Amelie Sophie Robrecht
Measuring User Understanding in Dialogue-based XAI Systems
Aug 14, 2024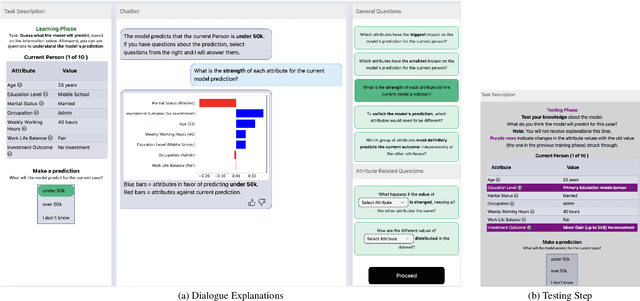
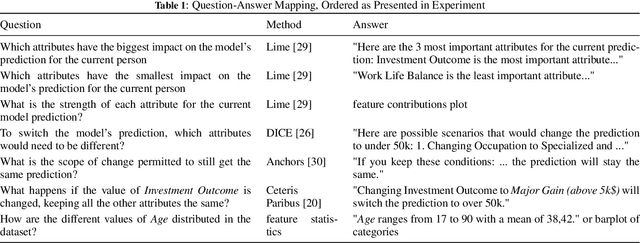
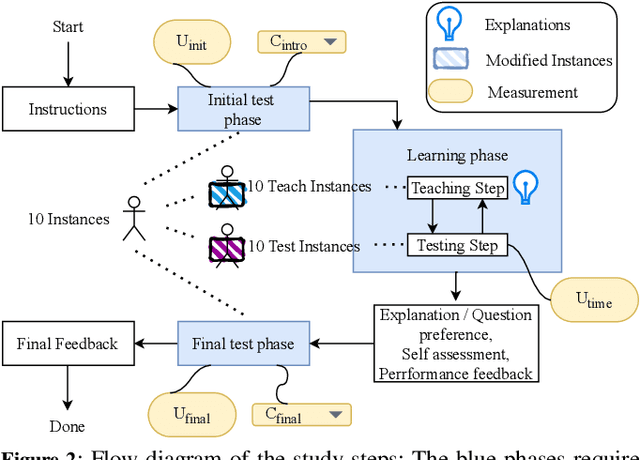
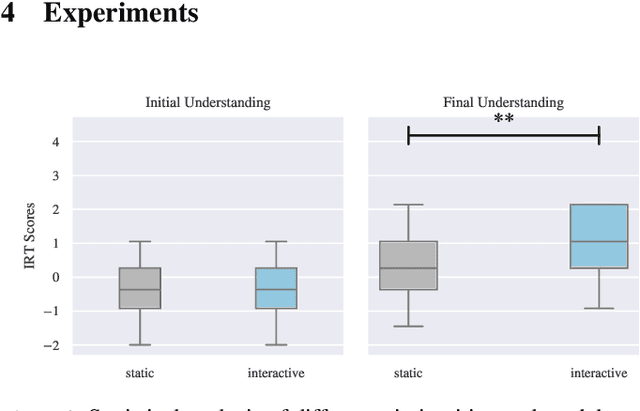
Abstract:The field of eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) is increasingly recognizing the need to personalize and/or interactively adapt the explanation to better reflect users' explanation needs. While dialogue-based approaches to XAI have been proposed recently, the state-of-the-art in XAI is still characterized by what we call one-shot, non-personalized and one-way explanations. In contrast, dialogue-based systems that can adapt explanations through interaction with a user promise to be superior to GUI-based or dashboard explanations as they offer a more intuitive way of requesting information. In general, while interactive XAI systems are often evaluated in terms of user satisfaction, there are limited studies that access user's objective model understanding. This is in particular the case for dialogue-based XAI approaches. In this paper, we close this gap by carrying out controlled experiments within a dialogue framework in which we measure understanding of users in three phases by asking them to simulate the predictions of the model they are learning about. By this, we can quantify the level of (improved) understanding w.r.t. how the model works, comparing the state prior, and after the interaction. We further analyze the data to reveal patterns of how the interaction between groups with high vs. low understanding gain differ. Overall, our work thus contributes to our understanding about the effectiveness of XAI approaches.
Integrating Representational Gestures into Automatically Generated Embodied Explanations and its Effects on Understanding and Interaction Quality
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:In human interaction, gestures serve various functions such as marking speech rhythm, highlighting key elements, and supplementing information. These gestures are also observed in explanatory contexts. However, the impact of gestures on explanations provided by virtual agents remains underexplored. A user study was carried out to investigate how different types of gestures influence perceived interaction quality and listener understanding. This study addresses the effect of gestures in explanation by developing an embodied virtual explainer integrating both beat gestures and iconic gestures to enhance its automatically generated verbal explanations. Our model combines beat gestures generated by a learned speech-driven synthesis module with manually captured iconic gestures, supporting the agent's verbal expressions about the board game Quarto! as an explanation scenario. Findings indicate that neither the use of iconic gestures alone nor their combination with beat gestures outperforms the baseline or beat-only conditions in terms of understanding. Nonetheless, compared to prior research, the embodied agent significantly enhances understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge