Amir Azizi
A Hippocampus Model for Online One-Shot Storage of Pattern Sequences
May 30, 2019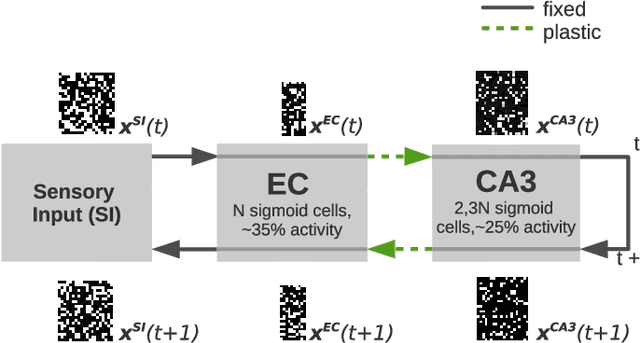
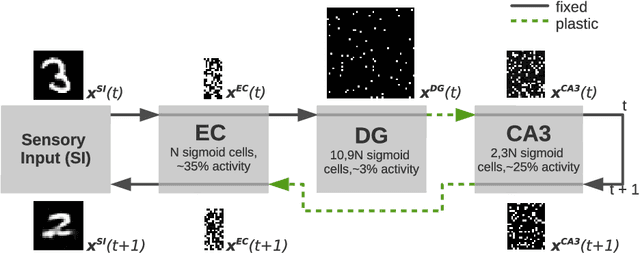
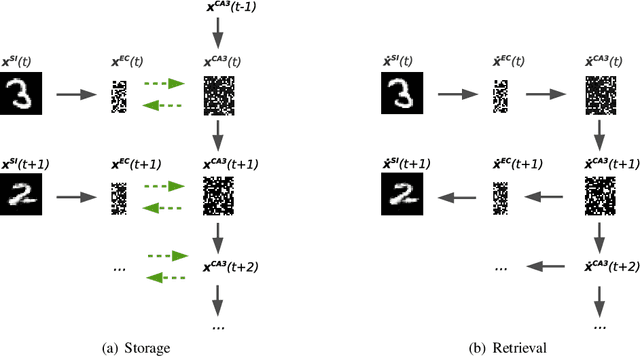
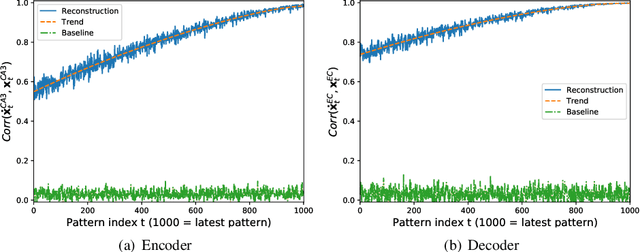
Abstract:We present a computational model based on the CRISP theory (Content Representation, Intrinsic Sequences, and Pattern completion) of the hippocampus that allows to continuously store pattern sequences online in a one-shot fashion. Rather than storing a sequence in CA3, CA3 provides a pre-trained sequence that is hetero-associated with the input sequence, which allows the system to perform one-shot learning. Plasticity on a short time scale therefore only happens in the incoming and outgoing connections of CA3. Stored sequences can later be recalled from a single cue pattern. We identify the pattern separation performed by subregion DG to be necessary for storing sequences that contain correlated patterns. A design principle of the model is that we use a single learning rule named Hebbiand-escent to train all parts of the system. Hebbian-descent has an inherent forgetting mechanism that allows the system to continuously memorize new patterns while forgetting early stored ones. The model shows a plausible behavior when noisy and new patterns are presented and has a rather high capacity of about 40% in terms of the number of neurons in CA3. One notable property of our model is that it is capable of `boot-strapping' (improving) itself without external input in a process we refer to as `dreaming'. Besides artificially generated input sequences we also show that the model works with sequences of encoded handwritten digits or natural images. To our knowledge this is the first model of the hippocampus that allows to store correlated pattern sequences online in a one-shot fashion without a consolidation process, which can instantaneously be recalled later.
Efficient IRIS Recognition through Improvement of Feature Extraction and subset Selection
Jun 25, 2009
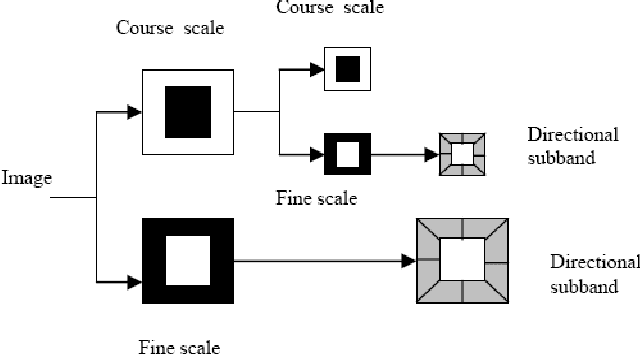
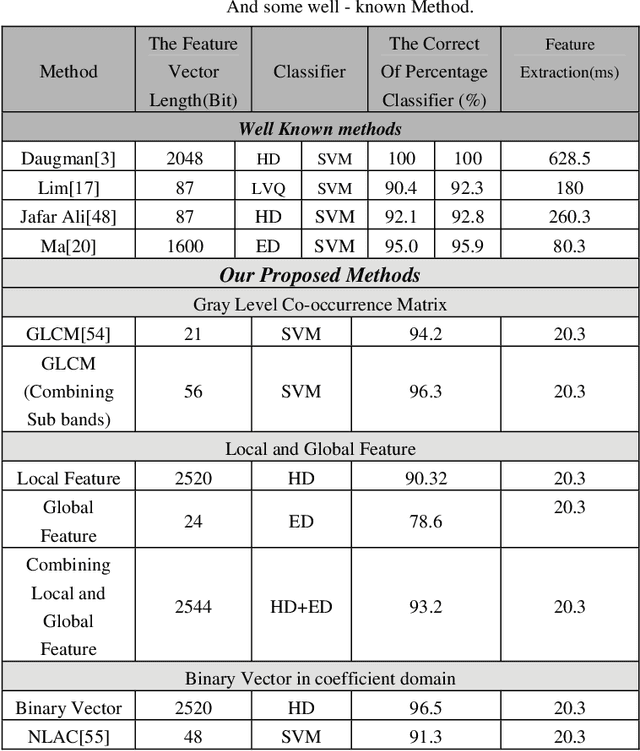
Abstract:The selection of the optimal feature subset and the classification has become an important issue in the field of iris recognition. In this paper we propose several methods for iris feature subset selection and vector creation. The deterministic feature sequence is extracted from the iris image by using the contourlet transform technique. Contourlet transform captures the intrinsic geometrical structures of iris image. It decomposes the iris image into a set of directional sub-bands with texture details captured in different orientations at various scales so for reducing the feature vector dimensions we use the method for extract only significant bit and information from normalized iris images. In this method we ignore fragile bits. And finally we use SVM (Support Vector Machine) classifier for approximating the amount of people identification in our proposed system. Experimental result show that most proposed method reduces processing time and increase the classification accuracy and also the iris feature vector length is much smaller versus the other methods.
* 10 pages, International Journal of Computer Science and Information Security (IJCSIS)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge