Anand Panchbhai
Malaria Detection and Classificaiton
Nov 29, 2020Abstract:Malaria is a disease of global concern according to the World Health Organization. Billions of people in the world are at risk of Malaria today. Microscopy is considered the gold standard for Malaria diagnosis. Microscopic assessment of blood samples requires the need of trained professionals who at times are not available in rural areas where Malaria is a problem. Full automation of Malaria diagnosis is a challenging task. In this work, we put forward a framework for diagnosis of malaria. We adopt a two layer approach, where we detect infected cells using a Faster-RCNN in the first layer, crop them out, and feed the cropped cells to a seperate neural network for classification. The proposed methodology was tested on an openly available dataset, this will serve as a baseline for the future methods as currently there is no common dataset on which results are reported for Malaria Diagnosis.
Exploring Sequence-to-Sequence Models for SPARQL Pattern Composition
Oct 21, 2020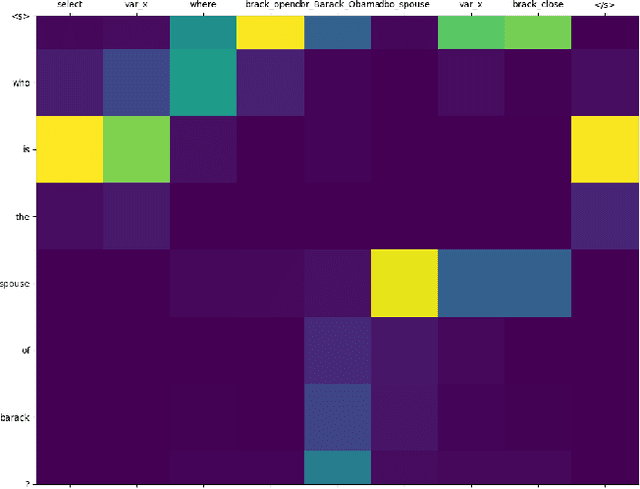
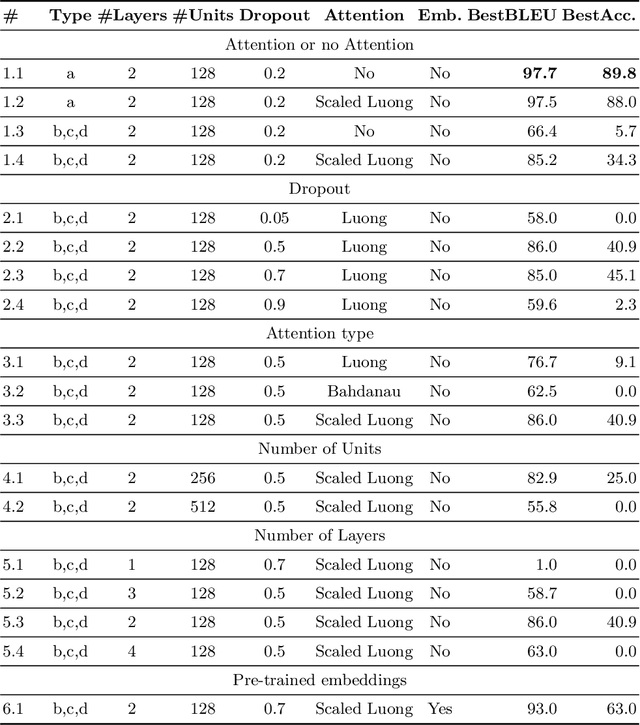
Abstract:A booming amount of information is continuously added to the Internet as structured and unstructured data, feeding knowledge bases such as DBpedia and Wikidata with billions of statements describing millions of entities. The aim of Question Answering systems is to allow lay users to access such data using natural language without needing to write formal queries. However, users often submit questions that are complex and require a certain level of abstraction and reasoning to decompose them into basic graph patterns. In this short paper, we explore the use of architectures based on Neural Machine Translation called Neural SPARQL Machines to learn pattern compositions. We show that sequence-to-sequence models are a viable and promising option to transform long utterances into complex SPARQL queries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge