reward function. We performed the experiments on 10 real datasets and compare the suggested method with the existing one implemented in Auto-WEKA. The results show that our method is significantly better in most of the cases and never worse than the Auto-WEKA.
Symmetry Breaking Predicates for SAT-based DFA Identification
Feb 17, 2016



Abstract:It was shown before that the NP-hard problem of deterministic finite automata (DFA) identification can be effectively translated to Boolean satisfiability (SAT). Modern SAT-solvers can tackle hard DFA identification instances efficiently. We present a technique to reduce the problem search space by enforcing an enumeration of DFA states in depth-first search (DFS) or breadth-first search (BFS) order. We propose symmetry breaking predicates, which can be added to Boolean formulae representing various DFA identification problems. We show how to apply this technique to DFA identification from both noiseless and noisy data. Also we propose a method to identify all automata of the desired size. The proposed approach outperforms the current state-of-the-art DFASAT method for DFA identification from noiseless data. A big advantage of the proposed approach is that it allows to determine exactly the existence or non-existence of a solution of the noisy DFA identification problem unlike metaheuristic approaches such as genetic algorithms.
An Asynchronous Implementation of the Limited Memory CMA-ES
Oct 01, 2015



Abstract:We present our asynchronous implementation of the LM-CMA-ES algorithm, which is a modern evolution strategy for solving complex large-scale continuous optimization problems. Our implementation brings the best results when the number of cores is relatively high and the computational complexity of the fitness function is also high. The experiments with benchmark functions show that it is able to overcome its origin on the Sphere function, reaches certain thresholds faster on the Rosenbrock and Ellipsoid function, and surprisingly performs much better than the original version on the Rastrigin function.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge