Aminur Rahman
Deep Learning Based Object Tracking in Walking Droplet and Granular Intruder Experiments
Jan 27, 2023Abstract:We present a deep-learning based tracking objects of interest in walking droplet and granular intruder experiments. In a typical walking droplet experiment, a liquid droplet, known as \textit{walker}, propels itself laterally on the free surface of a vibrating bath of the same liquid. This motion is the result of the interaction between the droplets and the surface waves generated by the droplet itself after each successive bounce. A walker can exhibit a highly irregular trajectory over the course of its motion, including rapid acceleration and complex interactions with the other walkers present in the same bath. In analogy with the hydrodynamic experiments, the granular matter experiments consist of a vibrating bath of very small solid particles and a larger solid \textit{intruder}. Like the fluid droplets, the intruder interacts with and travels the domain due to the waves of the bath but tends to move much slower and much less smoothly than the droplets. When multiple intruders are introduced, they also exhibit complex interactions with each other. We leverage the state-of-art object detection model YOLO and the Hungarian Algorithm to accurately extract the trajectory of a walker or intruder in real-time. Our proposed methodology is capable of tracking individual walker(s) or intruder(s) in digital images acquired from a broad spectrum of experimental settings and does not suffer from any identity-switch issues. Thus, the deep learning approach developed in this work could be used to automatize the efficient, fast and accurate extraction of observables of interests in walking droplet and granular flow experiments. Such extraction capabilities are critically enabling for downstream tasks such as building data-driven dynamical models for the coarse-grained dynamics and interactions of the objects of interest.
GPU Accelerated Fractal Image Compression for Medical Imaging in Parallel Computing Platform
Apr 03, 2014
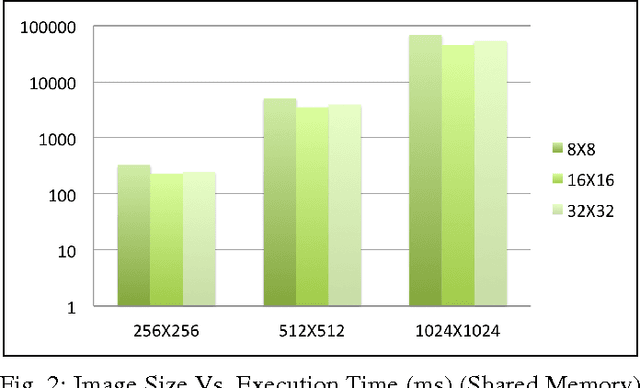
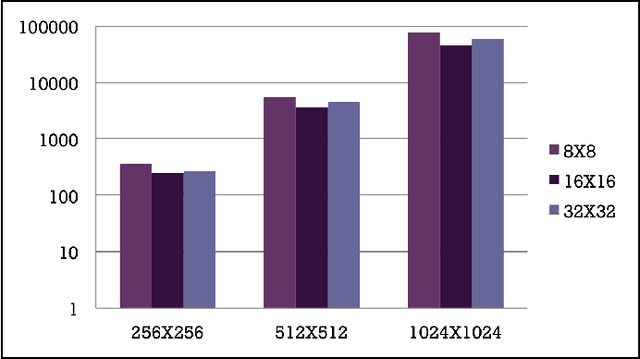
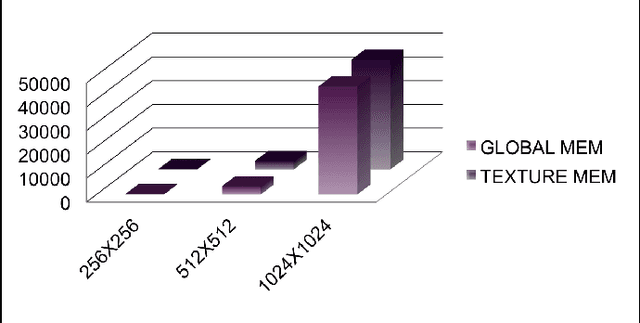
Abstract:In this paper, we implemented both sequential and parallel version of fractal image compression algorithms using CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) programming model for parallelizing the program in Graphics Processing Unit for medical images, as they are highly similar within the image itself. There are several improvement in the implementation of the algorithm as well. Fractal image compression is based on the self similarity of an image, meaning an image having similarity in majority of the regions. We take this opportunity to implement the compression algorithm and monitor the effect of it using both parallel and sequential implementation. Fractal compression has the property of high compression rate and the dimensionless scheme. Compression scheme for fractal image is of two kind, one is encoding and another is decoding. Encoding is very much computational expensive. On the other hand decoding is less computational. The application of fractal compression to medical images would allow obtaining much higher compression ratios. While the fractal magnification an inseparable feature of the fractal compression would be very useful in presenting the reconstructed image in a highly readable form. However, like all irreversible methods, the fractal compression is connected with the problem of information loss, which is especially troublesome in the medical imaging. A very time consuming encoding pro- cess, which can last even several hours, is another bothersome drawback of the fractal compression.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge