Amanda Buddemeyer
Dominance as an Indicator of Rapport and Learning in Human-Agent Communication
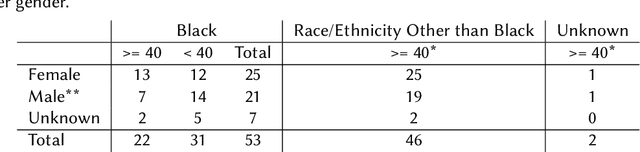
Dec 05, 2022Abstract:Power dynamics in human-human communication can impact rapport-building and learning gains, but little is known about how power impacts human-agent communication. In this paper, we examine dominance behavior in utterances between middle-school students and a teachable robot as they work through math problems, as coded by Rogers and Farace's Relational Communication Control Coding Scheme (RCCCS). We hypothesize that relatively dominant students will show increased learning gains, as will students with greater dominance agreement with the robot. We also hypothesize that gender could be an indicator of difference in dominance behavior. We present a preliminary analysis of dominance characteristics in some of the transactions between robot and student. Ultimately, we hope to determine if manipulating the dominance behavior of a learning robot could support learning.
Words of Wisdom: Representational Harms in Learning From AI Communication
Nov 16, 2021
Abstract:Many educational technologies use artificial intelligence (AI) that presents generated or produced language to the learner. We contend that all language, including all AI communication, encodes information about the identity of the human or humans who contributed to crafting the language. With AI communication, however, the user may index identity information that does not match the source. This can lead to representational harms if language associated with one cultural group is presented as "standard" or "neutral", if the language advantages one group over another, or if the language reinforces negative stereotypes. In this work, we discuss a case study using a Visual Question Generation (VQG) task involving gathering crowdsourced data from targeted demographic groups. Generated questions will be presented to human evaluators to understand how they index the identity behind the language, whether and how they perceive any representational harms, and how they would ideally address any such harms caused by AI communication. We reflect on the educational applications of this work as well as the implications for equality, diversity, and inclusion (EDI).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge