Anamitra Bardhan Roy
Wavelet Based QRS Complex Detection of ECG Signal
Sep 07, 2012



Abstract:The Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a sensitive diagnostic tool that is used to detect various cardiovascular diseases by measuring and recording the electrical activity of the heart in exquisite detail. A wide range of heart condition is determined by thorough examination of the features of the ECG report. Automatic extraction of time plane features is important for identification of vital cardiac diseases. This paper presents a multi-resolution wavelet transform based system for detection 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T' peaks complex from original ECG signal. 'R-R' time lapse is an important minutia of the ECG signal that corresponds to the heartbeat of the concerned person. Abrupt increase in height of the 'R' wave or changes in the measurement of the 'R-R' denote various anomalies of human heart. Similarly 'P-P', 'Q-Q', 'S-S', 'T-T' also corresponds to different anomalies of heart and their peak amplitude also envisages other cardiac diseases. In this proposed method the 'PQRST' peaks are marked and stored over the entire signal and the time interval between two consecutive 'R' peaks and other peaks interval are measured to detect anomalies in behavior of heart, if any. The peaks are achieved by the composition of Daubeheissub bands wavelet of original ECG signal. The accuracy of the 'PQRST' complex detection and interval measurement is achieved up to 100% with high exactitude by processing and thresholding the original ECG signal.
* 5 pages, 8 figures, ISSN: 2248-9622
FCM Based Blood Vessel Segmentation Method for Retinal Images
Sep 06, 2012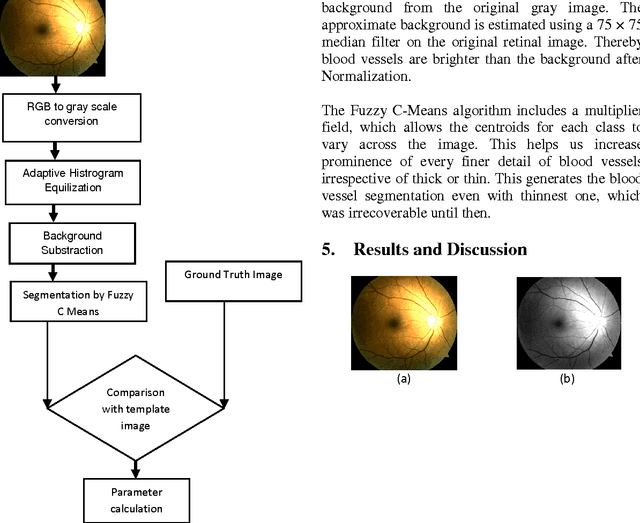
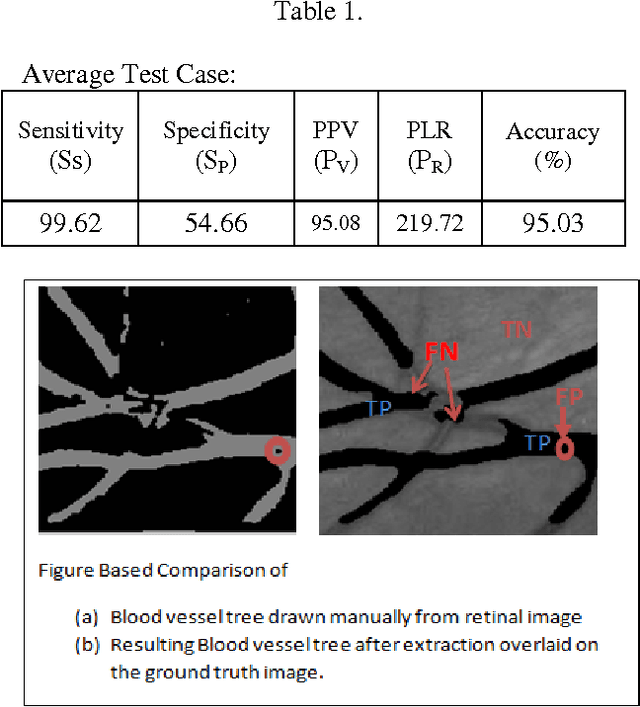
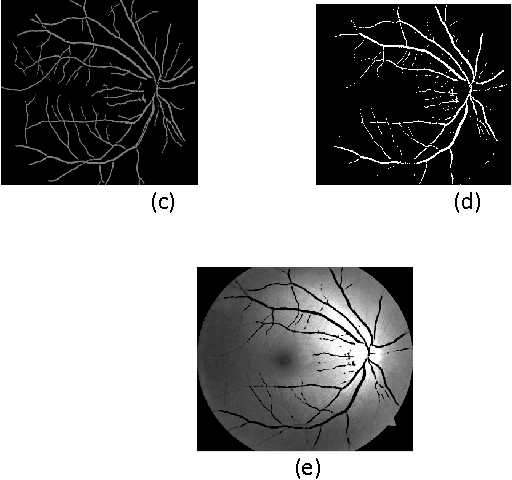
Abstract:Segmentation of blood vessels in retinal images provides early diagnosis of diseases like glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy and macular degeneration. Among these diseases occurrence of Glaucoma is most frequent and has serious ocular consequences that can even lead to blindness, if it is not detected early. The clinical criteria for the diagnosis of glaucoma include intraocular pressure measurement, optic nerve head evaluation, retinal nerve fiber layer and visual field defects. This form of blood vessel segmentation helps in early detection for ophthalmic diseases, and potentially reduces the risk of blindness. The low-contrast images at the retina owing to narrow blood vessels of the retina are difficult to extract. These low contrast images are, however useful in revealing certain systemic diseases. Motivated by the goals of improving detection of such vessels, this present work proposes an algorithm for segmentation of blood vessels and compares the results between expert ophthalmologist hand-drawn ground-truths and segmented image(i.e. the output of the present work).Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), positive likelihood ratio (PLR) and accuracy are used to evaluate overall performance.It is found that this work segments blood vessels successfully with sensitivity, specificity, PPV, PLR and accuracy of 99.62%, 54.66%, 95.08%, 219.72 and 95.03%, respectively.
* 5 pages,3figures
A Novel Approach of Color Image Hiding using RGB Color planes and DWT
Aug 03, 2012



Abstract:This work proposes a wavelet based Steganographic technique for the color image. The true color cover image and the true color secret image both are decomposed into three separate color planes namely R, G and B. Each plane of the images is decomposed into four sub bands using DWT. Each color plane of the secret image is hidden by alpha blending technique in the corresponding sub bands of the respective color planes of the original image. During embedding, secret image is dispersed within the original image depending upon the alpha value. Extraction of the secret image varies according to the alpha value. In this approach the stego image generated is of acceptable level of imperceptibility and distortion compared to the cover image and the overall security is high.
* 6 pages, 14 figures, Published with International Journal of Computer Applications (IJCA)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge