Amogh Gulati
Rethinking MUSHRA: Addressing Modern Challenges in Text-to-Speech Evaluation
Nov 19, 2024Abstract:Despite rapid advancements in TTS models, a consistent and robust human evaluation framework is still lacking. For example, MOS tests fail to differentiate between similar models, and CMOS's pairwise comparisons are time-intensive. The MUSHRA test is a promising alternative for evaluating multiple TTS systems simultaneously, but in this work we show that its reliance on matching human reference speech unduly penalises the scores of modern TTS systems that can exceed human speech quality. More specifically, we conduct a comprehensive assessment of the MUSHRA test, focusing on its sensitivity to factors such as rater variability, listener fatigue, and reference bias. Based on our extensive evaluation involving 471 human listeners across Hindi and Tamil we identify two primary shortcomings: (i) reference-matching bias, where raters are unduly influenced by the human reference, and (ii) judgement ambiguity, arising from a lack of clear fine-grained guidelines. To address these issues, we propose two refined variants of the MUSHRA test. The first variant enables fairer ratings for synthesized samples that surpass human reference quality. The second variant reduces ambiguity, as indicated by the relatively lower variance across raters. By combining these approaches, we achieve both more reliable and more fine-grained assessments. We also release MANGO, a massive dataset of 47,100 human ratings, the first-of-its-kind collection for Indian languages, aiding in analyzing human preferences and developing automatic metrics for evaluating TTS systems.
Psychometric Analysis and Coupling of Emotions Between State Bulletins and Twitter in India during COVID-19 Infodemic
May 13, 2020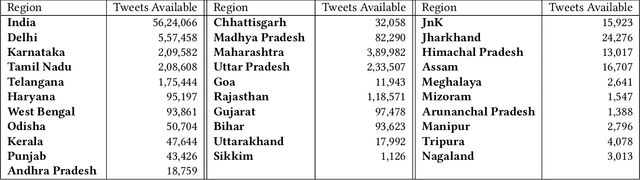
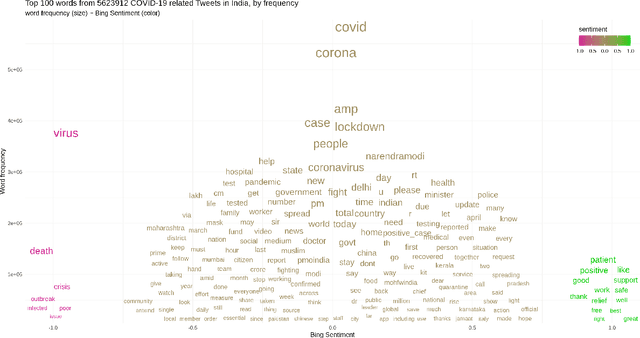
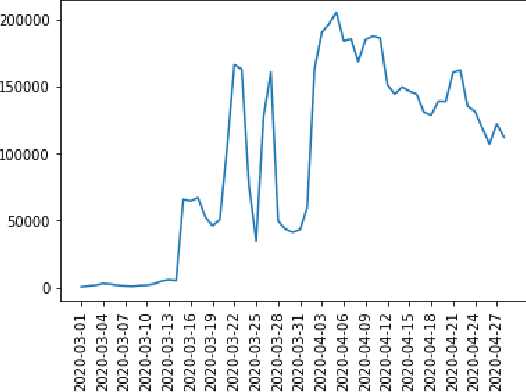
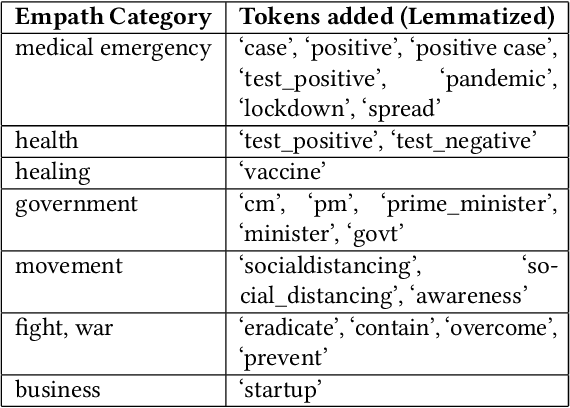
Abstract:COVID-19 infodemic has been spreading faster than the pandemic itself. The misinformation riding upon the infodemic wave poses a major threat to people's health and governance systems. Since social media is the largest source of information, managing the infodemic not only requires mitigating of misinformation but also an early understanding of psychological patterns resulting from it. During the COVID-19 crisis, Twitter alone has seen a sharp 45% increase in the usage of its curated events page, and a 30% increase in its direct messaging usage, since March 6th 2020. In this study, we analyze the psychometric impact and coupling of the COVID-19 infodemic with the official bulletins related to COVID-19 at the national and state level in India. We look at these two sources with a psycho-linguistic lens of emotions and quantified the extent and coupling between the two. We modified path, a deep skip-gram based open-sourced lexicon builder for effective capture of health-related emotions. We were then able to capture the time-evolution of health-related emotions in social media and official bulletins. An analysis of lead-lag relationships between the time series of extracted emotions from official bulletins and social media using Granger's causality showed that state bulletins were leading the social media for some emotions such as Medical Emergency. Further insights that are potentially relevant for the policymaker and the communicators actively engaged in mitigating misinformation are also discussed. Our paper also introduces CoronaIndiaDataset2, the first social media based COVID-19 dataset at national and state levels from India with over 5.6 million national and 2.6 million state-level tweets. Finally, we present our findings as COVibes, an interactive web application capturing psychometric insights captured upon the CoronaIndiaDataset, both at a national and state level.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge