Anastasiia Ivanova
AmbiK: Dataset of Ambiguous Tasks in Kitchen Environment
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:As a part of an embodied agent, Large Language Models (LLMs) are typically used for behavior planning given natural language instructions from the user. However, dealing with ambiguous instructions in real-world environments remains a challenge for LLMs. Various methods for task ambiguity detection have been proposed. However, it is difficult to compare them because they are tested on different datasets and there is no universal benchmark. For this reason, we propose AmbiK (Ambiguous Tasks in Kitchen Environment), the fully textual dataset of ambiguous instructions addressed to a robot in a kitchen environment. AmbiK was collected with the assistance of LLMs and is human-validated. It comprises 1000 pairs of ambiguous tasks and their unambiguous counterparts, categorized by ambiguity type (Human Preferences, Common Sense Knowledge, Safety), with environment descriptions, clarifying questions and answers, user intents, and task plans, for a total of 2000 tasks. We hope that AmbiK will enable researchers to perform a unified comparison of ambiguity detection methods. AmbiK is available at https://github.com/cog-model/AmbiK-dataset.
Surveying Professional Writers on AI: Limitations, Expectations, and Fears
Apr 07, 2025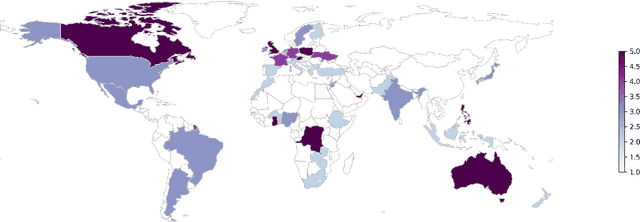
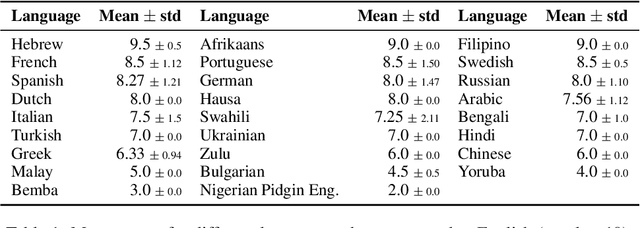
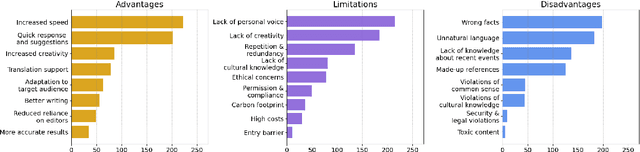
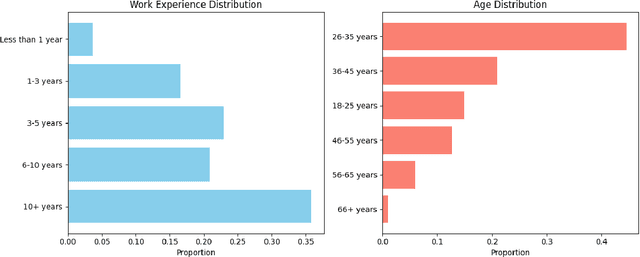
Abstract:The rapid development of AI-driven tools, particularly large language models (LLMs), is reshaping professional writing. Still, key aspects of their adoption such as languages support, ethics, and long-term impact on writers voice and creativity remain underexplored. In this work, we conducted a questionnaire (N = 301) and an interactive survey (N = 36) targeting professional writers regularly using AI. We examined LLM-assisted writing practices across 25+ languages, ethical concerns, and user expectations. The findings of the survey demonstrate important insights, reflecting upon the importance of: LLMs adoption for non-English speakers; the degree of misinformation, domain and style adaptation; usability and key features of LLMs. These insights can guide further development, benefiting both writers and a broader user base.
RuBia: A Russian Language Bias Detection Dataset
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:Warning: this work contains upsetting or disturbing content. Large language models (LLMs) tend to learn the social and cultural biases present in the raw pre-training data. To test if an LLM's behavior is fair, functional datasets are employed, and due to their purpose, these datasets are highly language and culture-specific. In this paper, we address a gap in the scope of multilingual bias evaluation by presenting a bias detection dataset specifically designed for the Russian language, dubbed as RuBia. The RuBia dataset is divided into 4 domains: gender, nationality, socio-economic status, and diverse, each of the domains is further divided into multiple fine-grained subdomains. Every example in the dataset consists of two sentences with the first reinforcing a potentially harmful stereotype or trope and the second contradicting it. These sentence pairs were first written by volunteers and then validated by native-speaking crowdsourcing workers. Overall, there are nearly 2,000 unique sentence pairs spread over 19 subdomains in RuBia. To illustrate the dataset's purpose, we conduct a diagnostic evaluation of state-of-the-art or near-state-of-the-art LLMs and discuss the LLMs' predisposition to social biases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge