Amir Hossein Taherinia
Deep learning and traditional-based CAD schemes for the pulmonary embolism diagnosis: A survey
Dec 03, 2023Abstract:Nowadays, pulmonary Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) is the main tool for detecting Pulmonary Embolism (PE). However, manual interpretation of CTA volume requires a radiologist, which is time-consuming and error-prone due to the specific conditions of lung tissue, large volume of data, lack of experience, and eye fatigue. Therefore, Computer-Aided Design (CAD) systems are used as a second opinion for the diagnosis of PE. The purpose of this article is to review, evaluate, and compare the performance of deep learning and traditional-based CAD system for diagnosis PE and to help physicians and researchers in this field. In this study, all articles available in databases such as IEEE, ScienceDirect, Wiley, Springer, Nature, and Wolters Kluwer in the field of PE diagnosis were examined using traditional and deep learning methods. From 2002 to 2023, 23 papers were studied to extract the articles with the considered limitations. Each paper presents an automatic PE detection system that we evaluate using criteria such as sensitivity, False Positives (FP), and the number of datasets. This research work includes recent studies, state-of-the-art research works, and a more comprehensive overview compared to previously published review articles in this research area.
WSMN: An optimized multipurpose blind watermarking in Shearlet domain using MLP and NSGA-II
May 07, 2020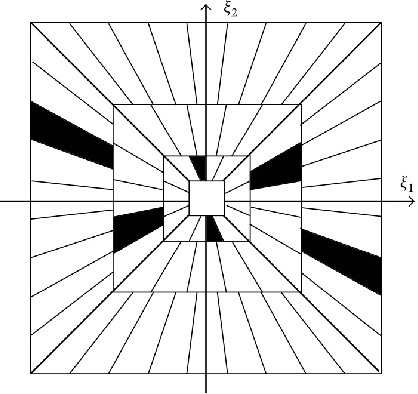
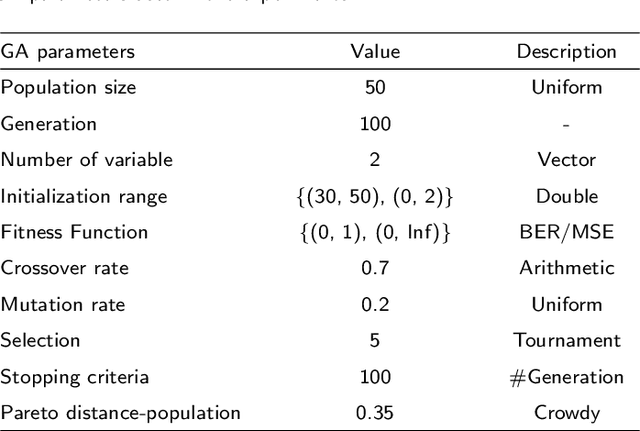

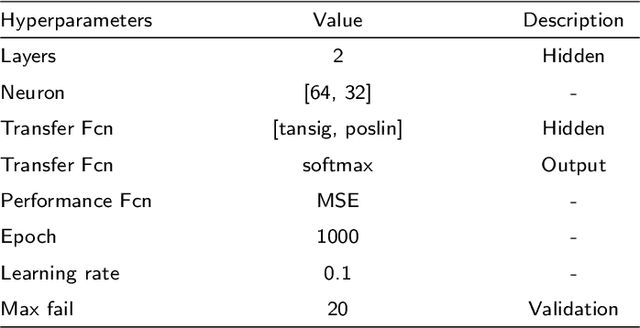
Abstract:Digital watermarking is a remarkable issue in the field of information security to avoid the misuse of images in multimedia networks. Although access to unauthorized persons can be prevented through cryptography, it cannot be simultaneously used for copyright protection or content authentication with the preservation of image integrity. Hence, this paper presents an optimized multipurpose blind watermarking in Shearlet domain with the help of smart algorithms including MLP and NSGA-II. In this method, four copies of the robust copyright logo are embedded in the approximate coefficients of Shearlet by using an effective quantization technique. Furthermore, an embedded random sequence as a semi-fragile authentication mark is effectively extracted from details by the neural network. Due to performing an effective optimization algorithm for selecting optimum embedding thresholds, and also distinguishing the texture of blocks, the imperceptibility and robustness have been preserved. The experimental results reveal the superiority of the scheme with regard to the quality of watermarked images and robustness against hybrid attacks over other state-of-the-art schemes. The average PSNR and SSIM of the dual watermarked images are 38 dB and 0.95, respectively; Besides, it can effectively extract the copyright logo and locates forgery regions under severe attacks with satisfactory accuracy.
TRLG: Fragile blind quad watermarking for image tamper detection and recovery by providing compact digests with quality optimized using LWT and GA
Mar 07, 2018



Abstract:In this paper, an efficient fragile blind quad watermarking scheme for image tamper detection and recovery based on lifting wavelet transform and genetic algorithm is proposed. TRLG generates four compact digests with super quality based on lifting wavelet transform and halftoning technique by distinguishing the types of image blocks. In other words, for each 2*2 non-overlap blocks, four chances for recovering destroyed blocks are considered. A special parameter estimation technique based on genetic algorithm is performed to improve and optimize the quality of digests and watermarked image. Furthermore, CCS map is used to determine the mapping block for embedding information, encrypting and confusing the embedded information. In order to improve the recovery rate, Mirror-aside and Partner-block are proposed. The experiments that have been conducted to evaluate the performance of TRLG proved the superiority in terms of quality of the watermarked and recovered image, tamper localization and security compared with state-of-the-art methods. The results indicate that the PSNR and SSIM of the watermarked image are about 46 dB and approximately one, respectively. Also, the mean of PSNR and SSIM of several recovered images which has been destroyed about 90% is reached to 24 dB and 0.86, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge